This week's COVID news 4/21/23
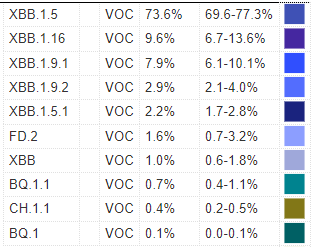
XBB1.16 levels are still increasing,but they did not double this week. XBB 1.9 continues to increase by about 1% each week and both subvariants are working to push XBB.1.5 out of first place. Wastewater virus levels look good at this time throughout most of the United States.
This week, the FDA and CDC approved a second dose of the bivalent booster vaccine for people over age 65 and for those who are immunocompromised. People over 65 should wait four months since their last vaccination to get their second booster and immunosuppressed people should wait at least two months before getting the booster. There was no guidance as to if someone should wait to get vaccinated if they recently had a COVID infection.
Initially, there were some concerns that there could be immune imprinting after the initial vaccinations with the original virus mRNA that could cause people to not make good antibodies to the bivalent booster, but this has not turned out to be the case. Real world studies show that the bivalent booster increases antibodies and protection against Omicron subvariants well.
We know that SARS-CoV-2 infects the body via ACE2 receptors on our cells. A new study shows that the virus then spreads from cell to cell in the human body via the tight junction Occludin protein.
A new study from British Columbia shows that there is a significant increase in Type II diabetes in the one year after a COVID infection. Most of the patients in the study were young and in their 30s. Eric Topol reviewed 12 studies that show an increased risk of diabetes after COVID infection including this latest study. SARS-CoV-2 infection can have a lifelong effect on people’s health.
Long COVID
People with Long COVID like Charlie McCone have asked us to take 2 minutes to support the CARE for Long COVID Act here. The CARE for Long COVID Act 2023 has been re-introduced as a bipartisan, bicameral effort by Senators Kaine, Markey and Duckworth, and Representatives Beyer and Bergman. STAT news reported that the NIH has wasted the $1 billion given to them by Congress in December 2020 to study Long COVID. So far, the NIH RECOVER initiative has had no results except for observational studies and the NIH did no studies on possible treatments for Long COVID. Drs. Putrino, Kell, and Pretorius wrote a comprehensive review of the pathophysiology of Long COVID, including abnormal clotting issues. It is a very detailed review that I plan on diving into further this weekend.
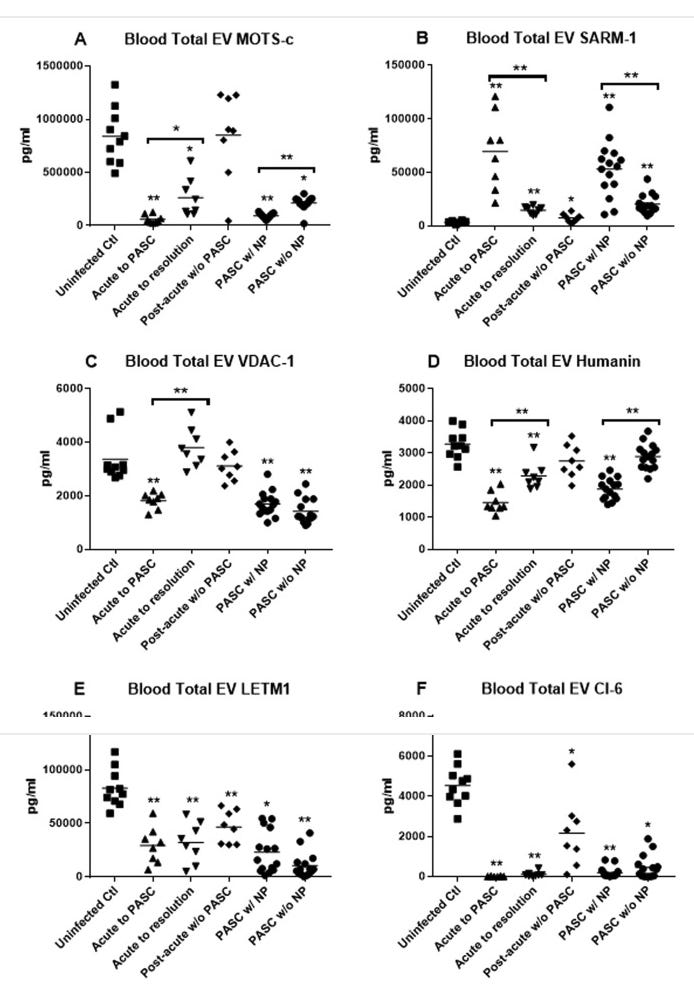
An interesting study from UCSF shows that there are biomarkers that can predict who will get Long COVID/PASC and who will get Long COVID with neurologic manifestations. Looking at extracellular vesicles in the blood during an acute COVID infection, the authors could predict who would get PASC (Long COVID) by looking at levels of mitochondrial proteins MOTS-c, VDAC-1, Humanin and SARM-1. Ed Yong wrote a piece in the Atlantic on how people with Long COVID are being forgotten. He speaks about how most people have moved on and no longer think about COVID, but that the virus is still infecting people and Long COVID patients are still suffering.
A rural school teacher named Ryan Hisner was featured in Nature magazine. Ryan is a self-taught COVID mutation hunter who helps the world by alerting scientists to possible troublesome new viral mutations. A large hospital in Santa Rosa, California had an outbreak of COVID in staff and patients since they dropped their mask mandates. Temporarily, the hospital has reinstated a mask mandate. The federal government announced that they will continue to pay for future COVID vaccinations for those who have no health insurance.
In non-Covid news, an Indian rapper named Saniya MQ has defied the odds of living in an extremely poor neighborhood in Mumbai and is having success rapping about teen girls creating their identity, about environmental justice and world peace. Injecting lidocaine around a breast cancer tumor 7 to 10 minutes before surgical removal may reduce the risk of metastasis and death for early cancers. A toddler crawled through the fence at the White House and was picked up by the police and was returned to his parents. This Saturday, April 22 from 10 am to 2pm is National Prescription Drug Take Back Day sponsored by the DEA. Your local collection site can be found here.
A new blood test that measures bisecting N-acetylglucosamine and Tau protein can predict progression to Alzheimer’s disease in combination with a person’s APOE4 allele status. Last week, we also learned about a blood biomarker called alpha-synuclein that could predict Parkinson’s disease. These discoveries could lead to new treatments for these neurodegenerative diseases.
Have a good weekend,
Ruth Ann Crystal MD
Twitter: https://twitter.com/CatchTheBaby
In other news:
4/16/23 NPR: The improbable fame of a hijab-wearing teen rapper from a poor neighborhood in Mumbai https://buff.ly/43H6ed0
Saniya MQ is a 16-year-old who raps about teen girls creating an identity, environmental justice and world peace. "My identity as a woman is important to my existence."
4/6/23 Journal of Clinical Oncology: Effect of Peritumoral Infiltration of Local Anesthetic Before Surgery on Survival in Early Breast Cancer https://buff.ly/3MTFkZO
Injecting 0.5% lidocaine around a breast tumor 7 to 10 minutes before surgical removal may reduce the risk for metastases and death in patients with early breast cancer.
5-year disease-free survival rates were 86.6% in the lidocaine group and 82.6% in the no-lidocaine group (hazard ratio [HR], 0.74; P = .017).
Five-year overall survival rates were also significantly improved among those who received lidocaine: 90.1% and 86.4%, respectively (HR, 0.71; P = .019).
4/18/23 AP: Littlest intruder: Toddler crawls through White House fence https://buff.ly/3ohZFxq
4/12/23 Alzheimer’s Journal: A glycan epitope correlates with tau in serum and predicts progression to Alzheimer's disease (AD) in combination with APOE4 allele status https://buff.ly/41rehZY
The bisecting N-acetylglucosamine glycan epitope is known to be elevated in cerebrospinal fluid in Alzheimer's disease.
A new blood test that measures Bisecting N-acetylglucosamine and Tau is a valuable blood biomarker for predicting Alzheimer's disease.
National Prescription Drug Take Back Day is April 22, 2023 – 10AM to 2PM
A safe, convenient, and responsible means of disposing of prescription drugs, while also educating the general public about the potential for abuse of medications.
COVID news:
Reported cases are not as reliable now. Wastewater gives the best picture of viral spread.
World reported cases https://medriva.com/charts/world-monitor.php
US reported cases https://medriva.com/charts/usa-monitor.php
Walgreens positivity rate: https://www.walgreens.com/businesssolutions/covid-19-index.jsp
Variant tracker in US: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions
XBB.1.16 did not double this week like previous weeks (2.1% to 3.9% to 7.2% to 9.6%)
XBB.1.9.1 is gaining about 1% per week.
Wastewater Monitoring:
CDC Wastewater Monitor https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#wastewater-surveillance
Biobot: https://biobot.io/data/
Sewer Coronavirus Alert Network (SCAN) project by Stanford University:
Please consider asking your members of Congress to support the CARE for Long COVID Act https://p2a.co/m3itjze
Led by Senators Kaine, Markey and Duckworth, and Representatives Beyer and Bergman, the CARE for Long COVID Act 2023 has been re-introduced as a bipartisan, bicameral effort.
4/20/23 SF Chronicle: COVID-19 outbreak hits large Bay Area hospital, prompting new mask rules https://buff.ly/3H1GQoF
Kaiser Permanente Santa Rosa Medical Center has reinstated a temporary mask mandate after more than a dozen hospital workers and patients at the medical center tested positive for the coronavirus this week.
The California Department of Public Health lifted the last of the statewide mask mandates on April 3, which included rules for health care settings.
4/19/23 Ed Yong, the Atlantic: Long COVID Is Being Erased—Again https://buff.ly/41FTMsm
Textise version: Long COVID Is Being Erased—Again https://buff.ly/41x6F8r
“Long COVID is a mirror on our society, and the image it reflects is deeply unflattering.
Most of all, long COVID is a huge impediment to the normalization of COVID. It’s an insistent indicator that the pandemic is not actually over; that policies allowing the coronavirus to spread freely still carry a cost; that improvements such as better indoor ventilation are still wanting; that the public emergency may have been lifted but an emergency still exists; and that millions cannot return to pre-pandemic life. “Everyone wants to say goodbye to COVID,” Duggal told me, “and if long COVID keeps existing and people keep talking about it, COVID doesn’t go away.” The people who still live with COVID are being ignored so that everyone else can live with ignoring it.”
4/22/23 Lancet: State-to-state differences in US COVID-19 outcomes: searching for explanations https://buff.ly/3ouqE9a
Review of paper by Thomas J Bollyky et al.
4/20/23 STAT News: The NIH has poured $1 billion into long Covid research — with little to show for it https://buff.ly/3V1QXQf
Congress gave the NIH $ 1.15 Billion in December 2020 to study Long COVID, but the NIH's RECOVER initiative has not studied possible treatments for Long COVID.
“There’s basically nothing to show for it.”
The Duke study of Paxlovid has not even started but a privately funded (by Pfizer) Stanford study of Paxlovid for Long COVID has been enrolling patients.
4/19/23 CDC ACIP meeting re: Bivalent booster plan for people age 65+ and for those immunocompromised https://buff.ly/3UR4HNN
4
/19/23 Cell Endocrine & Metab (Putrino, Kell, Pretorius):
Long COVID: Pathophysiological factors and abnormalities of coagulation https://buff.ly/41Hdjsn
Coagulation dysregulation including microclots and platelet hyperactivation.
4/19/23 Immunity: Immunological imprinting: Understanding COVID-19 https://buff.ly/41Q8361
Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 appears to broaden with new variant exposure after initial vaccinations or infection.
4/18/23 Reuters: US FDA authorizes second Omicron-updated COVID booster for older adults https://buff.ly/41opI4G
People aged 65 years and older can now receive a second dose of the updated "bivalent" booster four months after the first, while immunocompromised people can get an additional shot of the updated vaccine after two months.
4/18/23 Nature: How a rural school teacher became a top COVID sleuth https://buff.ly/43JyThK
Ryan Hisner, a school science teacher from rural Monroe, Indiana, has an uncanny ability to detect unusual mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 genome.
He and other self-taught citizen scientists flag concerning mutations via Pango so that they can be tracked.
4/18/23 JAMA: Association of COVID-19 Infection With Incident Diabetes https://buff.ly/3UMDb3O
n = 125,000 COVID positive individuals in British Columbia vs. 500,000 unexposed
In this cohort study, SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with a higher risk of diabetes and may have contributed to a 3% to 5% excess burden of diabetes at a population level.
NY Times commented on this study:
4/18/23 NY Times: Covid May Increase the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes, Researchers Find https://buff.ly/3LbgIu7
People infected with the coronavirus were significantly more likely to be diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes within a year of their infection.
“With a respiratory infection, you usually think, ‘Seven or eight days and I’m done with it, that’s it,’” he added. “Here we’re seeing lingering effects that are lifelong.”
Adults who had tested positive for the virus were 17% more likely to develop diabetes within a year of the positive test.
Men were 22% more likely to develop diabetes, compared with unexposed individuals.
The elevated risk for women was not statistically significant overall unless they were hospitalized or admitted to an intensive care unit.
Of all new cases of diabetes, some 3.4% could be attributed to a Covid infection.
For men, 4.8% of new cases were attributed to Covid.
4/18/23 Eric Topol: New diabetes post-acute Covid (PASC, Long Covid), an inconvenient truth https://buff.ly/3GWbZda
British Columbia study is the 12th to show increased risk of diabetes after COVID infection.
Dr. Topol references this interesting study from 2021:
9/15/21 Cell Metabolism: Hyperglycemia in acute COVID-19 is characterized by insulin resistance and adipose tissue infectivity by SARS-CoV-2 https://buff.ly/3mUu8RP
Insulin resistance is the main cause for hyperglycemia in patients with severe COVID-19.
Patients with COVID-19 and hamsters infected with SARS-CoV-2 have decreased adiponectin.
SARS-CoV-2 can directly infect human and mouse fat cells.
4/18/23 NY Times: Biden Administration Will Fund Program to Keep Covid Vaccines Free for the Uninsured https://buff.ly/41wKeA4
The program, which will include a partnership with pharmacy chains, will help cover the costs of vaccinating patients when the shots move to the commercial market later this year.
4/17/23 PNAS: Tight junction protein Occludin is an internalization factor for SARS-CoV-2 infection and mediates virus cell-to-cell transmission https://buff.ly/3GYmvAI
Initial infection by SARS-CoV-2 happens when the spike protein binds to ACE2 receptors.
Subsequent viral spread is through direct cell-to-cell transmission and syncytium formation.
The tight junction protein occludin (OCLN) binds the spike protein and mediates cell-to-cell virus transmission.
4/16/23 Am J of Medicine (UCSF): Prediction of Post-Acute-Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC, Long COVID) by Cargo Protein Biomarkers of Blood Total Extracellular Vesicles in Acute COVID-19 https://buff.ly/3N1CjX5
Blood samples taken 4/2020 to 12/2021 for the UCSF Biobank and/or UCSF LIINC study.
Six groups of participants were assembled for this study and are cited in each frame of the two figures:
Uninfected controls (n=10),
Acutely infected who would proceed to PASC (n=8),
Acutely infected whose COVID-19 would resolve (n=8),
Post-acute phase w/o PASC (n=8),
PASC with neuropsychiatric manifestations (n=15),
PASC without neuropsychiatric manifestations (n=15).
Figure 2: During acute infection, the levels of blood total extracellular vesicle levels of several mitochondrial proteins can predict:
⬇ MOTS-c, VDAC-1, Humanin and ⬆ SARM-1 predicts PASC
⬇ MOTS-c, Humanin and normal VDAC-1 levels and ⬆ SARM-1 predicts who will get PASC with neuropsychiatric (NP) manifestations
4/15/23 Lancet: Effects of sleep disturbance on dyspnoea and impaired lung function following hospital admission due to COVID-19 in the UK: a prospective multicentre cohort study https://buff.ly/3UQYIsk
Due to the association with multiple symptoms, targeting sleep disturbance might be beneficial in treating the post-COVID-19 condition."
Poor sleep may be related to lingering shortness of breath (dyspnea) and decreased lung function after a COVID infection that required hospitalization.
"Sleep disturbance following hospital admission for COVID-19 is associated with dyspnoea, anxiety, and muscle weakness.
6 months after hospitalization for COVID infection, 62% had poor sleep quality.