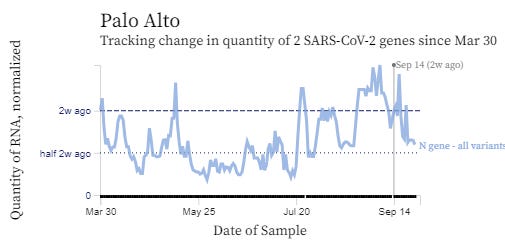
We reached the peak of this COVID wavelet and now cases are starting to decline. But, cases are still in the high range at this time. Emergency room visits have gone down some, and hospitalizations went down about 3% last week, although COVID deaths increased by about 8%.
JP Weiland uses waste water measurements and mathematical modeling to predict the true number of COVID cases. His calculations show that there are still about 570,000 new cases in the U.S. of COVID each day, or about 1 in every 58 Americans will get a COVID infection each day. In the Northeastern United States, cases are higher now with about 1 in every 42 people presently infected with COVID.
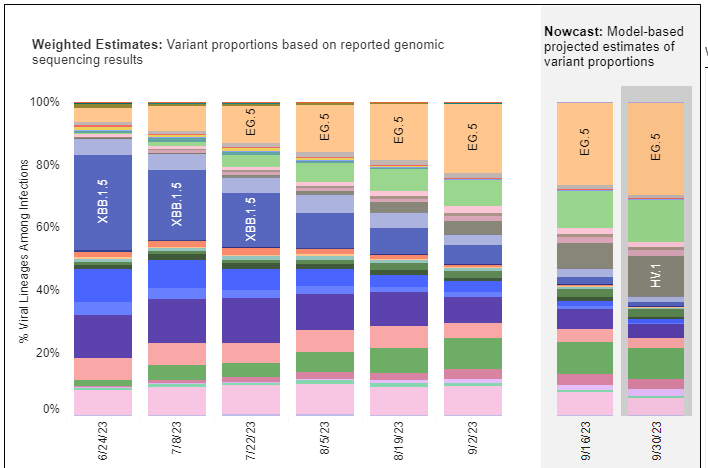
Looking at the CDC map of wastewater plants in the United States, we still see a lot of red and orange dots which represent high levels of the virus in wastewater. The most common variants circulating continue to be EG.5 and FL.1.5.1 which together make up about 53% of COVID cases in the US now. HV.1 and FLip variants are also starting to increase and HV.1 is almost doubling weekly. HV.1 levels were between 8.3% and 17.0% of cases in different parts of the U.S. this week.
As a reminder, you can still get 4 free COVID tests at covid.gov/tests. To check if expiration dates have been extended by the FDA on home rapid antigen COVID tests, click here. To find a pharmacy or clinic where you can get the updated 2023 fall booster, please see vaccines.gov.
Prior research has shown that there is an increase of heart attacks and strokes in the year after an acute COVID infection. A new study gives insight into why. It turns out that the SARS-2 (a.k.a. SARS-CoV-2) virus can directly infect the coronary arteries that feed the heart. SARS-2 infects monocytes which then cause inflammation in atherosclerotic plaques, and this can trigger heart attacks. Macrophages that consume cholesterol in atherosclerotic plaques are known as Foam cells. Foam cells are unable to clear the virus easily and are the most susceptible cell to SARS-2 infection in the heart. Therefore, foam cells may also act as a reservoir of SARS-2 in atherosclerotic plaques in coronary arteries and other blood vessels. Infection of the heart vessels with SARS-2 leads to inflammation and can trigger heart attacks and other cardiovascular complications.
In the beginning of the pandemic, when someone took a home rapid antigen COVID test, the test was positive as soon as someone had viral symptoms. Now, most people have had either a prior COVID infection or a vaccination against COVID and their immune system is ready to fight SARS-2 as soon as it encounters it. The release of cytokines and other factors to fight infection makes people feel sick much more quickly. Unlike earlier in the pandemic, COVID symptoms now happen before viral load levels rise high enough to be contagious and high enough to cause a positive test on the home rapid antigen tests.
Rapid antigen tests are negative for the initial days of a COVID infection now because the viral load is not high enough to trigger a positive test. A new study shows that on Day #1 the rapid antigen COVID test are only 30 to 60% sensitive, on Day #3 they are 59 to 75% sensitive and on Day #4 they are 80 to 93% sensitive. If have symptoms and you test negative on Day #1, #2 or #3, it is very important to test again on Day #4 and/or Day #5 to make sure that you have not become positive. If you only test on Day #1, you may not know that you actually have a COVID infection and you may go on to infect others.
Vaccines
According to a Kaiser Family Foundation poll, nearly half of adults plan on getting the new 2023 Fall COVID-19 vaccine. However, most parents say that they do not plan on getting it for their children. The poll shows that opinions on this year’s vaccine continue to follow political alignments.
Pancoronavirus vaccines and nasal vaccines are needed to provide better protection against new variants that may appear. Using artificial intelligence, engineers designed an antigen that triggers broad antibodies against many different kinds of sarbecoviruses including SARS-1, SARS-2 and some other viruses in animal models. The vaccine has not been tested in humans yet, but is promising.
Moderna paid for a pre-clinical study in hamsters using intranasal Moderna mRNA-LNP against SARS-2. This intranasal vaccine produced local immunity at upper respiratory sites creating a protective barrier which reduced viral infection and subsequent transmission. Other intranasal vaccines used in humans use either adenoviral vectors or live attenuated recombinant viruses which can have more side effects.
A new study shows that maternal first trimester COVID vaccination did not cause any increased risk of birth defects in the offspring. They concluded that COVID vaccines are safe at any time in pregnancy. The CDC just posted data showing that maternal mRNA COVID vaccination during pregnancy can help to protect newborn infants up to age 6 months against COVID related hospitalizations and serious complications. Babies under 6 months are not eligible for COVID vaccination themselves and may be at risk for serious COVID infections if they are not protected by antibodies from maternal COVID vaccination.
A Public Service Announcement from Mr. T:
Masks
Katelyn Jetelina wrote a piece on masks coming back to hospitals and nursing homes. She reviewed the science behind masks’ protection against aerosolized viruses. Several Bay Area Health Departments are reinstating mask mandates for healthcare personnel in hospitals. The Santa Clara County Public Health Department has gone a step further. Santa Clara will require masking for everyone in patient care areas of clinics, hospitals, and long-term facility long-term care facilities. Starting November 1st, visitors, patients and staff will need to wear masks. Other counties in the United States are also reinstating mask mandates because of high hospitalization rates and the anticipated rise in cases that happens during the winter holidays.
A new paper in Nature magazine, shows that Molnupiravir induces mutations in SARS-2 and those can be transmitted to other people. Molnupiravir does not reduce serious complications of COVID infection nearly as well as other antiviral treatments and it causes mutations in the virus as its mechanism of action. Because of this, I believe that Molupiravir should be recalled.
Brain specimens from patients who died of severe COVID sometimes have shown pathology changes consistent with Alzheimer's disease on autopsy. A new study shows that SARS-2 infection causes Tau proteins to be abnormally phosphorylated at binding locations for antibodies similar to what happens in Alzheimer’s disease. This abnormal phosphorylation of pathologic epitopes increases Tau’s ability to make insoluble clumps and aggregates as in Alzheimer’s disease. These changes in Tau by SARS-2 infection impairs the proper functioning of brain neurons.
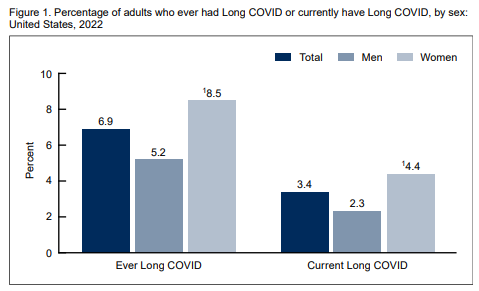
A new report of the CDC’s National Health Interview Survey, shows that nearly 18 million adults in the U.S. had Long COVID in 2022. About half of these people recovered by the time they were surveyed, but that means that about 9 million people, or 3.4% of people in the U.S., still had Long COVID. Long COVID was more common in women vs. men, in adults age 35 to 44 years, and in white or hispanic race. This is very concerning as we know that with the Omicron variants, vaccinated people have about a 10% rate of getting Long COVID. If half of cases resolve, that still leaves a lot of people disabled from Long COVID.
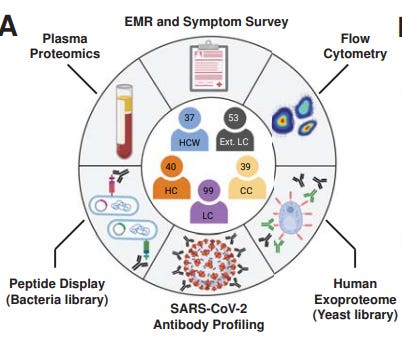
Probably the most talked about article this week is entitled “Distinguishing features of Long COVID identified through immune profiling” reported from Yale and Mount Sinai. Individuals with Long COVID (LC) frequently have debilitating fatigue, post-exertional malaise, cognitive issues like brain fog and POTS (postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome). Clinical symptom surveys using the Long COVID Propensity Score (LCPS) were 94% accurate for diagnosing Long COVID. When examining biomarkers in the blood, people with Long COVID had:
1) lower circulating cortisol (but normal ACTH)
2) higher activated B cells and cytokine-secreting T cells
Although these findings need to be confirmed in larger studies, this study gives new clues into the pathophysiology of Long COVID. Low cortisol levels can contribute to fatigue, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, weakness and pain. Low cortisol levels without compensatory increases in ACTH may reflect a problem with the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) axis in people with Long COVID. Higher anti-spike IgG antibodies, elevated activated B cells and exhausted T cells suggest persistent SARS-CoV-2 antigen and a viral reservoir somewhere in the body. Epstein Barr virus (EBV) causes mononucleosis (glandular fever) which can cause severe fatigue among other symptoms. Reactivation of EBV and VZV viruses appears to be common in Long COVID as well.
Some clinical trials are using the antiviral Paxlovid to try to treat persistent reservoirs of the SARS-2 virus. UCSF has started a clinical trial using the monoclonal antibody AER002 from Aerium Therapeutics to try to get rid of viral reservoirs of SARS-2 in people with Long COVID.
A new study from Oxford looked at MRIs taken 5 months after patients were discharged from the hospital for severe COVID. MRI exams showed that 1 out of 3 people who were hospitalized had damage to their lungs, brain or kidneys at 5 months. MRI results showed 14-fold risk of damage to the lungs, 3-fold the risk of brain damage such as scarring and shrinkage in certain areas of the brain and 2-fold the risk of kidney damage from COVID infection. The heart and the liver did not show significant damage at 5 months after hospital discharge in this study. Patients with multiorgan abnormalities tended to be older with more comorbidities and more severe acute COVID infection.
Arizonans can now receive Workers’ Compensation benefits if they contracted COVID-19 on the job. This could be helpful for many front line workers. A lawsuit was filed by the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) for a person with Long COVID who was not given appropriate accommodations from their employer. Chimere L. Smith and other Long COVID advocates in the Black Community will have a virtual event on October 15, 2023 entitled “Black Women and Families- from Dismissed to Diagnosed”.
Acute COVID infections can be associated with hyperglycemia (high blood sugar). Using a non-human primate (African Green Monkeys) Long COVID animal model, scientists showed that SARS-2 infection induced abnormal glucose regulation with hyperglycemia that persisted for at least 4.5 months. Vaccination 4 days after infection prevented hyperglycemia in the monkeys. The persistent hyperglycemia correlated with elevated glycogen in the liver, but there was no evidence of long-term SARS-CoV-2 replication in the liver or pancreas.
In non-COVID news, working remotely full-time from home could decrease greenhouse gas emissions by half. Microsoft opened an A.I. Co-Innovation Lab in San Francisco to work with startups. Psychiatric conditions like anxiety and depression may be a part of the Multiple Sclerosis (MS) prodrome in the 5 years leading to diagnosis. A Common Sense Media report finds that about half of 11- to 17-year-olds get at least 237 notifications on their phones each day and some get nearly 5,000 in 24 hours. Finally, using a smartwatch during pregnancy and A.I. analysis, Nima Aghaeepour’s lab was able to predict who was at increased risk for preterm delivery by looking at sleep and physical activity patterns.
Have a good rest of your weekend,
Ruth Ann Crystal MD
COVID news:
Walgreens positivity rate: https://www.walgreens.com/businesssolutions/covid-19-index.jsp
US Variant tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions
HV.1 is between 8.3% and 17.0% of cases in different parts of the U.S.
CDC COVID data tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-datatracker/index.html#datatracker-home
CDC COVID Hospitalizations (blue) and Emergency Room (orange) visits tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/index.html#trends_weeklyhospitaladmissions_7dayeddiagnosed_00
Weekly ED visits for respiratory illnesses, by age and disease: https://www.cdc.gov/ncird/surveillance/respiratory-illnesses/index.html
US Wastewater Monitoring:
CDC Wastewater Monitor https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#wastewater-surveillance
Wastewater from NWSS and Biobot in a US
Biobot: https://biobot.io/data/
California wastewater level updates:
–Wastewater SCAN:
https://data.wastewaterscan.org/
California statewide view https://buff.ly/3YObiul
Sewer Coronavirus Alert Network (SCAN) project by Stanford University:
JP Weiland: https://twitter.com/JPWeiland
9/26/23
Order 4 Free COVID tests here: https://www.covid.gov/tests
Home COVID tests- Extended Expiration Dates https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/coronavirus-covid-19-and-medical-devices/home-otc-covid-19-diagnostic-tests#list
9/28/23 Nature CV Research: SARS-CoV-2 infection triggers pro-atherogenic inflammatory responses in human coronary vessels https://buff.ly/3EVcVgv
Patients with COVID infections have an increased risk for ischemic cardiovascular complications up to 1 year after infection.
SARS-CoV-2 can directly infect coronary arteries that feed the heart causing inflammation (macrophages) in atherosclerotic plaques which can trigger acute CV complications (heart attacks) and increase long-term cardiovascular risk.
Getting infected will increase the risk of heart attack.
SARS-CoV-2 infects coronary arteries, increases plaque inflammation
9/28/23 NIH: SARS-CoV-2 infects coronary arteries, increases plaque inflammation https://buff.ly/3ry5wAO
SARS-CoV-2 was found to infect and replicate in the arteries no matter the levels of plaque, so this could affect the cardiovascular system of anyone who gets COVID-19.
People who had COVID-19 have an increased risk for cardiovascular disease or stroke up to one year after infection.
SARS-CoV-2 infects macrophages at a higher rate than other arterial cells.
Cholesterol + Macrophages = Foam Cells
Cholesterol-laden foam cells were the most susceptible to infection and were unable to readily clear the virus.
Foam cells might act as a reservoir of SARS-CoV-2 in the atherosclerotic plaque.
The findings conclusively show that SARS-CoV-2 (2020 to 2021) can infect and replicate in the macrophages of plaques and arterial cells.
9/28/23 Clinical Infectious Diseases: The New Normal: Delayed Peak SARS-CoV-2 Viral Loads Relative to Symptom Onset and Implications for COVID-19 Testing Programs https://buff.ly/3PzKmdu
Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, peak viral loads coincided with symptom onset.
Now, in a highly immune population, symptoms start earlier in infection with lower viral levels and therefore the rapid antigen tests are negative for the initial days.
In a highly immune adult population, median SARS-CoV-2 viral loads peaked around the fourth day of symptoms.
Influenza A viral loads peaked soon after symptom onset.
These findings have implications for ongoing use of Rapid antigen tests for COVID-19 and influenza.
9/28/23 CIDRAP: Evolving peak SARS-CoV-2 loads relative to symptom onset may influence home-test timing https://buff.ly/3EXYBE6
Estimated rapid antigen test sensitivity:
Day 1: 30.0% to 60.0%
Day 3: 59.2% to 74.8%
Day 4: 80.0% to 93.3%
The timing of symptom onset in a highly immune population is very different from what was seen early in the pandemic.
EEOC Sues Appliance Factory for Disability Discrimination https://buff.ly/456tG2V
9/28/23
9/25/23 Nature: A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes https://buff.ly/3REPS13
Onward transmission of molnupiravir-derived lineages seen.
Direct association between these high G-to-A branches and the use of molnupiravir.
9/27/23 KFF Poll: Nearly Half of Adults Expect to Get the New COVID-19 Vaccine, But Most Parents Don’t Expect to Get It for Their Children; More Eligible Adults Expect to Get a Flu Shot and the New RSV Vaccine https://buff.ly/3t8FPap
9/26/23 The Hill: Nearly 18M adults in US have struggled with long COVID in 2022: CDC survey https://buff.ly/3thRkw6
In the 2022 survey:
All adults: Overall, 6.9% ever had Long COVID and 3.4% currently had LC in 2022.
Women: 8.5% ever had Long COVID and 4.4% currently had LC in 2022.
Men: 5.2% ever had Long COVID and 2.3% currently had LC in 2022
CDC Data: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/databriefs/db480.pdf
Key findings Data from the National Health Interview Survey:
In 2022, 6.9% of adults ever had Long COVID and 3.4% had Long COVID at the time of interview (currently have Long COVID);
Long COVID was more common in:
Women vs. men
Adults ages 35–49.
Varied by race and Hispanic origin.
9/25/23 Nature (Iwasaki, Putrino): Distinguishing features of Long COVID identified through immune profiling https://buff.ly/3PShYEJ
Individuals with LC frequently report unremitting fatigue, post-exertional malaise, and a variety of cognitive and autonomic dysfunctions.
9/25/23 Dr. Iwasaki’s tweet thread explaining study findings:
https://twitter.com/VirusesImmunity/status/1706332965792272722
N = 268 total (LC= Long COVID, CC= COVID controls, HC= no COVID)
Most were infected in 2020, and studied on average about a year after the infection.
95% mild acute COVID infections and 2/3 were female.
The clinical symptom surveys by @PutrinoLab of these people alone were able to accurately differentiate those with vs. without long COVID with 94% accuracy.
Blood test Key findings
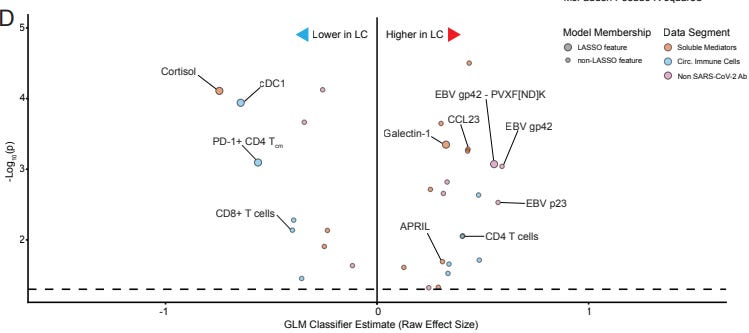
People with Long COVID had:
1) lower circulating cortisol,
2) higher activated B and cytokine-secreting T cells
3) higher anti-Spike IgG antibodies,
4) higher EBV reactive Abs.
No significant differences in the number of autoantibodies.
(Elevated activated B cells and exhausted T cells suggest persistent SARS-CoV-2 antigen).
Machine learning identified key immune factors that can distinguish those with long COVID. These factors included:
Lower levels of cortisol, conventional DC1, central memory T
Higher levels of EBV IgG, galectin-1, APRIL...etc.
What does this mean? The study is exploratory and signal seeking, not hypothesis testing. It is a first step in identifying biomarkers that can be used in the future to diagnose long COVID. To get there, we still need to validate these markers in external cohorts. Study was limited in size.
The study gives us new insights on EBV reactivation and Th2 correlation, hormonal dysregulation suggestive of HPA axis defect in Long COVID.
*Th2 are a type of Helper T cells which send out cytokines to get B cells to make antibodies.
* HPA is the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis.
The study is explained here:
9/25/23 CNN: Scientists edge closer to finding a biomarker for long Covid, which could lead to better tests and treatments https://buff.ly/48rzGpZ
Potential biomarkers for the Long COVID, which affects an estimated 6% of all American adults or >15 million people, according to the latest data from the US CDC.
Most common symptoms in the Long Covid group were fatigue, brain fog and memory deficits and POTS (postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome).
Long COVID had low morning cortisol, which can lead to fatigue, nausea, vomiting, weight loss, weakness and pain.
The long Covid group had immune dysregulation (an immune system out of whack):
Higher non-conventional monocytes
Lower levels of conventional type 1 dendritic cell.
Reactivation of Epstein Barr Virus (EBV) which causes mononucleosis and multiple sclerosis.
CNN article continued:
The second study, from researchers at Oxford (see below) used MRI, to scan 259 people who’d been hospitalized with Covid-19.
An average of five months after discharge, researchers found evidence of damage to the lungs, brain or kidneys in 1 out of 3 people who’d been hospitalized with Covid-19.
People who had been hospitalized for their COVID infections:
3x brain changes like scarring and shrinkage in certain areas,
14x the risk of damage in their lungs
2x the risk of injuries to their kidneys.
The heart or liver did not show damage.
9/22/23 Lancet: Multiorgan MRI findings after hospitalisation with COVID-19 in the UK (C-MORE): a prospective, multicentre, observational cohort study https://buff.ly/48uEM4E
Median of 5 months after discharge from hospital for COVID infection.
Compared with controls, patients were more likely to have MRI evidence of
lung abnormalities (p=0·0001; parenchymal abnormalities),
brain abnormalities (p<0·0001; more white matter hyperintensities and regional brain volume reduction), and
kidney abnormalities (p=0·014; lower medullary T1 and loss of corticomedullary differentiation), whereas
cardiac and liver MRI abnormalities were not different from controls.
The patients with multiorgan abnormalities tended to be older with more comorbidities and more severe acute COVID infection.
9/25/23 BioRxiV: Immune Correlates of Hyperglycemia and Vaccination in a Non-human Primate Model of Long COVID https://buff.ly/3PUM0HZ
In a non-human primate model (African Green Monkeys) of Long Covid, SARS-2 infection induced abnormal glucose regulation (hyperglycemia) persisting at least 4.5 months.
Vaccination 4 days after infection prevented hyperglycemia.
They “identified a dysregulated chemokine signature and hypersensitive T cell population during acute COVID-19 that correlates with elevated and persistent
hyperglycemia four months post-infection. This persistent hyperglycemia correlates with elevated hepatic glycogen, but there was no evidence of long-term SARS-CoV-2 replication in the liver and pancreas.”
9/25/23 Nature Biomed Engineering: A computationally designed antigen eliciting broad humoral responses against SARS-CoV-2 and related sarbecoviruses https://buff.ly/3RGNK95
A computer designed single antigen based on the receptor binding domain of the spike protein of sarbecoviruses elicits broad humoral responses against SARS-CoV-1, SARS-CoV-2, WIV16 and RaTG13 in mice, rabbits and guinea pigs.
The antigen was tested in a vector based vaccine and an mRNA vaccine in animals with good results.
9/23/23 SF Chronicle: UCSF tries new antibodies tactic to eradicate Long COVID symptoms https://buff.ly/3ZCH9yn
Dr. Michael Peluso, principal investigator of the trial dubbed outSMART-LC.
Study will use monoclonal antibody AER002 from Aerium Therapeutics to try to rid the body of viral reservoirs.
9/22/23 Science: Intranasal mRNA-LNP vaccination protects hamsters from SARS-CoV-2 infection https://buff.ly/3EWa0o0
Intranasally administered mRNA-LNP vaccine (like Moderna who paid for the study) caused local immunity at upper respiratory sites to make a protective barrier to reduce viral infection and subsequent transmission.
Other intranasal vaccines have used adenoviral vectors, live attenuated recombinant viruses, or adjuvant protein subunits, but these can have some down sides.
9/22/23 BDR: Maternal first trimester COVID‐19 vaccination and risk of major non‐genetic congenital anomalies https://buff.ly/453itA9
There was no increased risk of major congenital anomalies in the offspring after maternal 1st trimester COVID-19 vaccination. “COVID-19 vaccines are safe during early pregnancy."
9/29/23 CDC MMWR: Effectiveness of Maternal mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination During Pregnancy Against COVID-19–Associated Hospitalizations in Infants Aged <6 Months During SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Predominance — 20 States, March 9, 2022–May 31, 2023 https://buff.ly/3LGRlAk
Infants aged <6 months are not eligible for COVID-19 vaccination and are at risk for COVID-19–associated complications.
During the period of recent SARS-CoV-2 Omicron predominance, maternal receipt of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine during pregnancy reduced the likelihood of COVID-19-related hospitalizations and serious complications among infants aged <6 months.
9/26/23 Katelyn Jetelina: Don't be surprised if masks come back to hospitals and nursing homes https://buff.ly/467qGEP
YLE reviews the science behind mask's protection
9/19/23 KTVU: Several Bay Area health departments issue new mask mandates, amid rising COVID cases https://buff.ly/3Pwi6s7
With rising hospitalizations, Contra Costa, Sonoma, and San Mateo counties all issued mask orders for health care personnel in hospitals and other patient care facilities. All three orders were set to go into effect on Nov. 1 and last through April 30.
The County of Santa Clara Public Health Department said, "The health order goes into effect November 1, extends through next March, and requires masking for everyone in patient-care areas of clinics, hospitals, long-term care facilities, and other health care facilities."
9/19/23 PNAS Nexus: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection leads to Tau pathological signature in neurons https://buff.ly/3LF1qxx
SARS-CoV-2 infection is known to cause neurologic problems and can worsen Alzheimer's disease.
In vitro, SARS-CoV-2 infection in neuronal cells causes abnormal phosphorylation of Tau at several pathological epitopes- binding locations for antibodies- similar to what happens in Alzheimer's disease. This increases Tau's ability to make insoluble clumps and alters Tau's subcellular location which can impair neuron function.
9/23/23 Arizonans can now receive Workers Comp benefits for getting Covid-19 on the job. https://buff.ly/3rufdAb
If a worker dies from the virus, their next of kin will receive financial support.
9/22/23 CNN: As Covid-19 hospitalizations climb, rates among seniors and children raise concern https://buff.ly/3PxWoUC
Weekly COVID admissions now more than triple what they were two months ago.
Seniors have the highest rates of Covid hospitalizations by far, but hospitalizations among children — especially among those younger than 5 — are rising fast.
9/22/23 Science: Genetically determined thymic function affects strength and duration of immune response in COVID patients with pneumonia https://buff.ly/46lK94m
The GG genotype at the rs2204985 locus was associated, independently of age and sex, with stronger and long-lasting anti–SARS-CoV-2 helper and cytotoxic T cell responses 6 months after recovery.
The GG genotype was also associated with less severe lung involvement, and more activated stem cell memory CD4+ T cells.
Overall, GG patients developed a more robust and sustained immunity to SARS-CoV-2.
Polymorphism at rs2204985 locus should be considered as an additional predictive marker of anti–SARS-CoV-2 immune response.
8/27/23 Tara Haelle: A Call for Long COVID Writers for a New Medium Publication https://buff.ly/3rv4dm8
7/20/23 From Charlie McCone: Latest on Long COVID: NIH Study Leader Leora Horwitz, MD https://buff.ly/3M4b7pJ
“When we look at people infected with the most recent, omicron variant, & were vaccinated we are still seeing a pretty substantive rate of Long Covid — about 10%.”
Other news:
9/18/23 Washington Post: Working from home could slash emissions by half, study finds https://buff.ly/3ZxUybe
Fully remote workers may produce less than half the climate-warming emissions of people who spend their days in offices according to a new study.
9/25/23 Neurology: Psychiatric Comorbidity During the Prodromal Period in Patients With Multiple Sclerosis https://buff.ly/3tbkNrT
Psychiatric conditions like anxiety and depression represent a significant burden before Multiple Sclerosis (MS) onset and may be a feature of the MS prodrome in the 5 years leading to diagnosis.
9/28/23 Nature Digital Medicine (Aghaeepour): Deep representation learning identifies associations between physical activity and sleep patterns during pregnancy and prematurity https://buff.ly/45esjiG
Using a smartwatch during pregnancy and A.I. analysis, the authors predicted who was at increased risk for preterm delivery.
9/26/23 NBC: 'Constant buzzing': Some teens get thousands of phone notifications in a day, research finds https://buff.ly/45exBL4
A Common Sense Media report finds about half of 11- to 17-year-olds get at least 237 notifications a day. Some get nearly 5,000 in 24 hours. What does that do to their brains?
Exclusive: Microsoft opens AI Co-Innovation Lab in San Francisco to empower Bay Area startups https://buff.ly/3RHEphg





























Thank you very much (as always).