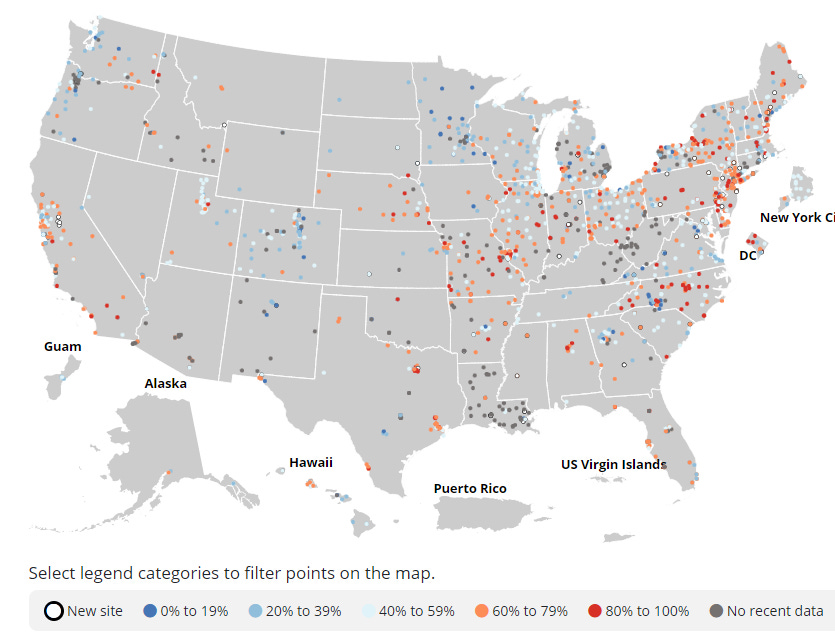
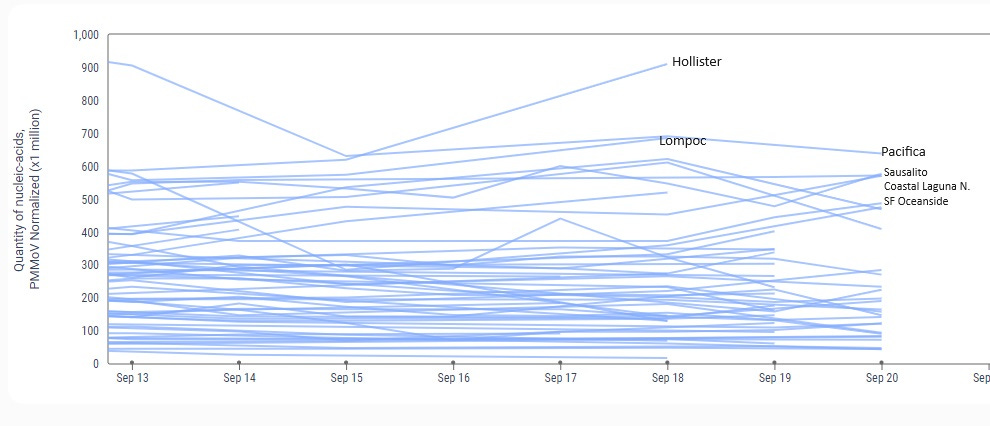
COVID hospitalizations have continued to rise over the last 10 weeks, with an increase of 7.7% this week. However, Emergency Department (ED) visits for COVID decreased by 19% over the last week when looking at the entire United States. Overall, respiratory illness seen in the ED has continued to be mostly for COVID infections, although there is a slight increase in influenza. In the southeastern United States, RSV (respiratory syncytial virus) season has started. Also in the Southeast, SARS-CoV-2 levels have started to decrease in wastewater, although viral levels continue to increase in the rest of the U.S. and especially in the Northeast. Here in California, San Francisco Oceanside has had a huge jump in virus levels in wastewater in the last 2 days, followed by high levels in Hollister, Lompoc and Pacifica.
Variants EG.5 and FL.1.5.1 continue to dominate, but HV.1 and some FLip mutations are starting to increase as well and may have a growth advantage. Per Federico Guele, the FLip mutations have a much faster doubling time. FLip variants have a double mutation in the spike (F456L and L455F). “Watch out for HK.3, EG.5.1.3 and XBB.1.16.6, all of which contain this FLip that are on the move in the US.” Although many variants are neutralized by antibodies from the fall XBB.1.5 COVID vaccines, the FLip mutations are not. Shan-Lu Liu, however, noted that the monoclonal antibody S309 can neutralize FLip variants.
The New Fall XBB.1.5 COVID Vaccines
Last week, I published a blog post detailing what you need to know about the newly approved fall COVID vaccines. All people in the U.S. over age 6 months qualify to receive a dose of the new fall COVID vaccines. So far, Moderna and Pfizer mRNA updated vaccines are being distributed. Novavax has not been FDA approved yet, but they have applied.
If you were recently vaccinated, you should wait 2 months before getting the updated vaccine.
If you had a recent COVID infection, you can wait 3 months to be vaccinated, or you could get the updated vaccine as soon as you feel better.
If you have not been vaccinated and have not had an infection recently, your immunity may have waned. Since there are many people getting COVID infections now, you may want to schedule your updated XBB.1.5 booster vaccine soon.
Definitely plan on getting a booster by the end of October since a winter COVID surge is expected after holiday get-togethers in November, December, January.
Go to vaccines.gov to check which pharmacies and clinics near you have appointments for the new Pfizer and Moderna fall COVID vaccines. The CDC’s Bridge Access Program provides no-cost COVID vaccines to all people with and without health insurance. If a pharmacy says that you have to pay for your vaccine, refer them to the CDC’s Bridge Access website. A recent poll shows that half of Americans are considering getting the updated COVID vaccine.
For Pediatricians, Family Practitioners and parents, here is the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) Pediatric COVID-19 Vaccine Dosing Quick Reference Guide. It is important to note that several vaccines have blue caps, so it is critical to double check the caps and labels before administering the new COVID vaccines. Dosages depend on age (see chart below).
By the way, you can order 4 free COVID tests per address starting September 25th at https://www.covid.gov/tests.
Masks
A CDC advisory committee proposed changes to standards for infection control in hospitals suggesting that surgical face masks are equivalent to N95 face masks (respirators) for treatment of respiratory viruses like influenza. This is contrary to findings by the CDC in 2022 which showed that an N95 mask cuts the odds of testing positive for the coronavirus by 83%, compared with 66% for surgical masks and 56% for cloth masks. A large clinical trial published from 2017 showed that N95 masks were far superior to surgical masks in protecting health workers from influenza infections. A Cochrane review of masks and COVID-19 infections was updated earlier this month showing that the previous review had flaws and that "masking is an effective intervention to reduce transmission of SARS-CoV-2.”
Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 virus
Although most attention has been focused on the spike protein of the SARS-CoV-2 virus, a new review looked at other proteins in the virus. SARS-CoV-2 has 16 non-structural proteins (nsp1-16), 4 structural proteins (Spike (S), Envelope (E), Membrane (M), Nucleocapsid (N)), and 6 accessory proteins (ORF3a, ORF6, ORF7a, ORF7b, ORF8, and ORF10). It turns out that the N protein contributes to immune evasion of the virus by suppressing the IFNβ-mediated immune response, and by antagonism of type I interferon signaling. Another group also showed that the ORF6 protein can also antagonize innate immunity (IFN-induced signaling) to help the virus to better evade our immunity.
COVID and Neurologic disease
A new Lancet paper entitled “Long-COVID cognitive impairments and reproductive hormone deficits in men may stem from GnRH neuronal death”, shows that SARS-CoV-2 can invade the hypothalamus in the brain via olfactory sensory neurons and via hypothalamic glia called tanycytes. The virus can then attack GnRH neurons in the hypothalamus causing them to die. The dramatic decrease in GnRH expression in the brain, causes cognitive defects and low testosterone (hypogonadism). SARS-CoV-2 can also lead to death of brain cells related to GnRH in the developing fetus, which may cause neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative pathologies.
Many people initially thought that children were not really affected by COVID infection. A new study from Italy, shows that children who had COVID infections in 2020-2021 had a 78% higher risk of new‐onset conditions with almost a 2-fold the risk of mental health issues and 2.4-fold risk of new neurologic problems. Fortunately, the U.S. CDC is allowing all people over age 6 months to get the new COVID fall vaccine.
The New York Times wrote a piece on how COVID affects the heart. From March 2020 to March 2022, there were approximately 90,000 more deaths in the United States from cardiovascular disease than in previous years. The sharpest rise in deaths from heart attack during that time occurred in 25- to 44-year-olds. COVID infections can increase both inflammation and blood clotting which can lead to heart attacks and strokes. Fortunately, vaccination against COVID reduced the risk of heart attack or stroke by 40% to 60%. And while there is a small risk of inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis) after vaccination, the risk of getting myocarditis from a COVID infection is much, much higher.
Long COVID
This week, there was a comprehensive review on the possible causes and future treatments for Long COVID. Possible causes of Long COVID include viral persistence; immune dysregulation including autoantibodies; microclots made from fibrinogen, amyloid and antiplasmin; thrombotic endotheliitis; and mitochondrial dysfunction.
Long COVID and Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Newer studies point to how SARS-CoV-2 can hijack human mitochondria to inhibit gene expression, leading to sluggish cell energy production and eventually mitochondrial death. Mitochondria are important because they make energy for cells, but they also are very important to our immune system. Mitochondrial metabolic pathways, amino acid metabolism, antioxidant systems, mitophagy, and mtROS are critical for immune functions. While making energy, mitochondria can produce reactive oxygen species (ROS), which can damage cells if they are not neutralized by enzymes found in mitochondria. “As SARS-CoV-2 tampers with these abilities [of mitochondria], the body careens toward constant inflammation and a diminished ability to generate energy.”
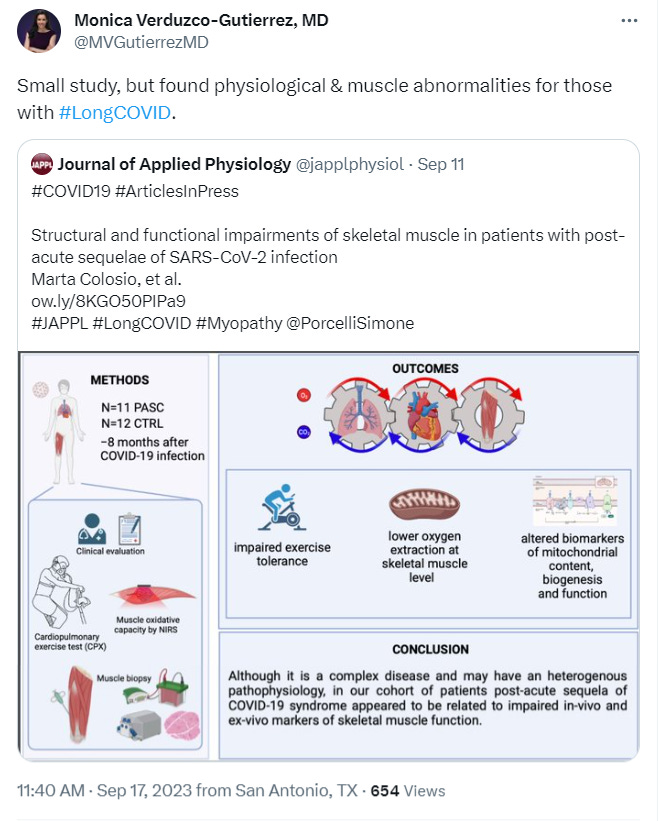
Mitochondria are also important in skeletal muscle function. Patients with post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) syndrome, also known as Long COVID, often have exercise intolerance, muscle weakness and fatigue. A new, small study (n = 11) shows that the main limitations to exercise tolerance in people with Long COVID is from impairment of skeletal muscle function with a “lower fractional O2 extraction and impaired muscle oxidative capacity, substantial reductions in biomarkers of mitochondrial function and content, and overall reduced mitochondrial sensitivity to [ADP].”
These findings of mitochondrial damage in skeletal muscle are consistent with a recent poster from Rob Wust’s lab showing that “altered skeletal muscle structure and function contribute to exercise intolerance in Long COVID patients”. They found that an increase in glycolytic fibers and a lower mitochondrial respiration contribute to exercise intolerance in Long COVID. In addition, they found that Post Exertional Malaise (PEM) in people with Long COVID is related to severe exercise-induced myopathy, amyloid deposits and skeletal muscle metabolic disturbances.
This week, the Washington Post featured a story about a woman who had extreme fatigue. A lawyer by profession, she went back to school to get a masters degree in public health. She then reached out to an NIH scientist regarding her exhaustion. A muscle biopsy showed that she had very high levels of WASF3 protein which was stopping her mitochondria from being able to produce energy, leading to extreme fatigue and ME/CFS (myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome).This discovery may help other people with chronically fatiguing illnesses, including ME/CFS and Long COVID.
Another recent study measured thousands of proteins in the blood of people with Neuro-PASC (or Neuro Long COVID) who suffer from neurologic symptoms, have a decreased quality of life, and have cognitive dysfunction (brain fog). The tests showed an increase of mitochondrial protein COX7A1 in Neuro-PASC, as well as other inflammatory and mitochondrial protein changes in the blood.
At the recent CDC ACIP meeting, they discussed Long COVID (PASC) which they stated refers to a wide range of physical and mental health consequences that continue or develop at least 4 weeks after initial COVID infection. They showed that the prevalence of Long COVID decreased from June 2022 to January 2023, but unfortunately has not decreased any further. Although fewer people are getting Long COVID since vaccinations became available, one in four of those who have Long COVID are severely disabled. So if 4.7% of all people age 35-49 years old have Long COVID currently, 1/4th of them or 1.2% of all people age 35-49 are severely disabled from Long COVID. That's a huge number that is affecting the workforce in countries around the world.
Doctors and other healthcare workers are not immune to Long COVID. In fact, 4.4% of healthcare workers in the UK have Long COVID presently. An article in the BMJ discusses how “doctors’ lives [have been] destroyed by an illness [Long COVID] they caught while doing their jobs.” Personal protective equipment (PPE) including N95 respirator masks was not available to doctors, nurses and other healthcare workers at the beginning of the pandemic. Now, they are having a tough time getting disability pay and clinical support. As one doctor said in the article, “I feel completely let down by the NHS. I told my GP that we’ve just been left to rot."
Healthcare workers are not the only front line workers affected by Long COVID. A Journal of Rural Health article reports that 62% of California farmworkers surveyed earlier in the pandemic had Long COVID symptoms at >28 days after infection. Farmworkers with Long COVID had higher body mass index, and CRP levels, greater fatigue, dyspnea, taste and smell problems, and overall poorer mental and physical health, than those with no COVID history. The authors noted that 62% “prevalence of long COVID is higher than the 45% estimated worldwide, but is in line with a recent report demonstrating higher odds of Long COVID among hospitalized Hispanic compared to White patients.”
Many people have asked if vaccination can help people with Long COVID (aka PASC or PCC) to get better. Researchers from Quebec found that COVID-19 vaccination post-PCC, reduced the number of Long COVID symptoms and increased well-being and down-regulated cytokines related to inflammation. But, vaccination post-Long COVID did not decrease the persistence of viral fragments (SARS-CoV-2 spike and nucleocapsid proteins) in plasma, and therefore a viral reservoir may persist after vaccination.
Dr. Eric Topol reminds us in his recent Substack post that vaccines and boosters given before a COVID infection provide some protection against getting Long COVID. Studies show that on average, vaccines reduce the risk of Long COVID by about 40%. COVID reinfections are not benign. As Dr. Ziyad Al-Aly states “the results are very, very clear that a second infection or reinfection is consequential. It adds or contributes additional risks both in the acute phase, it can put even reinfection can put people in the hospital, can also result in some death that's very, very clear in our data and is very clear in other data as well. [Reinfection with COVID] can also contribute to the risk of long COVID.” "Two infections are worse than one and three are worse than two."
In non-COVID news, Eric Topol reviewed the use of artificial intelligence (AI) in medicine. The New York Times told the story of how Black nurses were recruited to Staten Island in the 1940s to help cure Tuberculosis. Anthos stopped their trial of Abelacimab, a monoclonal antibody that inhibits Factor XI and XIa, due to “unprecedented efficacy”. As Angela Weyand MD said on Twitter, “Very exciting news! A blood thinner (anticoagulant) that is effective but doesn’t cause bleeding is the holy grail of hemostasis.”
Jeffrey Hubbell’s lab at the University of Chicago was able to reverse autoimmune diseases like Multiple Sclerosis and Type I Diabetes using an “inverse vaccine” in animals. By tagging autoimmune targets (such as myelin in Multiple Sclerosis) with a sugar called N-acetylgalactosamine (pGal), the tagged molecule is sent to the liver where the immune system is taught to tolerate it. This type of targeted treatment could be so much better than using medications that suppress the entire immune system to treat autoimmune diseases.
Have a good rest of your weekend,
Ruth Ann Crystal MD
P.S. This week's newsletter is longer because it represents two weeks of news.
COVID news:
Walgreens positivity rate: https://www.walgreens.com/businesssolutions/covid-19-index.jsp
US Variant tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions
Variants in different locations:
https://outbreak.info/
CDC COVID data tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/index.html#datatracker-home
CDC COVID Hospitalizations (blue) and Emergency Room (orange) visits tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/index.html#trends_weeklyhospitaladmissions_7dayeddiagnosed_00
Hospitalizations continue to increase and went up 7.7% in the last week.
ED visits down 19%
Weekly ED visits for respiratory illnesses, by age and disease: https://www.cdc.gov/ncird/surveillance/respiratory-illnesses/index.html
Inside Med Dashboard (Benjy Renton): Hospital capacity, ICU capacity https://buff.ly/3s36yop
COVID, Influenza, RSV Hospitalizations, by age, gender, state: https://public.tableau.com/app/profile/benjamin.renton/viz/InsideMedicineCOVID-19MetricsDashboard/Dashboard1
US Wastewater Monitoring:
CDC Wastewater Monitor https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#wastewater-surveillance
Wastewater from NWSS and Biobot in a US
Biobot: https://biobot.io/data/
Decrease of virus in Southern states
California wastewater level updates:
–Wastewater SCAN:
https://data.wastewaterscan.org/
California statewide view https://buff.ly/3YObiul
As of 9/22/23, SF Oceanside just shot up with virus in their wastewater
Sewer Coronavirus Alert Network (SCAN) project by Stanford University:
JP Weiland: https://twitter.com/JPWeiland
The New Fall XBB.1.5 COVID Vaccines:
9/15/23 Dr. Ruth: What to know about the newly approved fall COVID vaccines
Q&A about the new fall COVID vaccines
The new COVID vaccines should be at no cost whether or not you have insurance via the CDC’s Bridge Access Program.
Free COVID tests: 4 tests per address available after 9/25/23 at https://www.covid.gov/tests
AAP Pediatric COVID-19 Vaccine Dosing Quick Reference Guide
9/20/23 BMJ: Long COVID: the doctors’ lives destroyed by an illness they caught while doing their jobs https://buff.ly/450qCFE
Healthcare workers did not have access to PPE including respirator masks.
Office for National Statistics (ONS) in UK:
1.9 million people in the UK have Long COVID— 2.9% of the population. Globally the estimate is 10%.
4.4% of healthcare workers have Long COVID.
The British Medical Association (BMA) and LCD4A survey last year:
18% of doctors were no longer able to work.
Half (49%) lost income because of long covid.
“I feel completely let down by the NHS. I told my GP that we’ve just been left to rot."
9/18/23 Viral Immunology: What do we know about the function of SARS-CoV-2 proteins? https://buff.ly/3t6rgEo
Other reviews have focused on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. In this review, they focus on other protein parts of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
SARS-CoV-2 has 16 non-structural proteins (nsp1-16), 4 structural proteins (Spike (S), Envelope (E), Membrane (M), Nucleocapsid (N)), and 6 accessory proteins (ORF3a, ORF6, ORF7a, ORF7b, ORF8, and ORF10)
The N protein contributes to immune evasion of the virus.
The N protein can suppress the IFNβ-mediated immune response, is an antagonist of type I interferon signaling by inhibiting the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of STAT1 and STAT2 (Figure 5).
9/21/23 Cell: Impact of SARS-CoV-2 ORF6 and its variant polymorphisms on host responses and viral pathogenesis https://buff.ly/3sWWOMI
Immune evasion strategies of the SARS-CoV-2 virus include other proteins than just the spike protein.
The ORF6 protein can also antagonize innate immunity (IFN-induced signaling) and contributes to SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis.
9/16/23 J of Rural Health: SARS‐CoV‐2 infection and Long COVID among California farmworkers https://buff.ly/3RtJREo
62% of California farmworkers had Long COVID symptoms at 28 days after infection.
Farmworkers with long COVID had higher body mass index, and CRP levels, greater fatigue, dyspnea, taste and smell problems, and overall poorer mental and physical health, than those with no COVID-19 history.
9/15/23 Int J of Infectious Disease (Quebec): Vaccination after developing long COVID: impact on clinical presentation, viral persistence and immune responses https://www.ijidonline.com/article/S1201-9712(23)00720-8/fulltext#%20
COVID-19 vaccination post-PCC
reduced number of symptoms and increased well-being
down-regulated systemic markers of inflammation (cytokines)
did not decrease the persistence of viral fragments (SARS-CoV-2 spike and nucleocapsid proteins) in plasma.
A viral reservoir may persist after vaccination.
Conclusion: There is a potential benefit of vaccination for Long COVID (PCC). However, the persistence of viral compounds, independently of vaccination, may perpetuate inflammation.
Twitter thread with responses on things that people found helped their MECFS and Long COVID
9/17/23 Dr. Kimberly Prather, professor of airborne transmission, aerosols, bioparticles
9/16/23 NBC: Expected CDC guidance on N95 masks outrages health care workers https://buff.ly/3sWbSue
The CDC proposed that N95 respirators are equivalent to surgical masks. But they are not!
9/6/23 AJPH: Unpacking Cochrane’s Update on Masks and COVID-19 https://buff.ly/3t6Mu4X
Review of flaws with studies discussed.
"masking is an effective intervention to reduce transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and should be considered to protect those most vulnerable from severe COVID-19 illness (wearer protection) as a general nonpharmaceutical intervention during times of high transmission."
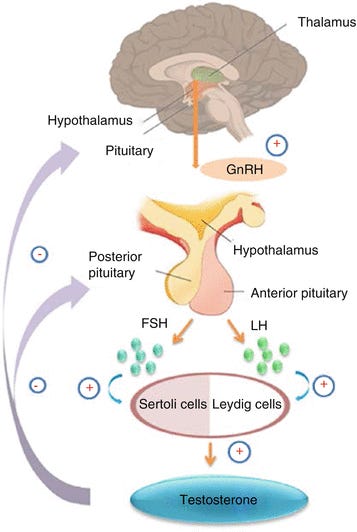
9/12/23 Lancet (Lille, France) Long-COVID cognitive impairments and reproductive hormone deficits in men may stem from GnRH neuronal death https://buff.ly/3PP5FJB
Neuroinvasion of GnRH neurons in the hypothalamus of adult men and male fetuses by the SARS-CoV-2 virus can lead to a dramatic decrease in GnRH expression in the brain, causing cognitive defects and low testosterone (hypogonadism).
2 routes of infection of GnRH neurons: via SARS-CoV-2 infection of olfactory sensory neurons and multifunctional hypothalamic glia called tanycytes.
“GnRH neuron and tanycyte dysfunction following SARS-CoV-2 neuroinvasion could be responsible for serious reproductive, metabolic, and mental health consequences in long-COVID and lead to an increased risk of neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative pathologies over time in all age groups.”
Image from GnRH, anosmia and hypogonadotropic hypogonadism – Where are we?
Image from HPG Axis: The Central Regulator of Spermatogenesis and Male Fertility
9/9/23 Acta Paediatrica (Italy): Comparative study showed that children faced a 78% higher risk of new‐onset conditions after they had COVID‐19 https://buff.ly/48qsfz9
n =1656 exposed and n =1656 unexposed children from 1 February 2020 to 30 November 2021.
The overall excess risk for new-onset conditions after COVID-19 was 78% higher in the exposed than unexposed children.
There were significantly higher risks for some new conditions in COVID exposed children, including 1.8x risk of mental health issues and 2.4x the risk of neurological problems.
9/16/23 LA Times: Terror of long COVID remains common even as pandemic eases, data show https://buff.ly/45W1pNZ
The prevalence of Long COVID decreased from June 2022 to January 2023 but remained steady through the first half of this year, according to survey data.
“However, approximately one in four adults who currently report having long COVID report that it includes significant activity limitations. And this proportion has not changed in the past year,” Saydah said.
Vaccination reduces the risk of Long COVID.
Although fewer people are getting Long COVID since vaccination, one in four of those who have Long COVID are severely disabled.
9/12/23 CDC ACIP meeting on Long COVID https://buff.ly/3RroBzk
So if 4.7% of all people age 35-49 years old have Long COVID currently, 1/4th of them or 1.2% of all people age 35-49 are disabled. That’s huge.
9/17/23 Washington Post: She wrote to a scientist about her fatigue. It inspired a breakthrough. https://buff.ly/45W952v
Story of a patient with overexpression of WASF3 protein which stopped her mitochondria from working to produce energy, leading to fatigue and ME/CFS.
8/14/23 PNAS: WASF3 disrupts mitochondrial respiration and may mediate exercise intolerance in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome https://buff.ly/3sg3khl
9/11/23 Brain, Behavior, and Immunity: Plasma proteomics show altered inflammatory and mitochondrial proteins in patients with neurologic symptoms of post-acute sequelae (PACS, Long COVID) of SARS-CoV-2 infection https://buff.ly/3Rs4Kju
Studied the proteome of n = 92 unvaccinated individuals, including:
n = 48 NP (Neuro-PASC or Neuro Long COVID) patients,
n = 20 COVID-19 convalescents (CC) without lingering symptoms, and
n = 24 unexposed healthy controls (HC)
Increase in plasma concentration of mitochondrial protein COX7A1 is associated with Neuro-PASC (neurologic symptoms, decreased quality of life, and cognitive dysfunction.)
Proteomic differences suggest inflammation and mitochondrial involvement in Neuro-PASC.
9/17/23
https://twitter.com/MVGutierrezMD/status/1703478963417256341
9/7/23 Journal of Applied Physiology: Structural and functional impairments of skeletal muscle in patients with post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC, Long COVID) https://buff.ly/3sQUJSq
“In conclusion, present findings indicate that the main limitation to exercise tolerance in post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (PASC, Long COVID) syndrome can be mainly “peripheral”.
The origin of such peripheral limitation to exercise is indicated by impairment in skeletal muscle function underlined by in-vivo lower fractional O2 extraction and impaired muscle oxidative capacity, substantial reductions in biomarkers of mitochondrial function and content, and overall reduced mitochondrial sensitivity to [ADP].”
This reminds me of this tweet and these posters at #KSLongCOVID24
8/28/23 Resia Pretorius comments on work of Rob Wust mitochondrial scientist from Amsterdam UMC
Poster 1: “Muscle abnormalities contribute to Post-Exertional Malaise in Long COVID patients”, Wust lab, Email: b.appelman@amsterdamumc.nl
Poster 1, Conclusion:
This study reveals that severe exercise-induced myopathy, tissue infiltration with amyloid-containing deposits and metabolic disturbances in skeletal muscles of Long COVID are key characteristics of Post Exertional Malaise.
These muscle abnormalities help to explain the worsening of symptoms, including muscle pain and extreme fatigue during Post Exertional Malaise (PEM) in patients with Long COVID.
Poster 2)“Altered skeletal muscle structure and function contribute to exercise intolerance in Long COVID patients”, Wust lab, Braeden T. Charlton, Email: b.t.charlton@vu.nl
Take home message:
More glycolytic fibers and a lower mitochondrial respiration contribute to exercise intolerance in Long COVID.
An increased presence of amyloid-containing deposits in skeletal muscle contribute to PEM pathophysiology.
3/10/23 Vaccine: Protective effect of COVID-19 vaccination against long COVID syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis https://buff.ly/3raK9Wb
3/23/23 JAMA: Risk Factors for Post−COVID-19 Condition https://buff.ly/46cHABE
9/8/23 Eric Topol MD: The BA.2.86 variant and the new booster https://buff.ly/44Rbied
9/15/23 Half of Americans interested in getting updated COVID shot, Reuters/Ipsos poll shows https://buff.ly/44WTcrm
9/11/23 C&EN: Long COVID: The hunt for causes and cures https://buff.ly/3ZosoPL
Great review of possible causes of Long COVID including:
Viral persistence, immune dysregulation including autoantibodies, microclots made from fibrinogen, amyloid and antiplasmin, thrombotic endotheliitis, mitochondrial dysfunction
and possible treatments.
SARS-CoV-2 and human Mitochondria:
“The damage that SARS-CoV-2 inflicts on the vital organelles is manifold: it can hijack mitochondria to inhibit gene expression, reduce membrane potential, toggle them to a sluggish metabolic pathway, inhibit energy transduction, and eventually cause organelle death. In the aftermath of an acute infection, the detritus of free-floating mitochondrial DNA circulates in the blood like scattered bank notes at a crime scene.
Mitochondria aren’t just the energy reactors of the cell but gatekeepers of the immune system. They are hubs of metabolic processes that inadvertently generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), but they also produce key enzymes to neutralize those harmful oxidizers and limit their damage before they pinball around the cell. As SARS-CoV-2 tampers with these abilities [of mitochondria], the body careens toward constant inflammation and a diminished ability to generate energy.”
9/11/23 Eric Topol interviews Ziyad Al-Aly on his blog Ground Truths:
Illuminating Long Covid https://buff.ly/3r3nCuo
Dr. Al-Aly discusses his huge medical record data set at the V.A. and the long term risks of COVID infection.
"two infections are worse than one and three are worse than two"
9/10/23 Eric Topol
https://twitter.com/EricTopol/status/1701026111717773694
“As Fede aptly points out below, it's the many emerging FLip variants that are the main concern now (not EG.5.1, FL.1.5.1 or BA.2.86).”
See Dr. Topol’s blog post https://buff.ly/44Rbied
FLip variants have a double mutation in the spike (F456L and L455F) and are seen in higher proportions of circulating variants, so they have a growth advantage over other current variants. “Watch out for HK.3, EG.5.1.3 and XBB.1.16.6, all of which contain this FLip that are on the move in the US.”
Per Federico Guele, the FLip mutations have a much faster doubling time.
9/10/23
https://twitter.com/
ShanLuLiu1/status/1701028831937609784
Distinct from XBB and other Omicron variants, the class III mAb S309 cannot neutralize BA.2.86, yet monoclonal antibody S309 efficiently neutralizes FLip.
9/10/23 Jeff Gilchrist tweet thread on Novavax vs. mRNA vaccines (Moderna, Pfizer)
Novavax uses an adjuvant called Matrix-M made from the soapbark tree which improved magnitude and quality of the antibody response to the Spike protein (antigen) and importantly broadened recognition of locations on the Spike (epitopes).
Fewer side effects with Novavax noted:
6/4/23 MedRxiV: Protein Vaccine (Novavax) Demonstrates Less Reactogenicity (77.6%) vs (95.9%) for mRNA – A Real World Study https://buff.ly/3r2pCD8
9/8/23 JAMA: SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Islet Autoimmunity in Early Childhood https://buff.ly/3sMOKhu
In young children with high genetic risk of type 1 diabetes, SARS-CoV-2 infection was temporally associated with the development of islet autoantibodies.
9/13/23 Katie Mack on Bluesky
9/7/23 NY Times: How Covid Affects the Heart https://buff.ly/3sReObx
Excess CV deaths: During the first two years of the pandemic, from March 2020 to March 2022, there were approximately 90,000 more deaths in the United States attributed to cardiovascular disease than were expected for that span of time.
The sharpest rise in deaths from heart attack during that period occurred in 25- to 44-year-olds.
COVID causes inflammation but also can cause the blood to clot which can lead to a heart attack or stroke.
Covid leads to hypertension as well as inflammation and blood clotting.
A large 2022 study tracking medical records of 691,455 patients in the United States found that people had a significantly higher risk of developing virtually all heart-related diseases in the year after a Covid infection.
1.5x stroke,
2x heart attack
1.6 and 2.4x arrhythmias.
Vaccination against COVID reduced the risk of heart attack or stroke by 40% to 60%.
There is a small risk of developing myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle) in the weeks after getting an mRNA Covid vaccine made by Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna. However, the risk of myocarditis after having Covid is much higher.
Other news:
9/11/23 Hill: The American Red Cross has declared a national blood supply emergency, citing weather and travel issues https://buff.ly/44VTheN
Emergency need for platelet donors and type O blood donors especially.
Last month, Hurricane Idalia caused >700 units of blood to go uncollected.
9/8/23 NY Times: How Black Nurses Were Recruited to Staten Island to Fight a Deadly Disease https://buff.ly/3ZfEXg1
“The Black Angels: The Untold Story of the Nurses Who Helped Cure Tuberculosis,” will be published on Sept. 19.
At Sea View, virtually the entire nursing staff was Black. Sea View recruited Black nurses from the Jim Crow south, enticing them with offers of education, a career and a living wage. At the time, Sea View was one of only four municipal hospitals in New York that did not discriminate against Black nurses.
9/13/23 Nature: RETFound, a foundation model for generalizable disease detection from retinal images https://buff.ly/3ECjlRt
Medical artificial intelligence (AI) RETFound uses 2 million retina images to recognize eye diseases and systemic diseases like heart failure, myocardial infarction, stroke and Parkinson’s disease.
Large Language Model in medicine
7/27/23 TIME magazine: AI (Artificial Intelligence) By the People, For the People https://buff.ly/44RZnNs
There is a huge demand for datasets—collections of text or voice data—in languages spoken by some of the poorest people in the world. Part of that demand comes from tech companies seeking to build out their AI tools.
Karya is paying people in India 20 times the Indian minimum wage to read a text aloud in their native language to help train their artificial intelligence systems.
9/15/23 Eric Topol MD: All Eyes on Medical A.I. https://buff.ly/45Wk4Jk
A Review of Medical A.I Randomized Trials
A Foundation Model of Retinal Images
ChatGPT to the rescue- diagnosed a boy's rare disease
His recent article in Science: As artificial intelligence goes multimodal, medical applications multiply https://buff.ly/3PCaHZA
9/19/23 Nature: AI can help to speed up drug discovery — but only if we give it the right data https://buff.ly/48foNHT
9/18/23 How Investors Evaluate Digital Health Startups by Halle Tecco https://buff.ly/44TC5Xr
9/18/23 BioSpace: Anthos Stops Mid-Stage Atrial Fibrillation Trial Due to ‘Unprecedented’ Efficacy https://buff.ly/3RnjVud
Abelacimab is a highly selective and fully human monoclonal antibody that works by inhibiting both Factor XI and its active form Factor XIa.
The study was stopped early because Abelacimab was effective in preventing strokes and clots, and it did not cause bleeding problems.
9/7/23 Nature Biomedical Engineering (Hubbell lab): Synthetically glycosylated antigens for the antigen-specific suppression of established immune responses https://buff.ly/3rly3JM
"pGal–antigen therapy invokes mechanisms of immune tolerance to resolve antigen-specific inflammatory T-cell responses and suggest that the therapy may be applicable across autoimmune diseases."
9/11/23 U Chicago: “Inverse vaccine” shows potential to treat multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases https://buff.ly/3sX9uDs
9/17/23 Eric Topol: An Exciting New Approach to Autoimmune Diseases https://buff.ly/48jcJ8p
“A new type of vaccine… has shown in the lab setting that it can completely reverse autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes—all without shutting down the rest of the immune system.” by leveraging the liver.
9/18/23 HealthDay: Older Americans' Finances Decline in Years Before Dementia Diagnosis https://buff.ly/3t1yk5b
Seniors who develop dementia begin to lose wealth in the eight years before a definitive diagnosis.
9/20/23 Stanford Class of 2027 Move-in Day video https://buff.ly/45YPdMq































This is such an excellent roundup and review - thank you 🙏🏻
Will a booster after two months even be allowed?