We are still at about 1,000,000 new COVID cases each day. Per JP Weiland, the prevalence of COVID infections is:
National 1 in every 34 people
Midwest 1 in 47 people
South 1 in 26 people
Northeast 1 in 49 people
West 1 in 21 people
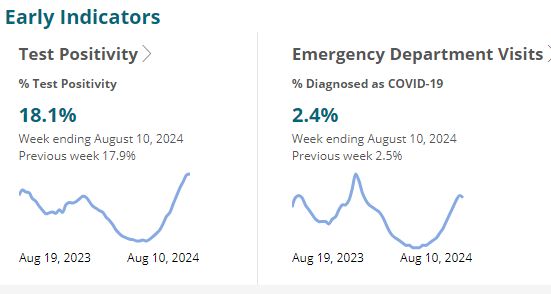
Most states have VERY, VERY HIGH, VERY HIGH or HIGH levels of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater according to the CDC. COVID test positivity is 18.1%. School has started in some locations and already some schools like JAG High School in Montgomery, Alabama have had to close because so many teachers and staff are absent with COVID.
JAG High School said that they are focusing on “sanitizing” the schools for the COVID outbreak, but schools should really prioritize improving indoor air quality to help prevent transmission. JAG high school will offer “masks and disinfectant wipes” when they reopen. Since COVID levels are VERY HIGH in most states right now, I am concerned that schools across the country will have similar COVID outbreaks given the lax CDC guidelines telling people to stay home from work or school until COVID symptoms are better and the person has no fever for 24 hours. The problem with that recommendation is that most people will still be infectious and will transmit COVID to other people if they follow the CDC guidelines.
Lucky Tran’s corrected version of the CDC recommendations:
From: https://x.com/luckytran/status/1808903219671663053
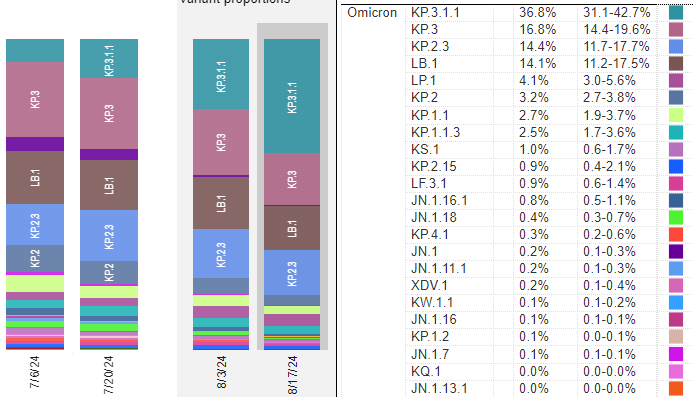
KP.3.1.1 is the dominant variant and with its strong ability to evade our immunity combined with the fact that most people have not had an updated booster in almost a year, it is prolonging the summer wave that started with KP.2 with its FLiRT mutations. The new KP.2 mRNA vaccines were expected out sometime in early September for everyone age 6 months and older. CNN posted yesterday that because of the large summer wave, the US FDA may approve the new KP.2 mRNA COVID vaccines as soon as next week according to unnamed sources at the FDA. Emergency department visits for COVID may be peaking now, so hopefully this COVID wave will also peak soon.
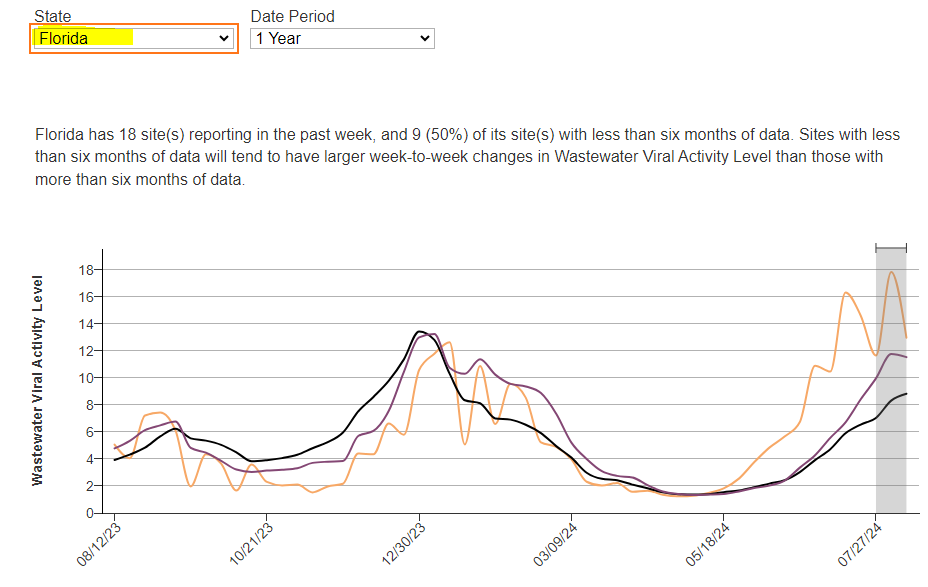
CDC: US SARS-CoV-2 wastewater levels are VERY HIGH
From: CDC wastewater reporting: https://www.cdc.gov/nwss/rv/COVID19-nationaltrend.html
From CDC wastewater map (8/15/24): https://www.cdc.gov/nwss/rv/COVID19-currentlevels.html
The WHO posted a new COVID update on 8/14/24 stating that globally, SARS-CoV-2 PCR percent positivity increased from 7.4% to 13.0% across 85 countries during the four-week reporting period from 24 June to 21 July 2024. Worldwide, new COVID cases increased 30% and deaths increased 26% during the same time period.
Vaccines
A study based on the EHR records of 186,990 pregnant individuals in 2021 and 2022
shows that receiving COVID-19 vaccination within 12 months before pregnancy was associated with lower risks of very and extremely preterm birth and small-for-gestational age in term babies for any vaccine type. There was also a lower stillbirth risk in those people who received an mRNA vaccine.
Antiviral treatments, prevention
In a proof of concept study, researchers from the NIH made a protein called RBD-62 which can block the ACE2 receptor so that SARS-CoV-2 cannot enter and infect cells. Tests in macaque monkeys showed that treatment with RBD-62 stopped viral replication in upper and lower airways with various SARS-2 variants. "Importantly, RBD-62 does not block the development of virus-specific T- and B-cell responses and does not elicit anti-drug immunity."
Pediatrics
A study looked at which age groups were more likely to be hospitalized with a COVID infection. Among children, teenagers had a higher risk for being hospitalized as compared to younger children. For adults, people age 50 to 64 years old were at greatest risk for severe COVID including the highest odds of requiring mechanical ventilation and ICU admission.
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) cases peaked in January 2021, with more than 200 cases weekly. In 2023, only 117 cases of MIS-C were reported to the CDC during the entire year, most likely due to lower incidence and also incomplete reporting.
More than 5.8 million American kids have Long COVID which is a multisystem disease that is still poorly understood by many people who work with children. Lisa Lombardi is the mother of a teenage son with Long COVID. She discusses symptoms in teens versus younger children and the difficulty finding healthcare providers who understand Long COVID in children.
Long COVID
A small study from Albany, NY of 103 patients with Long COVID as compared to two control groups,15 COVID recovered patients and 27 healthy controls, used whole genome methylation sequencing and found 39 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) that were specific to Long COVID and not the two control groups. DNA studies from whole blood mostly reflect the DNA from white blood cells circulating in the blood. The blood DNA methylation levels in Long COVID were related to circadian rhythm-regulating pathways and could be used to identify and stratify the severity of people with Long COVID regardless of the phenotype. Larger studies are needed to confirm these findings.
Another small study from Yale shows that neurologic symptoms in Long COVID appear to be associated with vascular inflammation and specifically with abnormal inflammation of the endothelium, which are the cells that line blood vessels. The authors compared 28 people with acute COVID infection (AC) to 50 people with neuro Long COVID (N-LC) and 29 controls who had recovered from COVID infection without Long COVID. Patients with N-LC had brain fog and cognitive issues, headache, neuropathy, altered mood and altered sleep which affected their quality of life and ability to function.
In general, vascular inflammation was found to be highest in acute COVID infection (AC), medium in N-LC, and lowest in the recovered control group. However, three vascular biomarkers were highest in N-LC: α-2 macroglobulin and L-selectin (related to white blood cell adhesion to the vascular endothelial lining) and Fetuin (related to vascular calcification and atherosclerosis). Other biomarkers that were higher in N-LC than in recovered controls “are involved in vascular remodeling and atherogenesis, suggesting that N-LC symptoms may relate to vascular regulation or may heighten risk for long-term vascular sequelae.”
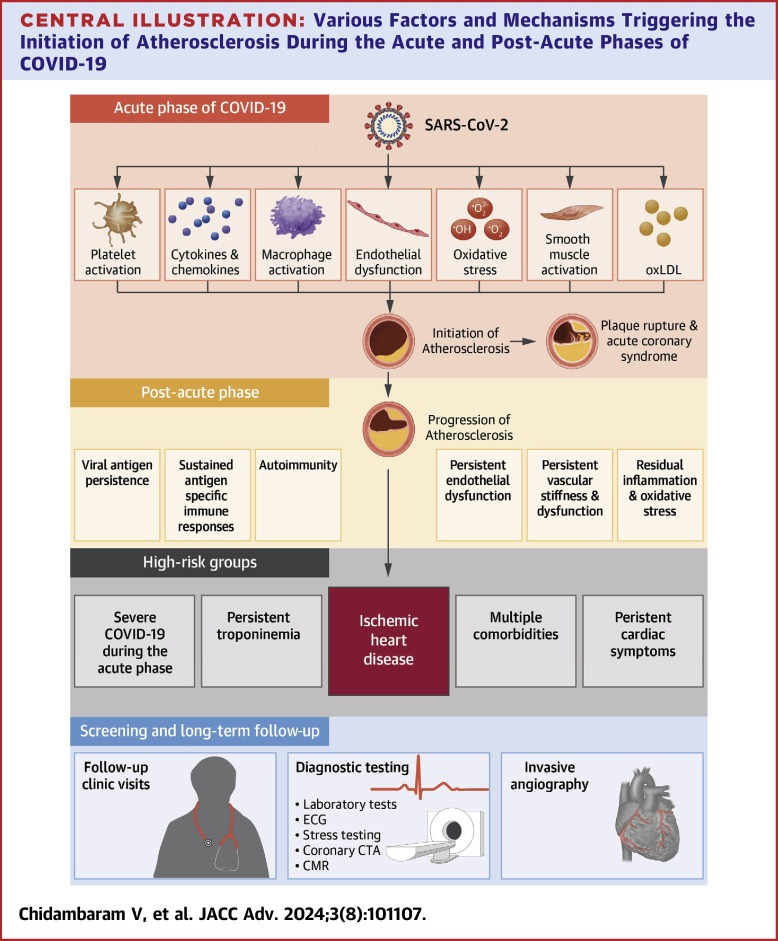
A review from this week looked at the pathogenesis of vascular disease in Long COVID and at mechanisms that promote atherosclerotic lesions after a COVID infection. Endothelial cells line blood vessels including those that feed the heart. Endothelial dysfunction, platelet activation and inflammation from COVID infection may increase the risk of atherosclerosis which can reduce blood flow to the heart and can lead to heart attacks. It can also cause strokes if blood vessels to the brain are inflamed and become blocked.
The authors note that “endothelial cell dysfunction, an early event, and the subsequent platelet activation and adhesion to the activated endothelium are central to both atherosclerosis and COVID-19, suggesting a major link between them. Though other viral infections can trigger pro-inflammatory cytokine release, the immune overactivation in SARS-CoV-2 infection is particularly severe, enhancing endothelial cell dysfunction and perpetuating this vicious cycle.”
From: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2772963X24003016
Researchers from the RECOVER program looked at 25 common blood tests trying to find a biomarker for Long COVID. Unfortunately, they were unable to find a difference in these tests between people with Long COVID and controls.
From: https://x.com/sunsopeningband/status/1823206687974809933
Chronic diseases after COVID
A group from Stony Brook University looked at people who had previously undergone cognitive testing in 2015 to 2019. Using longitudinal causal modeling they found that COVID infection leads to cognitive decline consistent with 10.6 years of brain aging. COVID-19-related Cognitive Decline (CRCD) manifests as executive dysfunction and was seen more commonly in people who had prior severe acute COVID infection and those with Long COVID. They recommend that Long COVID (PASC) patients undergo routine cognitive testing. They concluded, “These results imply an increase in cognitive dysfunction and poorer brain health after COVID-19 [infection], notably in those who experienced severe COVID-19 and PASC.”
Figure 1. Expected Trajectories of Change in Cognition Before and After the Onset of COVID-19
From: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S266703642400013X#fig0001
Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 were followed for three years, with their lung function and radiological abnormalities monitored longitudinally. While most patients showed improvement, more than one-third continued to experience persistent lung abnormalities, including symptoms, reduced diffusion capacity and fibrotic-like changes on CT scans. People with pulmonary damage after COVID infection should be followed.
Mpox
On 8/13/24, the Africa CDC declared its first public health emergency of continental security (PHECS) regarding the rapid spread of Mpox (a.k.a. monkeypox) across several African countries. The type of Mpox spreading now is the more virulent Clade 1b virus, which is different from the milder Clade 2 Mpox that spread globally in 2022. Clade 1 causes more severe disease and has a higher fatality rate. While Clade 2 is a milder disease that spreads through sexual contact, Clade 1 can be transmitted to household contacts and often spreads to children. The Jyyneos smallpox vaccine also protects against Mpox.
On 8/13/24, the non-profit Save the Children warned that newborn babies are contracting Mpox in hospitals in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) because of overcrowding. Mpox Clade 1b can be transmitted by touching surfaces and objects like towels and bed linens and even cooking utensils of people who have the pox rash. It is also spread by respiratory droplets and from talking face-to-face. Save the Children said that “70% of the DRC's nearly 15,000 cases involve children, 39% of them kids younger than 5 years old.” Per the WHO, the case fatality rate for Clade 1 for children under the age of one is 8.6%, compared to 2.4% in people aged 15 and over. In comparison, the global Clade 2 outbreak in 2022 had a fatality rate of 0.2%.
On 8/14/24, the WHO declared Mpox a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC). WHO Director Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus tweeted “it’s clear that a coordinated international response is needed to stop these outbreaks and save lives.”
On 8/15/24, the Public Health Agency of Sweden reported that a person who was visiting Africa had returned with Mpox, Clade 1. This is the first time that the more severe Clade 1 Mpox was seen outside of the African continent.
In Africa, human contact with infected small animals like squirrels have sometimes led to Mpox infection. A new US study shows that 12% of pets living with Mpox patients were positive for Mpox viral DNA, but no live virus. It is recommended that people infected with Mpox avoid contact with animals until their lesions have completely healed over.
The incubation period for Mpox is 1 to 21 days of exposure and the illness lasts about 2 to 4 weeks. For most people, the infection is mild. Common flu-like symptoms include fever, sore throat, headache, muscle ache, back pain, low energy, and swollen lymph nodes. The telltale rash starts out like a pimple or bump and then becomes a fluid or pus filled blister before it turns into an ulcer and then a scab. The rash can be seen on the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet or anywhere on the body. The lesions are contagious until they are completely gone and have been replaced by a new layer of skin.
From: https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/mpox/clinicians/clinical-recognition.html
Other news
Normally, the glymphatic system helps clear debris and excess proteins out of the brain. In diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, certain proteins like beta amyloid and tau protein and alpha-synuclein accumulate in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). As we age, the lymphatic system does not wash away these proteins as well because valves controlled by smooth muscle cells do not work as well. Using prostaglandin F2α, researchers were able to help the lymphatic smooth muscle cells pump the “dirty” CSF out of the brain for it to be cleaned. The authors were able to see this happen in an in vivo mouse model.
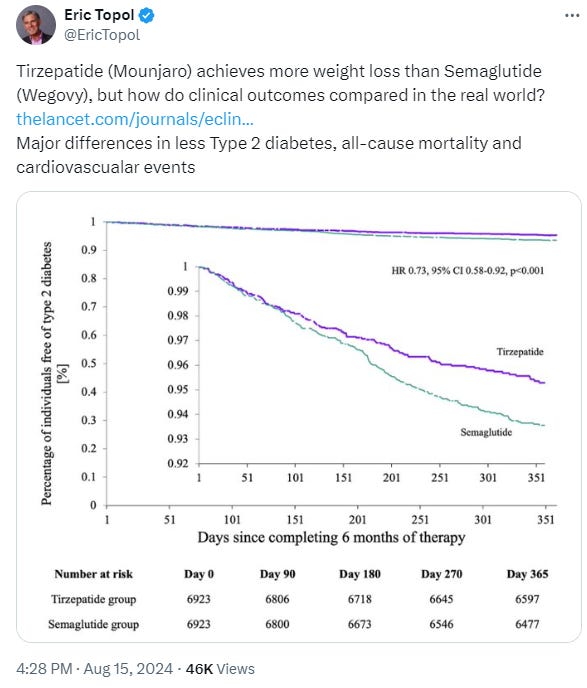
A new study shows that in obese adults, Tirzepatide (Mounjaro) caused a greater weight loss than Semaglutide (Wegovy). Tirzepatide was also associated with less Type 2 diabetes, cerebral infarction type stroke and all-cause mortality.
This week, the FDA approved a nasal spray with epinephrine called Neffy that treats severe allergic reactions as an alternative to injected epinephrine medications like the EpiPen.
Parvovirus B19, also known as Fifths Disease or "Slapped Cheek" disease, is a seasonal respiratory virus that is transmitted through respiratory droplets by people with symptomatic or asymptomatic infection. Europe had an increase in Parvovirus B19 earlier this year and now data shows that Parvovirus B19 is increasing in the United States. Most adults are immune to Parvovirus B19, but Parvovirus B19 can cause complications during pregnancy and is high risk for people with sickle cell disease and other hematologic disorders as well as immunocompromised individuals including those on chemotherapy. The CDC warned healthcare providers to have increased suspicion for Parvovirus B19 among people presenting with compatible symptoms (i.e. fever, rash, arthropathy, or unexplained anemia with low reticulocyte count).
California has proposed a bill to require a state review of private equity deals in healthcare. There is "mounting evidence that the [private equity] deals often lead to higher prices, lower-quality care and reduced access to core health services."
A huge study of 1000 villages in China shows that giving one short course of antibiotics for H. pylori reduced the risk of stomach cancer over the next decade by 13% to 19%.
Ying Ying the Giant Panda was 1 day shy of her 19th birthday, which is the equivalent of 57 in human years, when she went into labor. The tiny twin panda cubs are a female and a male and will stay in the intensive care unit at Ocean Park in Hong Kong for several months. Giant pandas are only fertile once each year for 1 to 3 days.
From: Ocean Park Hong Kong
Have a good rest of your weekend,
Ruth Ann Crystal MD
COVID news notes:
US Variant tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions
KP.3.1.1 is now at 36.8% of US cases
CDC COVID data tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/index.html#datatracker-home
Through August 10
COVID Emergency Dept visits: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#ed-visits_all_ages_combined
Walgreens positivity rate: https://www.walgreens.com/businesssolutions/covid-19-index.jsp
US Wastewater Monitoring:
CDC wastewater reporting: https://www.cdc.gov/nwss/rv/COVID19-nationaltrend.html
Last updated 8.15.24
California SARS-2 in wastewater:
CDC wastewater map: https://www.cdc.gov/nwss/rv/COVID19-currentlevels.html
From Aug 15
CDC data: Most states are in the VERY, VERY HIGH, VERY HIGH, or HIGH levels of SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater.
https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#wastewater-surveillance
Through 8/12/24
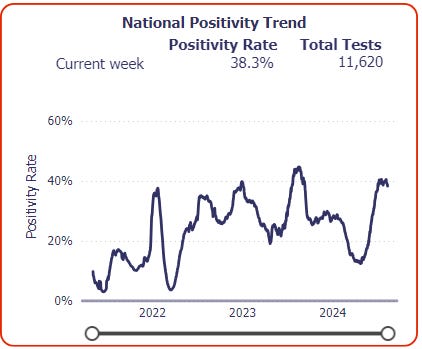
National SARS-CoV-2 data from Sara Anne Willette: https://iowacovid19tracker.org/
8/13/24 SARS-CoV-2 in Wastewater by NWSS (CDC)
Wastewater SCAN: https://data.wastewaterscan.org/
California statewide view https://buff.ly/3YObiul
Sewer Coronavirus Alert Network (SCAN) project by Stanford University:
Over the last year:
Santa Clara County wastewater: https://publichealth.santaclaracounty.gov/health-information/health-data/disease-data/covid-19/covid-19-wastewater
Marin county: https://coronavirus.marinhhs.org/surveillance
8/16/24 JP Weiland update: https://twitter.com/JPWeiland/status/1824608723685232964
August 16th update:
Cases flat this week near 1 million. This is likely the national summer peak. Some states in Midwest and Northeast are expected to increase further.
980,000 new infections/day
1 in every 34 people currently infected
68% higher than 12 month avg.
Prevalence by region:
The South and West are at roughly 12 month highs.
Midwest: 1 in 47
South: 1 in 26
Northest: 1 in 49
West: 1 in 21
8/14/24 https://x.com/JPWeiland/status/1823930436587815015
JP Weiland: This summer wave is likely peaking very soon, despite KP.3.1.1 recent dominance, due to the large number of people infected in this wave already.
We were aware that a highly divergent variant like Pirola had a lot of evolutionary space to explore, and it has not underperformed.
World
8/14/24 WHO: COVID-19 epidemiological update https://buff.ly/3SRAMVR
https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-epidemiological-update-edition-170
SARS-CoV-2 PCR percent positivity during the four-week reporting period from 24 June to 21 July 2024, increased from 7.4% to 13.0% across 85 countries. Globally, new COVID cases increased 30% and deaths increased 26%.
Acute COVID infections, General COVID info
8/15/24 https://twitter.com/CAPublicHealth/status/1824113936465023131
Pediatrics
8/13/24 JAG High School in Montgomery, Alabama goes to remote classes due to COVID outbreak https://buff.ly/4dGDmGd
The school "made the decision to transition to “asynchronous learning” due to a high number of the school’s staff currently being absent with COVID."
8/14/24 Health Central: Kids With Long COVID: The Post Pandemic Issue We’re Not Talking About https://buff.ly/46SFtEO
https://www.healthcentral.com/condition/coronavirus/pediatric-long-covid
More than 5.8 million American kids have Long COVID which affects many organs and is poorly understood by many people who work with children. Lisa Lombardi is the mother of a teenage son with Long COVID. She discusses symptoms in teens versus younger children and the difficulty finding healthcare providers who understand Long COVID in children.
8/12/24 JAMA: Hospitalizations for MIS-C in US Children’s Hospitals in 2023 vs 2021 https://buff.ly/3X0rlWG
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapediatrics/article-abstract/2822090
Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) cases peaked in January 2021, with more than 200 cases weekly. In 2023, only 117 cases of MIS-C were reported to the CDC during 2023 most likely due to lower incidence and likely incomplete reporting.
8/10/24 Open Forum Infectious Diseases, Oxford Press: Clinical Features and Outcomes of Pediatric and Adult Patients Hospitalized for Covid-19: A Comparison across Age Strata https://buff.ly/4djGx72
Among children, teens were the most likely to be hospitalized for COVID infection. For adults, people age 50 to 64 years old were at greatest risk for severe COVID including the highest odds of requiring mechanical ventilation and ICU admission.
Vaccines
8/16/24 CNN: FDA may greenlight updated Covid-19 vaccines as soon as next week, sources say https://buff.ly/3yRrDpl
Because of the large summer wave happening now, the US FDA may approve the new KP.2 mRNA COVID vaccines as soon as next week according to unnamed sources at the FDA.
8/13/24 Lancet Regional Health: COVID-19 vaccination and birth outcomes of 186,990 women vaccinated before pregnancy: an England-wide cohort study https://buff.ly/4dJVWgK
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanepe/article/PIIS2666-7762(24)00192-3/fulltext
Review of EHR records of pregnant people in 2021 and 2022.
Based on 186,990 women, compared to starting a pregnancy unvaccinated, receiving COVID-19 vaccination within 12 months before pregnancy was associated with lower risks of very and extremely preterm birth and small-for-gestational age in term babies for any vaccine type (adjusted hazard ratio and 95% confidence interval: 0.74 [0.63, 0.88] and 0.94 [0.88, 1.00], respectively), and lower stillbirth risk in those receiving an mRNA vaccine (0.72 [0.52, 1.00]).
Antiviral treatments, prevention
8/12/24 Nature: Variant-proof high affinity ACE2 antagonist limits SARS-CoV-2 replication in upper and lower airways https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-51046-w
In a proof of concept study, researchers from the NIH made a protein called RBD-62 which can block the ACE2 receptor so that SARS-CoV-2 cannot enter and infect cells. Tests in macaque monkeys showed that treatment with RBD-62 stopped viral replication in upper and in lower airways. "Importantly, RBD-62 does not block the development of virus-specific T- and B-cell responses and does not elicit anti-drug immunity."
From: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-51046-w/figures/1
Long COVID
8/13/2024 eBioMedicine: Blood DNA methylation in post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC): a prospective cohort study https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352396424002871
A small study from Albany, NY of 103 patients with Long COVID as compared to two control groups,15 COVID recovered patients and 27 healthy controls, used whole genome methylation sequencing and found 39 differentially methylated regions (DMRs) that were specific to Long COVID and not the two control groups. DNA studies from whole blood mostly reflect the DNA from white blood cells circulating in the blood. The blood DNA methylation levels in Long COVID were related to circadian rhythm-regulating pathways and could be used to identify and stratify the severity of people with Long COVID. Larger studies are needed to confirm these findings.
Explainer: 8/13/24 New study identifies long Covid DNA profile https://buff.ly/4dMogPk
“This suggests that long Covid is a single disease and not an aggregation of multiple conditions,” said pulmonologist Ariel Jaitovich, MD..
8/13/24 Lancet preprint: Vascular Inflammation in Neuropsychiatric Long Covid
https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4920991
A group from Yale compared the blood of 28 people with acute COVID infection (AC) to 50 people with neuro Long COVID (N-LC) and 29 controls who had recovered from acute COVID infection without Long COVID.
"Most biomarkers were highest in acute COVID (AC) and lower in N-LC (AGP, CRP, haptoglobin, SAA, ADAMTS13, PF4, sP-selectin, sVCAM-1, and D-dimer)
Except three biomarkers were highest in N-LC compared to AC: Fetuin (vascular calcification), L-selectin (leukocyte adhesion), and α-2 macroglobulin.
Neuro-LC (N-LC) Elevations in blood biomarkers related to
systemic inflammation,
N-LC vs Acute COVID:
Vascular calcification (high Fetuin),
Endothelial adhesion/immune function (high α-2 macroglobulin)
Leukocyte adhesion to the endothelium (high L-selectin),
N- LC vs controls:
High Leukocyte endothelial adhesion and endothelial inflammation
L-selectin (p=0.01),
ADAMTS13 (p<0.0001),
sP-selectin (p=0.0001), and
sICAM1 (p=0.03).
Coagulopathy markers:
No difference in coagulopathy measures (D-dimer, fibrinogen)
Systemic Inflammation
Inflammatory cascade: High AGP (p=0.0005)
Acute and chronic inflammation: High C-reactive protein (p=0.04)
Cognitive:
Lower fluency and verbal learning (High sP-selectin)
Lower verbal memory, verbal learning, fluency, mood, and anxiety (Low α1-acid glycoprotein ( Low AGP)
We observed two main biomarker patterns between the three groups.
The most common pattern demonstrated high levels of the biomarkers in the AC group, moderate elevation in the N-LC group, and lowest in the control group. This pattern was seen in AGP, CRP, haptoglobin, SAA, SAP, ADAMTS13, sP-selectin, and sVCAM-1.
Several markers that were elevated in N-LC compared to controls are involved in vascular remodeling and atherogenesis, suggesting that N-LC symptoms may relate to vascular regulation or may heighten risk for long-term vascular sequelae.
The N-LC group was also characterized by elevation of markers that facilitate enhanced leukocyte adhesion to the endothelium. ADAMTS13, sP-selectin, sICAM-1
2. Marked elevation in N-LC compared to AC and the control groups.
Elevations in L-selectin, Fetuin, and α-2 macroglobulin in N-LC suggests a distinct pathophysiology from the pattern of resolving AC.
3. Lastly, it is important to note that we found no evidence of coagulopathy (D-dimer, fibrinogen) in the N-LC group compared to controls, which aligns with the clinically observed lack of clotting pathology in individuals with N-LC.
These findings suggest that persistent or emergent neurologic symptoms after COVID-19 are associated with abnormalities of the vascular endothelial function.
Figure 2. Plasma Inflammatory Vascular Biomarkers.
8/13/24 Annals of Internal Medicine: Differentiation of Prior SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Post-acute Sequelae by Standard Clinical Laboratory Measurements in the RECOVER Cohort
https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/10.7326/M24-0737
Researchers from the RECOVER program looked at 25 common blood tests trying to find a biomarker for Long COVID. Unfortunately, they were unable to find a difference between people with Long COVID and controls.
https://x.com/sunsopeningband/status/1823206687974809933
Chronic diseases after COVID
8/13/24 American Journal of Medicine Open (Stony Brook University): Characterization of change in cognition before and after COVID-19 infection in essential workers at midlife
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S266703642400013X#bib0011
A group from Stony Brook University looked at people who had previously undergone cognitive testing in 2015 to 2019. Using longitudinal causal modeling they found that COVID infection leads to cognitive decline consistent with 10.6 years of brain aging. COVID-19-related Cognitive Decline (CRCD) manifests as executive dysfunction and was seen more commonly in people who had prior severe acute COVID infection and those with Long COVID. They recommend that Long COVID (PASC) patients undergo routine cognitive testing.
“These results imply an increase in cognitive dysfunction and poorer brain health after COVID-19 [infection], notably in those who experienced severe COVID-19 and PASC.”
Figure 1. Expected Trajectories of Change in Cognition Before and After the Onset of COVID-19
From: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S266703642400013X#fig0001
8/2024 JACC: COVID-19 in the Initiation and Progression of Atherosclerosis: Pathophysiology During and Beyond the Acute Phase
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2772963X24003016
A new review looks at mechanisms that can initiate and promote atherosclerotic lesions after a COVID infection and the pathogenesis of vascular disease in Long COVID.
Endothelial dysfunction, platelet activation and inflammation from COVID infection may increase the risk of atherosclerosis which can reduce blood flow to the heart and can lead to heart attacks. It can also cause strokes if blood vessels to the brain are blocked.
From: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2772963X24003016
8/2024 European Respiratory Journal: Long-term radiological and pulmonary function abnormalities at 3 years after COVID-19 hospitalisation: a longitudinal cohort study https://buff.ly/3WOf4TF
Three years after hospitalization for COVID, more than one-third of patients have abnormal lung function and have residual lung abnormalities such as fibrotic-like changes on CT scan.
Patients hospitalized with COVID-19 were followed for three years, with their lung function and radiological abnormalities monitored longitudinally. While most patients showed improvement, more than one-third continued to experience persistent lung abnormalities, including symptoms, reduced diffusion capacity and fibrotic-like changes on CT scans. These long-term lung issues highlight the need for ongoing management strategies in post-COVID care.
10/6/2022 Forbes by Carolyn Barber MD: Strokes, heart attacks, sudden deaths: Does America understand the long-term risks of catching COVID? https://buff.ly/3SRwHAO
Mpox
8/15/24 The Public Health Agency of Sweden: One case of Mpox clade I reported in Sweden https://buff.ly/3YJ2JTp
The Public Health Agency of Sweden reported today that a person who was visiting Africa has returned with Mpox, Clade 1. This is the first time that the more severe Clade 1 Mpox has been seen outside of the African continent. Clade 1 causes more severe disease and has a higher fatality rate. While Clade 2 is a milder disease that spreads through sexual contact, Clade 1 can be transmitted to household contacts and often spreads to children.
8/14/24 Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, WHO
https://x.com/DrTedros/status/1823821630973362637
“The emergence of a new clade of #mpox, its rapid spread in eastern #DRC, and the reporting of cases in several neighbouring countries are very worrying. On top of outbreaks of other mpox clades in DRC and other countries in Africa, it’s clear that a coordinated international response is needed to stop these outbreaks and save lives.”
WHO has just declared the rise in #mpox cases a public health emergency of international concern (#PHEIC). "The detection and rapid spread of a new clade of mpox in eastern DRC, its detection in neighboring countries that had not previously reported mpox, and the potential for further spread within Africa and beyond is very worrying", @DrTedros said in the presser just now.
8/13/24 Africa CDC declares public health emergency for mpox https://www.cidrap.umn.edu/mpox/africa-cdc-declares-public-health-emergency-mpox
Factors included a high disease burden, accelerating spread, a concerning fatality rate, lack of diagnostics and vaccines, and a need for better coordination among countries.
The Africa CDC today declared its first public health emergency of continental security (PHECS) amid a complex and worsening mpox situation in Africa, especially a surge in the Democratic Republic of the Congo that partly involves a novel clade 1b virus.
8/12/24 Save the Children International: NEWBORN BABIES CATCHING DEADLY MPOX IN DRC’S OVERCROWDED HOSPITALS AS CASES SKYROCKET https://buff.ly/3yzx3Wa
Mpox causes fever, rash and lesions all over the body, severe headaches and fatigue. Some children also develop respiratory problems and have difficulty swallowing, and are at higher risk for secondary bacterial infections. In severe cases, mpox can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening response to infection that requires immediate specialist medical attention.
Save the Children said the close resemblance of some of the signs and symptoms of mpox to other common childhood illnesses - such as scabies and chickenpox - might be leading to late recognition and treatment, contributing to transmission and worse outcomes due to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
Additionally caregivers have to fight socio-cultural stigma around the virus due to a widespread belief that it is spread only through sexual contact. In fact, the virus can spread by any skin-to-skin contact, airborne contact in proximity – like COVID-19 – and even from contaminated surfaces and objects such as bedding, clothing, and cooking utensils.
8/15/24 CIDRAP: CDC investigation finds viral DNA, but no live virus, in pets of Mpox patients https://buff.ly/46LQCal
"Twelve percent of swabs taken from the fur, mouth, and anorectal area of pets living with an mpox patient tested positive for mpox virus DNA, but blood cultures showed no signs of infection, according to a new US study.
"Given high likelihood for exposure among most of these animals, the paucity of evidence indicating infection might indicate resistance to infection," the researchers concluded.
"They urged mpox patients to avoid contact with animals until their lesions have fully healed.
Other news:
8/15/24 Univ of Rochester: Cleaning up the aging brain https://www.rochester.edu/newscenter/cleaning-up-the-aging-brain-616872/
h/t John Chi
First described by Maiken Nedergaard and her colleagues in 2012, the glymphatic system is the brain’s unique waste removal process that uses cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to wash away excess proteins generated by energy-hungry neurons and other cells in the brain during normal activity. “Unlike the cardiovascular system, which has one big pump—the heart—fluid in the lymphatic system is instead transported by a network of tiny pumps,” says Kelley. These microscopic pumps, called lymphangions, have valves to prevent backflow and are strung together.
The team then set out to see if they could revive the lymphangions with prostaglandin F2α, known to aid smooth muscle contraction. The lymphangions are lined with smooth muscle cells, and when the researchers applied the drug to the cervical lymph vessels in older mice, the frequency of contractions and the flow of dirty CSF from the brain both increased, returning to a level of efficiency found in younger mice.
8/15/24 Nature Aging: Restoration of cervical lymphatic vessel function in aging rescues cerebrospinal fluid drainage https://buff.ly/4dujyGk
https://www.nature.com/articles/s43587-024-00691-3
Slowed CSF flow in aged mice was rescued using topical application of prostaglandin F2α, a prostanoid that increases smooth muscle contractility, which restored lymphatic function in aged mice and enhanced central nervous system clearance.
8/15/24 eClinical Medicine: Incidence of new onset type 2 diabetes in adults living with obesity treated with tirzepatide or semaglutide: real world evidence from an international retrospective cohort study https://buff.ly/3M8I6bR
Tirzepatide was associated with both lower risk for incident T2D (HR 0.73, 95% CI 0.58–0.92, p < 0.001) and greater weight loss (−7.7 kg, [95% CI −6.8, −8.5 kg], p < 0.001), compared to semaglutide (−4.8 kg, [95% CI −3.9, −5.6 kg], p < 0.001).
In individuals with pre-existing T2D (n = 8446), tirzepatide was associated with lower risk of the composite outcome (HR 0.54, 95% CI 0.38–0.76, p < 0.001), cerebral infarction (HR 0.45, 95% CI 0.24–0.84, p = 0.010) and all-cause mortality (HR 0.33, 95% CI 0.15–0.73, p = 0.004) compared to semaglutide.
From: https://x.com/EricTopol/status/1824226749225525636
8/11/24 AP: FDA approves first nasal spray to treat dangerous allergic reactions
https://apnews.com/article/epipen-nasal-spray-allergic-reaction-fda-32ef474cbe0a14bc854691ec44bbaf10
This week, the FDA approved a nasal spray called Neffy that treats severe allergic reactions as an alternative to injected medications like the EpiPen.
8/13/24 CDC Health Advisory: Increase in Human Parvovirus B19 Activity in the United States
https://emergency.cdc.gov/han/2024/han00514.asp
Parvovirus B19, also known as Fifths Disease or "Slapped Cheek" disease, is a seasonal respiratory virus that is transmitted through respiratory droplets by people with symptomatic or asymptomatic infection. Europe had an increase in Parvovirus B19 earlier this year and now data shows that Parvovirus B19 is increasing in the United States as well. Parvovirus B19 can cause complications including miscarriage in pregnancy and is high risk for people with sickle cell disease as well.
"The proportion of people with IgM antibodies, an indicator of recent infection, increased among all ages from <3% during 2022–2024 to 10% in June 2024; the greatest increase was observed among children aged 5–9 years, from 15% during 2022–2024 to 40% in June 2024. Among plasma donors, the prevalence of pooled samples with parvovirus B19 DNA >104 IU/mL increased from 1.5% in December 2023 to 19.9% in June 2024."
Recently, CDC has received reports indicating increased parvovirus B19 activity in the United States. These reports include data from commercial laboratories of increasing parvovirus B19 test positivity by nucleic acid amplification tests and serology in the general population and increased serological evidence of infection in plasma donors.
Recommendations for Healthcare Providers regarding Parvovirus B19:
Have increased suspicion for parvovirus B19 among people presenting with compatible symptoms (i.e., fever, rash, arthropathy, or unexplained anemia with low reticulocyte count).
Provide preventive counseling and have a low threshold to test people who present with compatible signs and symptoms if they are at higher risk of severe parvovirus B19 disease, including:
Pregnant people
People with severely immunocompromising conditions, including leukemia or other cancers, organ transplant, HIV infection, or who are receiving chemotherapy.
People with chronic hemolytic blood disorders, including sickle cell disease, thalassemia, and hereditary spherocytosis.
When treating people with suspected or confirmed parvovirus B19, inform them or their caregivers about high-risk groups and advise any exposed contacts in those groups (e.g., who may be pregnant) to consult with their healthcare providers.
Follow standard of care (e.g., professional society guidelines) for testing pregnant people reporting exposure to parvovirus B19 infection or who present with compatible signs and symptoms of maternal or fetal parvovirus B19 disease.
Promote CDC recommendations for core prevention strategies to prevent respiratory illness, including practicing good hand hygiene and taking steps for cleaner air to reduce spread of parvovirus B19 and other respiratory viruses.
People at higher risk of severe outcomes or complications who work in settings with higher risk of parvovirus B19 exposure should practice hand hygiene, avoid sharing food or drinks, and consider wearing a respirator or mask while at work. There is no proven benefit to removing someone from work in settings with higher risk of parvovirus B19 exposure.
Follow recommended infection control precautions for persons with parvovirus B19 in healthcare settings.
Recommendations for Health Departments
Ensure that healthcare providers are aware of increasing parvovirus B19 activity and identify people at higher risk of severe parvovirus B19 outcomes. Parvovirus B19 is not nationally notifiable.
Promote measures to prevent respiratory illness and share information about complications of parvovirus B19 with people at high risk of severe disease.
Raise awareness of parvovirus B19 activity among daycare and school providers, including who may be at higher risk of severe parvovirus B19 disease and when children and staff can return to school following an infection.
Recommendations for the Public
Learn about parvovirus B19 symptoms and who may be at higher risk of severe disease.
Seek medical care if you:
are pregnant and have been exposed to a person with suspected or confirmed parvovirus B19 or you have signs and symptoms of parvovirus B19.
have a weakened immune system or a chronic hemolytic blood disorder including sickle cell disease, thalassemia, and hereditary spherocytosis, and you have signs and symptoms of parvovirus B19.
Follow general respiratory precautions to prevent spread of parvovirus B19 and other respiratory viruses. People at higher risk of severe parvovirus B19 can consider using additional prevention strategies such as wearing a mask when around others.
Know that children and adults with parvovirus B19 are no longer contagious once the characteristic facial rash appears.
8/9/24 LA Times: California bill would require state review of private equity deals in healthcare
There is "mounting evidence that the [private equity] deals often lead to higher prices, lower-quality care and reduced access to core health services."
8/14/24 Cell Host & Microbe: Unlocking the mind-gut connection: Impact of human microbiome on cognition https://buff.ly/3yBf69D
Long review on the microbiome and the effect on human cognition including the importance of prebiotic and probiotic bacteria, bacteriophages (viruses of which there are many), etc.
8/14/24 SkyNews: Video shows the remarkable improvement after only 2 days made by patient after taking new Parkinson’s drug called Produodopa https://x.com/SkyNews/status/1823748025355002280
8/7/24 Science: Eliminating a gut microbe could slash gastric cancers https://buff.ly/4fJLvLV
https://www.science.org/content/article/eliminating-gut-microbe-could-slash-gastric-cancers
A huge study of 1000 villages in China shows that giving one short course of antibiotics for H. pylori reduced the risk of stomach cancer by 13% to 19%.
8/16/24 CNN: Oldest first-time panda mom gives birth to twins https://buff.ly/4csM8qd
Ying Ying was 1 day shy of her 19th birthday which is the equivalent of 57 in human years. The twins are a girl and a boy and will stay in the neonatal intensive care unit at Ocean Park in Hong Kong for several months. Giant pandas are only fertile once each year for 1 to 3 days.
Video from CNN and Ocean Park Hong Kong






































❤️❤️❤️❤️ Thank you for all the time and care you put in to this newsletter, week after week. I’m certain it’s appreciated—and helping— many many folks.