Similar to last week, there are about 1 million new COVID cases per day in the United States with about every 1 in 34 people infected nationally per JP Weiland. Wastewater and cases were starting to peak, but the curve is “shouldering” because children are returning to school and because of KP.3.1.1’s dominance. Hospitalizations are no longer reported by most states, but may be later this year.
From: https://twitter.com/JPWeiland/status/1827075333553607121
Emergency department visits for COVID have peaked in most places except the midwest region which is still increasing. Unfortunately, deaths from COVID infection are increasing in the US. According to BNO news, “1,134 new COVID deaths were reported during the week [of August 18], a notable uptick from 761 last week and 652 the week before. This marks the first week since March with more than 1,000 new deaths.”
A new Bloomberg article talks about the fact that COVID deaths are still significant 5 years into the pandemic. Other factors such as increased drug overdoses and higher stress on healthcare systems from COVID have contributed to the increase in deaths as well. Bloomberg reports that this somber trend has led to growing profits for companies in the funeral industry.
Regarding wastewater levels of SARS-2, the CDC reports VERY HIGH levels of virus nationally, with the highest levels in the West.
From: https://www.cdc.gov/nwss/rv/COVID19-nationaltrend.html
County SARS-CoV-2 wastewater levels from Sara Anne Willette: https://iowacovid19tracker.org/
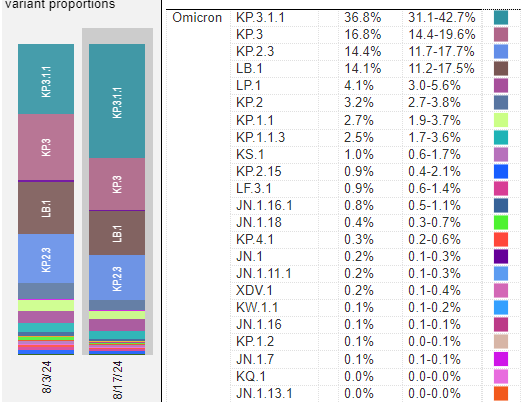
Variants
KP.3.1.1, a deFLuQE variant, is causing most cases of COVID now around the world. A new recombinant variant called XEC is being followed by the variant hunters of Twitter. XEC is a combination of KP.3.3 (FLuQE) and KS.1.1 and has spike mutations: F456L, Q493E, with 2 new mutations S:T22N and S:F59S. It does not have the R346T mutation like the FLiRT variants. Although XEC does appear to have a small growth advantage over KP.3.1.1, it is too early to tell if it will have an impact or not.
Vaccines
On Thursday, the FDA approved the updated KP.2 mRNA COVID vaccines which should be available in pharmacies soon. As of today, the CDC has not updated the vaccine locator (https://www.vaccines.gov/en/) yet, but I anticipate that they will very soon. The new updated KP.2 mRNA vaccines will be approved for all people age 6 months and older. People over age 12 who were recently vaccinated should wait 2 months to receive a new mRNA COVID KP.2 vaccine. Many people plan to get vaccinated now with the new KP.2 vaccine since wastewater levels and cases are very high, but others are considering waiting until the end of October in anticipation of the holidays and the winter wave.
Friday, Novavax updated their press release statement on the Novavax JN.1 vaccine stating that they were working to provide “additional information” requested by the FDA. It is unclear when the Novavax vaccine will be approved.
Starting in late September, the U.S. Federal government will offer 4 free COVID tests for Americans at COVIDtests.gov.
Researchers from the NIH put out a review on the next generation of coronavirus vaccines. They discussed coronaviruses (CoVs) including SARS-1, MERS and SARS-CoV-2 and how they are related to each other phylogenetically. In addition, they reviewed available vaccines for different types of CoVs, work being done towards creating pan-coronavirus vaccines that can fight many types of coronaviruses, and what vaccine technologies are expected in the near future.
Pediatrics
In an observational RECOVER trial study evaluating children with Long COVID, the most common Long COVID symptoms that school-age children (6-11 years) had were “headache (57%), followed by trouble with memory or focusing (44%), trouble sleeping (44%), and stomach pain (43%).” Other common symptoms included body, muscle, and joint pain; daytime tiredness/sleepiness or low energy; and feeling anxious. “In adolescents (12-17 years), the most common Long COVID symptoms were daytime tiredness/sleepiness or low energy (80%); body, muscle, or joint pain (60%); headaches (55%); and trouble with memory or focusing (47%).” Feeling anxious and sleep disturbances were other commonly reported symptoms for teens. The authors note that it is important to stratify the two different age groups when studying Long COVID because of the differences in symptom frequency.
Long COVID
A new study highlights "leaky gut" and autoimmune responses as key factors in Long COVID. Researchers discovered that damage to the gut's tight junctions from autoantibodies to tight junction proteins zonulin and occludin (ZOOC) allows bacteria to enter the bloodstream. This can trigger other autoimmune responses in Long COVID which are linked to depression and chronic fatigue. IgA-LPS (antibody against bacterial proteins) combined with IgG-ZOOC (antibody against zonulin + occludin proteins in tight junctions between cells) were the strongest biomarkers for Long COVID in this study. The study also found connections between Long COVID, reactivation of the HHV-6 virus, and autoimmune attacks on oligodendrocyte and neuronal proteins, including myelin basic protein (MBP). Targeting the damage to the gut and reducing autoimmune responses may be important in treating Long COVID.
The Patient-Led Research Collaborative wrote an article on how to best design clinical trials for Long COVID. They recommend drug trials that aim to cure Long COVID, by repurposing existing drugs and developing new ones. Studies should be rigorous, like triple-blinded randomized trials, and accessible so participants can join remotely from home. It is also important to include other chronic illnesses like ME/CFS and dysautonomia as comparison groups, and to screen for a wide range of symptoms. Trials should strive for diverse representation, including people of all races, ethnicities, genders, and severity levels of illness. The authors also recommend involving patients with lived experience and testing multiple therapies at once to make trials more effective.
An expert consensus report written by Long COVID all-star researchers from around the world highlights the complexity of Long COVID. The report emphasizes the need for improved diagnosis, treatment, and research into Long COVID, as well as better education for healthcare professionals. Key recommendations include prioritizing research on the mechanisms of Long COVID, including organ damage, immune dysfunction, and the impact on children. The panel also stresses the importance of multidisciplinary care, individualized treatment plans, and the development of biomarkers to aid diagnosis and treatment. The report calls for global collaboration and funding to address the long-term societal and economic impacts of Long COVID.
Skeletal muscle biopsies from people with Long COVID showed reduced mitochondrial respiration compared to healthy individuals. The low mitochondrial respiration was associated with high blood levels of soluble IL-2 receptor alpha subunit (sIL2R), a T cell-specific receptor. In vitro studies showed that sIL2R directly impairs mitochondrial oxygen consumption and reduces mitochondrial complex III subunit protein levels in cultured muscle cells. Targeting systemic sIL2R may be a potential treatment for PASC-related fatigue.
In an article entitled “A Virtuoso Cellist’s Painstaking Path From Long Covid Back to the Stage”, cellist Joshua Roman talked to the New York Times about what it has been like for him to have Long COVID. We were also fortunate to have Joshua speak at a Stanford CME on Long COVID last Thursday where he performed a musical piece that he wrote about Long COVID. It was very moving.
Card that Joshua Roman carries in case he has a Long COVID “crash”, From: https://buff.ly/3XezuFZ
Post COVID chronic illnesses
Anosmia and Brain damage
A group from Chile found that people who had anosmia (loss of smell) from a COVID infection have abnormal changes in brain function and structure including alterations in cortical thickness and white matter integrity. In 73 people with post-COVID anosmia, cognitive tests showed impulsive decision-making and functional MRI showed changes in brain activity, especially in brain regions associated with decision-making and learning. “These findings suggest that anosmia may be a sign of more serious neurological issues, even in patients with mild COVID-19 symptoms.”
Hyperglycemia
We are seeing a significant increase in Type 2 diabetes after COVID infection. A new study shows that SARS-CoV-2 infected African green monkeys have "a dysregulated blood chemokine signature during acute COVID-19 that correlates with elevated and persistent hyperglycemia four months post-infection." Interestingly, giving a COVID mRNA vaccine 4 days after the monkeys were infected, improved glycemic control. The authors concluded that the African green monkey model can be used to identify treatments for COVID-related metabolic problems.
Heart muscle abnormalities
In a preprint article, authors from China discuss a case series of 5 patients with viral myocarditis after COVID infection that were associated with cardiovascular diseases including sudden cardiac death during exercise, coronary atherosclerotic heart disease, acute inferior myocardial infarction, and acute myocarditis. Heart biopsies evaluated under electron microscopy showed "widespread mitochondrial vacuolations and the presence of myofilament degradation within the cardiomyocytes of these patients" that was similar to what was found in SARS-CoV-2-infected mice that the authors studied as well.
Mental Illness
COVID infection is associated with increased risks of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and other long term chronic illnesses. A new study shows that mental illness is increased after COVID infection as well, especially for unvaccinated people. A group from the United Kingdom studied more than 18 million people, of which 14 million were vaccinated against COVID-19. Unvaccinated people were found to have a higher risk of mental illness in the year after COVID infection, and if they were hospitalized for COVID and not vaccinated, they were 16.3x more likely to have depression in the year after COVID infection. Vaccination was found to reduce the risk of new onset and worsened mental illness after acute COVID infection.
H5N1
According to a tweet by Helen Branswell of STAT News, there are fewer new H5N1 outbreaks in cattle being reported in the last few weeks. Last week, there were only 2 new infected herds reported.
Mpox
Mpox, previously known as monkeypox, has been spreading in several countries in Africa with the highest numbers in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Last week, a Clade I mpox case was reported in Sweden and this week another case was noted in Thailand. Both people had just returned from traveling in Africa. The WHO Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) is helping to mobilize people and supplies to help curb the African outbreak. A new study from the NIH shows that the antiviral Tecovirimat (TPOXX) did not work against Clade I mpox in the DRC. But, they did find that hospitalization and high-quality supportive care results in better outcomes including a lower mortality rate from Clade 1 mpox.
I made an infographic summarizing Mpox that I put in a separate post here.
Other news:
Using the WHO database for a disproportionality study, researchers found an increased risk for suicidal ideation with semaglutide (Wegovy), a GLP-1 medication, that was not seen for liraglutide. Suicidal ideation was higher in patients taking semaglutide if they were already taking antidepressant medications. Of note, antidepressant use had been an exclusion criteria in premarketing clinical trials.
83 year old Dr. Fauci was hospitalized for a week for West Nile virus. He is now home and is expected to make a full recovery. About 1 in 150 infected people can develop a serious, sometimes fatal, case of West Nile virus. West Nile virus can be prevented by protecting oneself from mosquito bites.
A new mutation for "salmiak" (salty licorice) coats has been discovered in cats in Finland. The distinctive salt-and-pepper color pattern in the cats includes white tails and yellow or green eyes.
From: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/age.13438
Have a great rest of your weekend,
Ruth Ann Crystal MD
COVID news notes:
US Variant tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions
Updated only every 2 weeks, so no changes reported this week.
CDC COVID data tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/index.html#datatracker-home
Deaths: 8/18/24 BNO news: https://bnonews.com/index.php/2024/08/us-covid-update-august-18/
As of August 18, 1134 new COVID deaths were reported during the week, a notable uptick from 761 last week and 652 the week before. This marks the first week since March with more than 1,000 new deaths, the sixth week in a row with more than 500 new deaths, and the 231st week in a row with more than 400 new deaths.
COVID Emergency Dept visits: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#ed-visits_all_ages_combined
CDC Respiratory viruses (COVID, Flu, RSV) Hospitalizations (for those states reporting): https://www.cdc.gov/resp-net/dashboard/index.html
Walgreens positivity rate: https://www.walgreens.com/businesssolutions/covid-19-index.jsp
US Wastewater Monitoring:
CDC wastewater reporting: https://www.cdc.gov/nwss/rv/COVID19-nationaltrend.html
Last updated 8/22/24
CDC wastewater map: https://www.cdc.gov/nwss/rv/COVID19-currentlevels.html
Very high still in many places
National SARS-CoV-2 data from Sara Anne Willette: https://iowacovid19tracker.org/
8/15/24 WastewaterSCAN + NWSS wastewater
Wastewater SCAN: https://data.wastewaterscan.org/
California statewide view https://buff.ly/3YObiul
Sewer Coronavirus Alert Network (SCAN) project by Stanford University:
Santa Clara County wastewater: https://publichealth.santaclaracounty.gov/health-information/health-data/disease-data/covid-19/covid-19-wastewater
Marin county: https://coronavirus.marinhhs.org/surveillance
JP Weiland: https://twitter.com/JPWeiland
https://twitter.com/JPWeiland/status/1827075333553607121
August 23rd update:
Once again, infections are flat (peak) near 1 million per day. A high shoulder is anticipated as kids return to school and KP.3.1.1's recent dominance.
967,000 new infections/day
1 in every 34 people currently infected
66% higher than 12 month avg.
https://x.com/JPWeiland/status/1826391329355522072
https://x.com/EricTopol/status/1826059328534753506
8/20/24 Dr Topol speaks on PBS at 47:39
8/19/24 ER visits for COVID infection are starting to decline except in Midwest region
https://x.com/JPWeiland/status/1825689562519089169
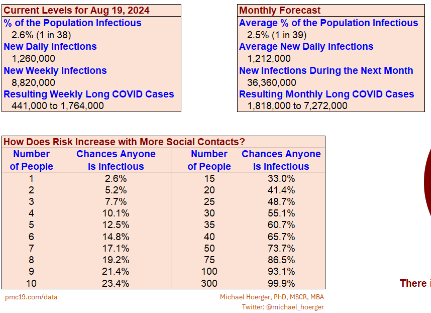
Michael Hoerger modeling: http://pmc19.com/data/, https://twitter.com/michael_hoerger
Variants
https://x.com/Mike_Honey_/status/1824759622101840041
8/17/24 @Mike_Honey_ thread on the XEC variant
“Recombinant variant XEC is continuing to spread very rapidly, and looks a likely next challenger against the now-dominant DeFLuQE variants (KP.3.1.1 and descendants).
“XEC first appeared in Berlin in late June. It has since spread quite rapidly across Europe, North America and Asia. Around 78 samples have now been reported, from 12 countries on 3 continents. Taiwan has reported it's first sample in the last week.
“XEC is a mix of KS.1.1 (FLiRT, although XEC did not get the R346T mutation) and KP.3.3 (FLuQE). XEC might have an advantage from it's unusual T22N mutation, in combination with the FLuQE mutations.
“Globally, XEC is showing a growth advantage of 3.5% per day (25% per week) over JN.1.* + DeFLuQE variants. This is the fastest growth of any contender I am aware of. As the starting frequencies are quite low, any crossover looks like happening in September or later.”
https://x.com/JPWeiland/status/1827377349383340188
Aug 24, 2024 @JPWeiland
XEC is a new recombinant of KS.1.1 and KP.3.3 that some of us have been tracking for the last couple of weeks. Though it's growing against KP.3.1.1, in my opinion it's too early to know if it will have any impact down the line. A lot of time for things to change.
XEC is a combination of KP.3.3 (FLuQE) and KS.1.1 and has spike mutations: F456L, Q493E, with 2 new mutations S:T22N and S:F59S. It does not have the R346T mutation like the FLiRT variants.
Acute COVID infections, General COVID info
8/19/24 Bloomberg; Deaths Are Up Post-Covid, and So Are Funeral Stocks: Prognosis https://buff.ly/4fUtWsC
Pediatrics
8/21/24 NIH: NIH-funded study finds long COVID affects adolescents differently than younger children https://buff.ly/3AzCuVL
Adolescents were most likely to experience low energy/tiredness while children were most likely to report headache.
8/21/24 JAMA: Characterizing Long COVID in Children and Adolescents https://buff.ly/3TprDEr
Because of these differences, it is important to stratify into the two different age groups when studying Long COVID.
Vaccines
8/22/24 FDA Approves and Authorizes Updated mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines to Better Protect Against Currently Circulating Variants https://buff.ly/3Xe5wCR
Novavax
8/23/24 Novavax Press Release Update
“Novavax is working expeditiously to provide the additional information the U.S. FDA requires to complete its review and we are grateful for their ongoing efforts and strong partnership. Novavax’s intent is to provide access to our vaccine as a choice for consumers this season.”
8/22/24 Nature: Beyond COVID-19: the promise of next generation coronavirus vaccines https://buff.ly/3ABdrl2
Fig. 2 | Different vaccination strategies and the resulting immune responses.
From: https://www.nature.com/articles/s44298-024-00043-3.pdf
8/23/24 NBC: U.S. will again offer free at-home Covid tests starting in late September https://buff.ly/3X0fneb
Long COVID
8/19/24 Journal of Medical Virology: From human herpes virus‐6 reactivation to autoimmune reactivity against tight junctions and neuronal antigens, to inflammation, depression, and chronic fatigue syndrome due to Long COVID https://buff.ly/3YTBupn
In summary, the presence of a leaky gut and bacterial translocation could potentially play a significant role in the development of autoimmunity caused by COVID-19 and Long COVID. It has been observed that dysfunctions in the tight junctions can lead to increased bacterial translocation, which has been linked to the development of autoimmune responses and autoimmune disease.63 An increased movement of luminal contents, such as microbiota, into the blood plays a key role in the development or worsening of human autoimmune disorders.24, 31, 63
leaky gut and resulting autoimmunity play a role in the pathophysiology of Long COVID,
This study enrolled a total of 180 individuals, namely 90 individuals diagnosed with Long COVID and 90 individuals who served as controls.
90 LC = 54 Immunosciences Lab Los Angeles + 58 LC Iraqi patients. All pts had a positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2. (54 + 58 = 112 LC patients)
Healthy control serum samples (n = 76) were supplied by Innovative Research, Novi, Michigan, 14 healthy controls from Iraq. (76 + 14 = 90 controls)
Figure 1
Results of neural network analysis showing the importance chart. The output variables are the diagnosis of Long COVID and healthy controls. Input variables are immune responses to lipopolysaccharides (LPS) and zonulin and occludin (ZOOC).
From: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/jmv.29864
h/t Vipin M. Vashishtha https://x.com/vipintukur/status/1825561230981108087
A NEW study shows that increased autoimmunity against components of the tight junctions as well as increased IgA levels to LPS of Gram-negative bacteria play a role in Long COVID and in its physio-affective phenome. 7/
Moreover, the responsivity to the tight junctions is associated with autoimmunity to neuronal antigens and the BBB. 8/
It may be suggested that dysfunctions in gut tight junctions caused by viral persistence or reactivation can lead to an increased entry of gut microbes into the bloodstream. 9/
These microbes, through structural similarities and molecular mimicry, or other mechanisms, can trigger cross-reactivity and subsequent autoimmune responses against the body's self-epitopes or modified neo-epitopes. 10/
These processes also lead to the activation of the IRS, inflammation, oxidative stress, nitrosative stress, and increased autoimmune responses to oxidatively modified neo-epitopes. All those factors together determine the physio-affective phenome of Long-COVID. 11/
In addition to viral infection and reactivation, as well as immune activation and oxidative stress, this research has demonstrated that targeting the damage to the gut tight junctions and subsequent autoimmune responses could be a potential strategy for treating Long COVID. 12/
Conclusion:
Leaky gut and resulting autoimmunity play a role in the pathophysiology of LongCOVID, particularly. This is connected to various pathways such as IRS activation, NLRP3 inflammasome activation @ oxidative stress. 13/13
From https://x.com/vipintukur/status/1825565208695431301
10/15/24 Life Sciences: Designing and optimizing clinical trials for long COVID, From Patient-Led Research Collaborative for Long COVID
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0024320524005605
We recommend several guidelines for Long COVID trials:
pharmaceutical trials with potentially curative, primary interventions should be prioritized, and both drug repurposing and new drug development should be pursued.
study designs should be both rigorous and accessible, e.g., triple-blinded randomized trials that can be conducted remotely, without participants needing to leave their homes.
studies should have multiple illness comparator cohorts for IACCIs such as myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME/CFS) and dysautonomia, and screen for the full spectrum of symptomatology and pathologies of these illnesses.
studies should consider inclusion/exclusion criteria with an eye towards equity and breadth of representation, including participants of all races, ethnicities, and genders most impacted by COVID-19, and including all levels of illness severity.
involving patient-researchers in all aspects of studies brings immensely valuable perspectives that will increase the impact of trials.
We also encourage the development of efficient clinical trial designs including methods to study several therapies in parallel.
8/21/24 Lancet preprint: Long COVID Clinical Evaluation, Research and Impact on Society: A Global Expert Consensus https://buff.ly/3XgeUpU
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4931063
Long COVID affects millions worldwide, with about 15% of people developing long-lasting symptoms after a COVID-19 infection.
There is a lack of guidelines and formal training for medical professionals on how to evaluate and treat Long COVID patients.
A global study using a consensus method gathered input from healthcare experts and patients, identifying key areas of agreement on diagnosis and research, but found less consensus on treatment approaches, highlighting the need for more research, especially on organ damage and the effects of vaccines.
8/19/24 MedRxiV (U Kentucky): Soluble IL-2R contributes to impaired muscle cell mitochondrial respiration in fatigued individuals with post-acute sequelae of COVID https://buff.ly/3Z2UWQq
Low mitochondrial respiration in skeletal muscles of LC patients with fatigue was associated with high blood levels of soluble IL-2 receptor alpha subunit (sIL2R), a T cell-specific receptor.
8/17/24 NY Times: A Virtuoso Cellist’s Painstaking Path From Long Covid Back to the Stage https://buff.ly/3XezuFZ
Cellist Joshua Roman talked to the New York Times about his Long COVID journey.
Post COVID chronic diseases
8/17/24 Nature Scientific Reports: Patients recovering from COVID-19 who presented with anosmia during their acute episode have behavioral, functional, and structural brain alterations https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-69772-y
“These findings suggest that anosmia may be a sign of more serious neurological issues, even in patients with mild COVID-19 symptoms.”
8/20/24 Nature Communications: Non-human primate model of long-COVID identifies immune associates of hyperglycemia https://buff.ly/3XpTqXL
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-50339-4
Post COVID cardiac disease
8/20/24 MedRxiV (preprint): SARS-CoV-2 Damages Cardiomyocytes Mitochondria and Implicates Long COVID-associated Cardiovascular Manifestations https://buff.ly/4cvAlaR
Authors from China discuss a case series of 5 patients with viral myocarditis after COVID infection that were associated with cardiovascular diseases including sudden cardiac death during exercise, coronary atherosclerotic heart disease, acute inferior myocardial infarction, and acute myocarditis.
All 5 patient heart biopsy samples showed:
1. local myofibrillar fibrosis
2. loss of integrity of myofibrillar bundles
3. Interstitial oedema and necrosis
4. lipofuscin granules accumulation
5. vacuolations in mitochondria
8/21/24 JAMA Psychiatry: COVID-19 and Mental Illness in Vaccinated and Unvaccinated People https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapsychiatry/fullarticle/2822342
Mental illness is increased after COVID infection, especially for unvaccinated people. A group from the United Kingdom studied more than 18 million people, of which 14 million were vaccinated against COVID-19.
Vaccination reduced the risk of new onset and worsened mental illness after acute COVID infection.
H5N1
https://x.com/HelenBranswell/status/1826978382631903727
8/23/24 @HelenBranswell
There hasn't been a new #H5N1 #birdflu infected dairy herd confirmed by @USDA this week. Only 2 last week. Does this mean the outbreak is coming under control? Colorado & Michigan's numbers are probably solid. Elsewhere refusal to test means we don't know what we're not seeing.
Avian Flu H5N1 Influenza A https://www.cdc.gov/nwss/wastewater-surveillance/Flu-A-data.html
https://bnonews.com/index.php/human-cases-of-h5n1-bird-flu/
Mpox
8/22/24 CIDRAP: More global mpox spread as clade 1b confirmed in Thailand, the 2nd case outside Africa https://buff.ly/3WZGDd7
8/15/24 NIH News Release: The antiviral Tecovirimat is safe but did not improve clade I mpox resolution in Democratic Republic of the Congo https://buff.ly/3yLWKCM
This shows that better outcomes among people with mpox can be achieved when they are hospitalized and provided high-quality supportive care.
5/2023 Airborne transmission of MPXV and its aerosol dynamics under different viral load conditions https://buff.ly/4cBKh2k
Other news:
8/20/24 JAMA: Disproportionality Analysis From WHO Data on Semaglutide, Liraglutide, and Suicidality https://buff.ly/4dThV4W
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2822453
Using the WHO database for a disproportionality study, the authors found a signal for suicidal ideation with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist semaglutide, but not for liraglutide. Suicidal ideation was higher in patients taking semaglutide if they were already taking antidepressant medications which had been an exclusion criteria in premarketing clinical trials.
8/24/24 NPR: Fauci is recovering at home after being hospitalized for West Nile virus https://www.npr.org/2024/08/24/nx-s1-5088635/fauci-west-nile-virus
5/2024 A new mutation for "salmiak" (salty licorice) coats has been discovered in cats in Finland. Distinctive salt-and-pepper color pattern. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/age.13438
































As always, thank you! (And salty licorice cats are a sweet diversion! 😻)
We may still have a COVID problem, but we also have cats, and that’s worth something. Thank you for your newsletters, Dr Ruth!