EG.5 and FL.1.5.1 are responsible for the most COVID infections in the United States now. Scientists are watching HV.1 (EG.5 + L452R mutation added) which is now at 5% of variants in the United States and XBB.1.5.70 which is at 3.5% and is a FLip variant with the L455F and F456L mutations which may make it more able to evade our immune responses to the virus.
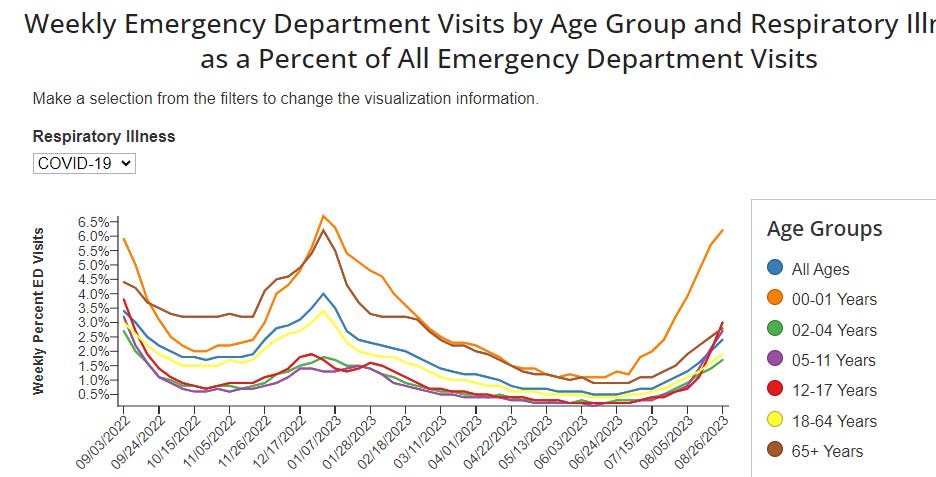
Hospitalizations are up 18.8% this week in the US for COVID infections and Emergency Department visits are increasing, especially for babies age 0 to 1 year old (orange on this chart) and for teens ages 12 to 17 (red on the chart).
Regarding COVID cases, not many are reported these days, so we need to rely on wastewater virus measurements to know what is really going on. The Santa Clara Department of Public Health shows this well on this graph.
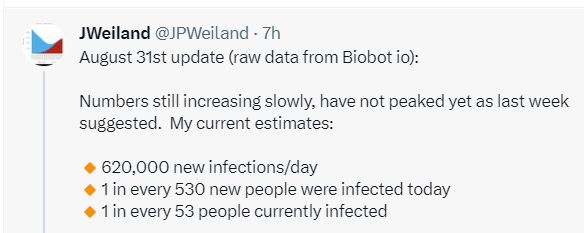
Using mathematical models to predict actual COVID cases from wastewater levels shows that we have more cases now than we did in the summer of 2020. In fact, JP Weiland calculates that there are 620,000 new infections each day in the United States. This would be a good time to improve indoor ventilation and/or to wear a KN95 or N95 mask indoors.
The CDC map of wastewater virus levels in the U.S. shows a lot more orange and red this week indicating higher virus levels. Here in California, Pacifica and Lompoc wastewater virus levels are high. Those from Sausalito and Laguna Niguel are on a downward slope.
The U.S. CDC reported that when China stopped their Zero-COVID policy after 3 years, 90% of the Chinese population was infected by Omicron and 1.4 million people died of COVID within 35 days of the policy change. If 90% of the 1.4 billion people in China got Omicron COVID infections, and if 10% (or more) of those went on to get Long COVID, then about 126 million (or more) should be expected to get Long COVID.
BA.2.86
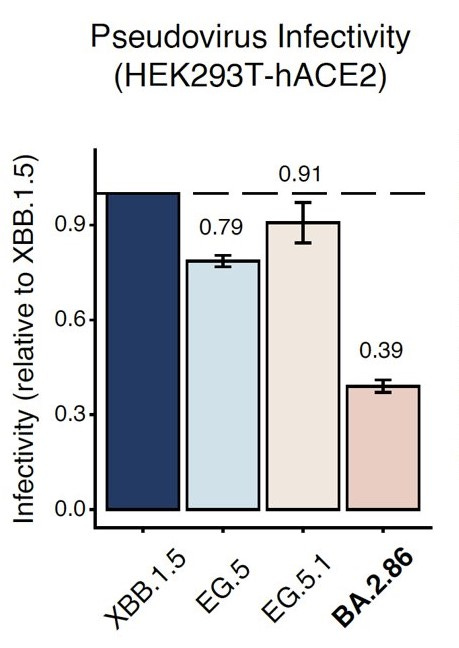
Yunlong Cao reported that BA.2.86 can evade our neutralizing antibodies, even if we had prior XBB.1.5 infections, meaning that the new fall vaccine may not protect well against BA. 2.86. But there is a caveat. It turns out that BA.2.86 can evade antibodies, but it is not as infectious or transmissible as other variants in circulation now. This is reassuring. We know that antibodies from the new Fall XBB.1.5 vaccine expected out in about 2 weeks, will protect us from EG.5 and FL.1.5.1 variants which are in circulation now in the U.S. and many parts of the world.
Ben Murrell’s lab in Sweden announced that eight out of twelve blood donors with prior XBB.1.5 infection had antibodies that could neutralize BA.2.86. The updated fall booster against XBB.1.5 may provide some protection against BA.2.86. We will have to wait and see.
Acute COVID
A new study shows that Native Americans have triple the risk of severe COVID and double the risk of in-hospital death as compared to their White and Hispanic peers, despite being younger and having fewer chronic conditions. Cancer patients who received systemic anticancer therapies (including endocrine therapy, immunomodulators, or chemotherapy) in the last 3 months had a 33% higher risk of dangerous blood clots if they got a COVID infection. Black cancer patients were noted to have a higher risk of thromboembolism than White cancer patients.
A new study of 171,564 hospitalizations with a positive SARS-CoV-2 test showed that 4.4% were COVID infections that patients contracted while in the hospital for another reason (i.e. nosocomial infection). Another 3.8% of cases were considered indeterminate meaning that the patient may have been infected with COVID during their hospital stay or just before they were hospitalized. When community-onset COVID infections were higher, there was an increase of hospital-onset SARS-CoV-2 infections as well.
In a prospective study of unvaccinated people hospitalized with severe COVID infection early in the pandemic, high fibrinogen and D-dimer levels during acute COVID infection predicted cognitive issues (brain fog) up to 1 year after infection. This may or may not apply to people with Long COVID who had mild infections. Fibrinogen and D-dimer are proteins involved in blood clotting.
This reminded me of a study from Emory in April 2023 that used microfluidic devices lined with human endothelial cells (microvasculature-on-chip devices) to act like tiny capillaries. In adults with severe acute COVID, high fibrinogen levels were found to cause red blood cells to clump together which then mechanically damaged the endothelial glycocalyx, a gelatinous protective layer lining the microvessels. Authors concluded that fibrinogen-induced red blood cell clumping and resulting microvascular damage could be a major pathway by which COVID causes organ damage and even death.
SARS-CoV-2 reprograms stem cell genes
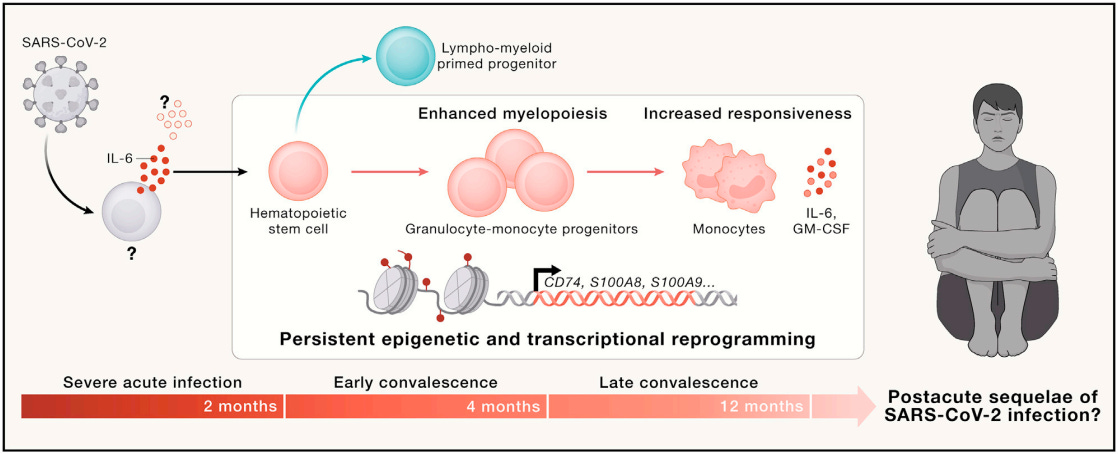
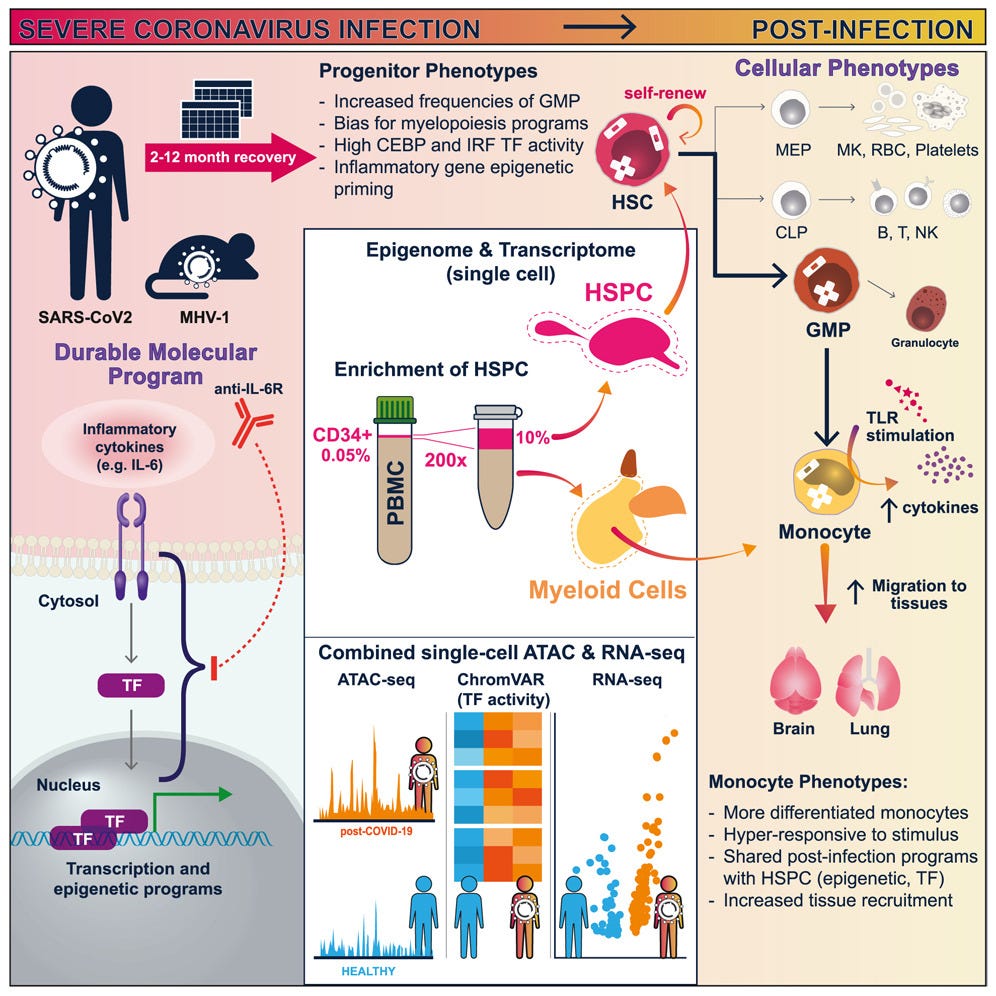
This week in Cell magazine, there was a review of the important article by Cheong et al. from two weeks ago showing that severe COVID infections can cause IL-6 induced epigenetic “poisoning” of hematopoietic stem cells to make more inflammatory monocytes instead of innate immune cells (B cells, T cells). The SARS-CoV-2 virus can go to our bone marrow and can reprogram genes in the cells that make all blood cells in the body (hematopoietic stem cells and myeloid progenitor cells). The virus can turn off the genes which instruct bone marrow stem cells to make immune cells like B cells and T cells that could fight the virus, and instead, the virus reprograms our bone marrow stem cells to make highly inflammatory monocytes. This reprogramming of bone marrow stem cells can cause permanent changes which theoretically could lead to the development of chronic conditions such as Long COVID.
Paxlovid, Metformin, Remdesivir iv and Molnupiravir are medicines used during acute COVID infections to decrease COVID hospitalizations and deaths. We know from the large randomized controlled PANORAMIC study that Molnupiravir does not decrease COVID hospitalizations or deaths. We also know that Molnupiravir works by causing mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 virus and can lead to hundreds of SARS-CoV-2 mutations in immunocompromised patients, potentially generating new variants. A new study shows that in countries that prescribe Molnupiravir, there are many more SARS-CoV-2 G-to-A mutations. The increase in these viral mutations is related to how many prescriptions for Molnupiravir were given in each country. In Canada, the Netherlands, France and Sweden, Molnupiravir is not available. These countries have the fewest G-to-A viral mutations seen. In contrast, Australia has the highest number of Molnupiravir prescriptions and they also have the highest amount of G-to-A mutations found in the virus. I believe that Molnupiravir should be recalled since it does not prevent hospitalizations and deaths, and it increases mutations in the virus.
Mitochondria
This week, an in-depth review article looked at how the SARS-CoV-2 virus can affect the mitochondria in our cells. Mitochondria make the energy needed to keep cells working. When a virus hijacks mitochondrial function, this allows the virus to control that host cell. Patients with COVID-19 have been found to have a population of T cells with mitochondrial dysfunction, as well as alterations in mitochondrial markers in monocytes. This can affect how the human body can fight off infection. The authors stated that given the important roles of mitochondria in viral infection, mitochondria could be considered a therapeutic target for COVID-19 disease.
The review also discussed a paper from April 2023 which postulated which antioxidants that may help prevent or possibly treat Long COVID stemming from SARS-CoV-2-induced mitochondrial dysfunction. This week, the NIH reviewed the recent seminal study from Doug Wallace’s lab showing that SARS-CoV-2 can cause lasting damage to energy production by mitochondria in many organs of the body and mitochondrial dysfunction could be a root cause of Long COVID. Stopping the virus from hijacking mitochondrial energy production could be a way to prevent serious complications from SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Last week, we learned that exercise intolerance in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) may be caused by high levels of WASF3 in skeletal muscles. High levels of WASF3 can interfere with the assembly of mitochondrial proteins that support normal energy production.
Long COVID
This past week, the Keystone Symposia Long COVID meeting (#KSLongCOVID24) took place with Long COVID researchers from around the world. Resia Pretorius posted on Twitter about two poster presentations from Rob Wust’s lab looking at the skeletal muscles of people with Long COVID. They found that Post Exertional Malaise (PEM) in people with Long COVID is associated with severe exercise-induced muscle damage, amyloid deposits and mitochondrial dysfunction in skeletal muscles and an increase in glycolytic muscle fibers. The authors concluded that “These muscle abnormalities help to explain the worsening of symptoms, including muscle pain and extreme fatigue during Post Exertional Malaise (PEM) in patients with Long COVID.”
The New Yorker had a very interesting piece on Dr. Lisa Sanders, a Yale physician who uses crowdsourcing to solve medical mysteries. She writes a monthly article in the New York Times Magazine called Diagnosis, has a Netflix show on mystery medical cases also called Diagnosis, and her medical sleuthing was the inspiration for the long-running television series House. Dr. Sanders is now running the Long COVID Clinic at Yale and is trying to understand the mysteries of Long COVID and other post-infection chronic diseases.
Drs. Iwasaki and Krumholz of Yale announced that they are working with Hugo Health to recruit Long COVID patients from around the United States for two studies. People with Long COVID can sign up for the 15 day Paxlovid trial (PAX LC) and/or the LISTEN (Listen to Immune, Symptom, and Treatment Experiences Now) study.
The New Yorker article on Lisa Sanders led me to an 173 page review from Ireland (HIQA) on interventions to improve Long COVID symptoms. Fifty-seven randomized controlled trials on possible treatments for Long COVID symptoms were reviewed. Although authors did not find a magic treatment that could cure Long COVID, they did find several small randomized clinical trials that may hold promise. A Phase II clinical trial of AXA1125 (five amino acids and N-acetylcysteine) showed large improvements in Long COVID fatigue in a small study of 41 people with Long COVID, half of whom received AXA1125.
A study from Russia of 444 people with Long COVID fatigue and cognitive impairment, showed that taking Actovegin (deproteinized hemodialysate of calf's blood) 400mg orally 3 times daily for 60 days improved cognitive function, fatigue and emotional wellness compared to the control group, although improvements were not statistically significant. According to Wikipedia, Actovegin has been used by cyclists to improve performance and has been implicated in doping scandals. It is not approved for sale in some countries.
Three other studies discussed in the HIQA review showed some Long COVID symptom improvement: Palmitoylethanolamide and luteolin (PEA + LUT) supplements for olfactory function, a fermented fruit supplement to help dyspnea and Long COVID symptom score and systemic enzymes and probiotics to improve fatigue. Although there were short-term improvements, long-term effects were not assessed and the studies were all fairly small. Further studies are needed to see if these improvements are reproducible.
In non-COVID news, Semaglutide (Wegovy) given to people with obesity and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction markedly improved symptoms, improved exercise ability, reduced inflammatory markers and caused weight loss. In 152 young amateur athletes in contact sports such as American football, hockey, soccer, rugby, and wrestling who died under age thirty, 41% were found to have Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) in their brains. The Biden administration announced the first 10 prescription drugs that will be subject to price negotiations between manufacturers and Medicare.
A new consensus guideline recommends screening for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in pregnant people with obesity, hypertension or diabetes. In a study with over 1 million people who underwent surgery, patients treated by female surgeons in any surgical specialty were less likely to experience hospital readmission, major medical complication or death for up to 1 year. A single dose of psilocybin combined with routine psychological support caused a rapid and sustained antidepressant effect in people with Major Depressive Disorder (MDD). Oprah Winfrey and Dwayne Johnson launched the People’s Fund of Maui that will give $1,200 a month to adults who cannot return home because of recent wildfires on Maui. People can donate to the fund so that support may continue for a longer period of time. And finally, police in Nebraska stopped a man driving down the freeway with a huge bull riding as a passenger in his car. Next time, his big friend will have to be towed behind in a trailer instead.
Have a good holiday weekend,
Ruth Ann Crystal MD
COVID news:
US Variant tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions
EG.5 and FL.1.5.1 are still in first place amongst variants.
XBB.1.5.70 (at 3.5%) is a FLip variant with the L455F and F456L mutations
HV.1 (now 5%) is EG.5 + L452R mutation
Variants in different locations: https://outbreak.info/
CDC COVID data tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/index.html#datatracker-home
Hospitalizations up 18.8% this week:
CDC COVID Hospitalizations (blue) and Emergency Room (orange) visits tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/index.html#trends_weeklyhospitaladmissions_7dayeddiagnosed_00
Weekly ED visits for respiratory illnesses, by age and disease: https://www.cdc.gov/ncird/surveillance/respiratory-illnesses/index.html
Respiratory infections in the ED are still all COVID
Respiratory infections (all COVID) in Babies age 0 to 1 year have taken off
COVID infections in teens age 12-17 also shows a steep curve upward
US Wastewater Monitoring:
CDC Wastewater Monitor https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#wastewater-surveillance
Wastewater SARS-CoV-2 virus levels are high in many areas of the country now (orange and red)
Charting of wastewater from individual states: https://iowacovid19tracker.org/
Biobot: https://biobot.io/data/
California wastewater level updates:
–Wastewater SCAN: https://data.wastewaterscan.org/
California statewide view https://buff.ly/3YObiul
Pacifica and Lompoc are going up; SF Oceanside, Sausalito and Laguna Niguel going down
Sewer Coronavirus Alert Network (SCAN) project by Stanford University:
This COVID wavelet has not peaked yet per JP Weiland: https://twitter.com/JPWeiland
8/29/23 Dr. Lucky Tran and 8/30/23 Angie Cibis graphic
8/30/23 Santa Clara Public Health shows the difference between reported COVID cases and the actual amount of SARS-2 virus in local wastewater https://covid19.sccgov.org/covid-cases-wastewater
8/31/23 Yunlong Richard Cao tweet thread on BA.2.86
BA.2.86 pseudovirus was tested.
BA.2.86 can evade our neutralizing antibodies, including antibodies after XBB.1.5, but it does not infect as well as other variants, so it may not be as big a concern for an Omicron-like wave.
9/1/23 Ben Murrell’s lab show similar findings to Yunlong Cao about BA.2.86 except that the updated Fall booster against XBB.1.5 may have some efficacy against BA.2.86 as seen by the antibodies of 8 out of 12 blood donors who had XBB.1.5 prior infection.
https://twitter.com/dfocosi/status/1697708804014538789
8/31/23 Nature: Acute blood biomarker profiles (fibrinogen and D-dimer) predict cognitive deficits 6 and 12 months after COVID-19 hospitalization https://buff.ly/44wlJE8
Prospective study of unvaccinated people hospitalized with severe COVID infection early in the pandemic shows that pro-clotting factors fibrinogen and D-dimer were biomarkers that could predict cognitive issues (brain fog) up to 1 year after infection.
This may or may not apply to people with Long COVID who had mild infections.
8/31/23 Science (review of Nature article above): Clotting proteins linked to Long Covid’s brain fog https://buff.ly/3OY0FRc
Two proteins involved in blood clotting (fibrinogen, D-dimer) predicted whether hospitalized COVID-19 patients would experience cognitive problems up to 1 year later.
8/31/23 Cell: Haunting innate immune memories of COVID-19 https://buff.ly/45INkD0
A review of the recent article by Cheong et al. (see below)
Severe COVID infections via IL-6 induce persistent epigenetic signatures in hematopoietic stem cells and their myeloid progenitors associated with increased inflammatory potential.
Figure 1. Maladaptive trained immunity upon severe SARS-CoV-2 infections
IL-6 released during severe COVID-19 contributes to the establishment of persistent and shared epigenetic and transcriptional programs within hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and their myeloid progenitors.
Epigenetic poisoning causes functional alterations of HSCs favoring differentiation of granulocyte-monocyte progenitors (GMPs) over lympho-myeloid primed progenitors (LMPPs). The developing monocytes show increased responsiveness and a high inflammatory potential.
It remains to be determined whether other signals apart from IL-6 induce the epigenetic modifications and whether the maladaptive trained immunity contributes to the development of chronic conditions such as PASC.
Original paper:
From 8/18/23 Cell (Cheong): Epigenetic memory of coronavirus infection in innate immune cells and their progenitors https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(23)00796-1#%20
Epigenetic reprogramming of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPC) may underlie altered immune function following COVID infection for up to a year.
IL-6 early in a COVID infection contributed to these persistent phenotypes in human COVID-19 and a mouse model.
The SARS-CoV-2 viral infection causes certain gene transcription factors to be turned on in HSPCs, leading to changes in usual inflammatory pathways and durable increases in myelopoiesis.
This increases monocytes who send out cytokines and then migrate to the brain and the lung.
Image of Hematopoietic Stem Cells and their progeny from Wikipedia for reference:
8/30/23 CIDRAP: Native Americans at outsized risk of severe COVID-19, death https://buff.ly/45wrKlz
American Indian/Alaska Native (AI/AN) COVID-19 patients were 3x more likely to become severely ill than their White or Hispanic peers and had 2x risk of in-hospital death—despite being younger and having fewer chronic conditions.
8/29/23 New Yorker, Intelligencer: The Mystery of Long COVID Is Just the Beginning https://buff.ly/44Ce86O
At Yale’s clinic, medical sleuth Dr. Lisa Sanders is trying almost everything.
"As she grows older, “I’m more interested in areas that are less clear. In helping people manage what’s going on. In continuously having to educate myself.”
"Long COVID provides science with an opportunity to learn how post-infection chronic disease originates and thereby to help hundreds of millions of people, Dr. Iwasaki told me."
7/27/23 HIQA (Ireland): Interventions to improve Long COVID symptoms: A systematic review https://buff.ly/45yd05o (see below)
8/28/23 NPR’s Rundown Podcast: “It's likely you know someone dealing with long COVID”, with Hannah Davis and Ed Yong https://buff.ly/3OVRPDv
8/28/23 Nature Scientific Reports: SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces endothelial inflammation via ACE2 independently of viral replication https://buff.ly/3Z1COon
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, S1 subunit (rS1p) induces endothelial inflammation via ACE2 through processes that are independent of ACE2 enzymatic activity and viral replication.
8/29/23 TIME: Long COVID Recovery Remains Rare https://buff.ly/3QWUKhF
Long COVID patients seen at Dr. Putrino's clinic at Mount Sinai:
10% do not get better, no matter what Putrino and his team try.
Many see some improvement, but remain sick.
15% to 20% report full recovery, although if they get a reinfection, they often get Long COVID symptoms again.
8/29/23 Eric Topol MD tweet
Long COVID at 2 years (11 studies):
8/28/23 JAMA: Hospital-Onset SARS-CoV-2 Infection Rates and Testing Practices in the US https://buff.ly/3OQbMeO
Nosocomial COVID infection means getting COVID from being in the hospital.
Among 171,564 hospitalizations with a positive SARS-CoV-2 test, 7591 (4.4%) were found to be hospital onset and 6455 (3.8%) were indeterminate onset.
Nosocomial infections acquired during hospitalization:
There was an increase of hospital-onset SARS-CoV-2 infections when community-onset infections were higher.
8/28/23 Resia Pretorius comments on work of Rob Wust, mitochondrial scientist from Amsterdam UMC
Poster 1: “Muscle abnormalities contribute to Post-Exertional Malaise in Long COVID patients”, Wust lab, Email: b.appelman@amsterdamumc.nl
CONCLUSION:
This study reveals that severe exercise-induced myopathy, tissue infiltration with amyloid-containing deposits and metabolic disturbances in skeletal muscles of Long COVID are key characteristics of Post Exertional Malaise.
These muscle abnormalities help to explain the worsening of symptoms, including muscle pain and extreme fatigue during Post Exertional Malaise (PEM) in patients with Long COVID.
Poster 2)“Altered skeletal muscle structure and function contribute to exercise intolerance in Long COVID patients”, Wust lab, Braeden T. Charlton, Email: b.t.charlton@vu.nl
Take home message:
More glycolytic fibers and a lower mitochondrial respiration contribute to exercise intolerance in Long COVID.
An increased presence of amyloid-containing deposits in skeletal muscle contribute to PEM pathophysiology.
8/28/23 Lancet: Long COVID in low-income and middle-income countries: the hidden public health crisis https://buff.ly/45O8srx
8/28/23 CDC: Estimate of COVID-19 Deaths, China, December 2022–February 2023 https://buff.ly/45PgpN4
Within 35 days following the relaxation of China's policy, 1.41 million Chinese people died of COVID-19.
90% of China’s population were infected during the study’s 35-day period.
8/28/23 CIDRAP: COVID-19 spillover to white-tailed deer may speed virus evolution https://buff.ly/3PjNUSe
30 human-to-animal spillover events of SARS-CoV-2 and fast virus evolution noted in a relatively small sample size of deer in northeastern Ohio.
Overall SARS-CoV-2 in white-tailed deer has decreased.
“Other than white-tailed deer, spillover from humans to wildlife is exceedingly rare."
8/26/23 Nature: Retrospective study of COVID-19 experiences in elite multinational aquatic athletes https://buff.ly/3qOhrKv
Most athletes experienced a benign disease course despite a relatively high infection rate.
49.4% of athletes had experienced SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The infection rates varied significantly across different aquatic sports, with open water swimmers having the lowest (28%) and water polo players (67%) and artistic swimmers (61%) having the highest infection rates (p < 0.0001).
10% of initial infections led to long COVID, with fatigue (65%) and shortness of breath (48%) being the most common long-term symptoms.
Significantly, 92% of athletes received at least two vaccine doses and reported a positive vaccination experience (median score of 8 out of 10 for each shot).
8/25/23 REVIEW article in Frontiers Cell. Infectious Microbiology:
Host mitochondria: more than an organelle in SARS-CoV-2 infection https://buff.ly/3YQVLKh
Viruses have evolved to modulate the immune system and mitochondrial function for survival and proliferation. Mitochondrial hijacking by SARS-CoV-2 could be a key factor in COVID-19 pathogenesis.
Mitochondria are the “powerhouse” of the cell. When a virus “hijacks” mitochondrial function, this allows it to control the entire cell.
SARS-CoV-2 appears to hijack the mitochondria of immune cells, proliferate in mitochondrial structures, and impairs mitochondrial functions.
Patients with COVID-19 have a population of T cells with mitochondrial dysfunction, as well as mitochondrial markers in monocytes have altered.
Monitoring mitochondrial function of immune cells in the blood could be a non-invasive marker to diagnose and predict the prognosis of COVID-19.
There are various strategies with pharmacological agents and lifestyle interventions to target mitochondria that could be promising to prevent SARS-CoV-2 infection or reduce disease progression. However, there is little empirical evidence of their potential.
Given the important roles of mitochondria in viral infection, mitochondria could be considered a therapeutic target for COVID-19 disease.
Figure 2 Changes in mitochondria-related events in SARS-CoV-2 infection.
antioxidant compounds to scavenge ROS (reactive oxygen species)
An article discussed in above paper:
4/2023 Int J of Molecular Sciences: Possible Pathogenesis and Prevention of Long COVID: SARS-CoV-2-Induced Mitochondrial Disorder https://buff.ly/45w6mgi
Several compounds, including
Antioxidants (N-acetylcysteine [184], glutathione [185], and catalase [186])
mitochondrion-targeting peptides, and
modulators of mitochondrial biogenesis, have shown promise for the treatment of mitochondrial dysfunction, in pre-clinical studies.
Mitochondrial oxidative stress can also be reduced using mitochondrion-targeted catalytic antioxidants such as MnTBAP [188], EUK-8, and EUK-134 [189], as well as Mito-TEMPO and mitoquinol [112,162,190].
In addition, mitochondrial quinone/mitochondrial phenol mesylate (Mito-MES) has been demonstrated to possess significant antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 and can reduce excessive inflammation in the host [191]. Effective treatment can also be obtained with mPTP inhibitors such as NIM811 [192,193].
SARS-CoV-2-infected cells mainly rely on glycolysis to meet their energy demands, due to mitochondrial respiratory dysfunction.
Inhibition of glycolysis in infected cells has been found to inhibit viral proliferation [107]. Ruthenium red—a mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) inhibitor—also normalizes mitochondrial morphology and function in HIV-infected cells [202]. Other known MCU inhibitors include ruthenium 265, mitoxantrone, and the antibiotic doxycycline [203].
All of these strategies may help to improve mitochondrial health in people with long COVID or chronic fatigue syndrome.
8/24/23 CIDRAP: Small study (see below) suggests many more people have long COVID than previously believed https://buff.ly/47OF2LO
41% of 29 patients with post-viral syndrome (PVS) resembling Neuro-PASC (aka Neuro Long COVID) actually had Long COVID as seen by advanced antibody tests and T cell analysis.
Lack of COVID-19 diagnosis probably delayed care for many PVS patients.
"Unlike our clinic, about 70% of post-COVID clinics in the U.S. do not accept people with long COVID symptoms who do not have a positive test result for COVID,"
Potentially 4 million hidden long-COVID patients who were never diagnosed.
When prior COVID infection was suspected, but not confirmed because testing wasn’t available.
8/23/23 Neurology: SARS-CoV-2–Specific Immune Responses in Patients With Post-viral Syndrome (PVS) After Suspected COVID-19 https://buff.ly/3PdqZI4
Yale Study on 15 days of Paxlovid for people with Long COVID in most U.S. states: https://www.kindred.hugo.health/pax-lc
LISTEN study: https://www.kindred.hugo.health/research/listen-study
8/26/23 https://medicine.yale.edu/cii/research/paxlc-study/
8/22/23 NIH: SARS-CoV-2 can cause lasting damage to cells’ energy production (mitochondria) https://buff.ly/44vwMNz
SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, can cause lasting damage to energy production by mitochondria in many organs of the body.
Stopping the virus from hijacking mitochondrial energy production may be a novel way to prevent serious complications from SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Review of study from 8/9/23
8/18/23 CIDRAP: COVID-19 tied to dangerous blood clots in cancer patients https://buff.ly/47Qz9xu
Cancer patients who received systemic anticancer therapies in the last 3 months such as endocrine therapy, immunomodulators, and chemotherapy had a 33% higher risk of venous thromboembolism if they got a COVID infection.
Black patients had a higher risk of thromboembolism than White cancer patients.
Original article in JAMA Oncology: Systemic Anticancer Therapy and Thromboembolism in Hospitalized Patients With Cancer and COVID-19 https://buff.ly/3OSA9sj
8/18/23 MedRxiV (UK): A Molnupiravir -associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes https://buff.ly/3PfL4xG
SARS-CoV-2 sequencing databases contain extensive evidence of Molnupiravir mutagenesis and some onward transmission of Molnupiravir-derived lineages was found.
There is a direct association between high G-to-A mutation branches and the use of Molnupiravir in different countries.
Figure 2F: Countries confirmed to have made molnupiravir available have more high G-to-A nodes than countries which have not. Numbers in brackets represent number of courses of molnupiravir supplied, normalized to the population.
7/27/23 HIQA (Ireland): Interventions to improve Long COVID symptoms: A systematic review https://buff.ly/45yd05o
173 page review
HIQA’s review found 57 randomized controlled trials that considered interventions for adults with symptoms of Long COVID.
A wide range of pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical interventions were identified, with most only examined in single studies. These studies were generally small, had short follow-up periods and typically only included people who had symptoms of Long COVID for less than one year.
No definitively effective treatments were identified.
There was also limited reporting on the safety of these interventions.
Pg. 65
One investigational study, a phase II clinical trial by Finnigan et al., investigated the therapeutic benefits of AXA1125 over four weeks among people with fatigue predominant Long COVID (n=41). (49) Participants who received the drug reported large improvements in fatigue relative to those who received a placebo.
Other news:
8/25/23 NEJM: Semaglutide (Wegovy) in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Obesity https://buff.ly/3QSZuVy
RCT in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and obesity:
Treatment with semaglutide (2.4 mg) markedly improved symptoms, improved exercise ability, reduced inflammatory markers and resulted in weight loss.
8/27/23 NYTimes: Covid Closed the Nation’s Schools. Cleaner Air Can Keep Them Open. https://buff.ly/3szTGGh
The average American school building is about 50 years old. The HVAC systems need to be replaced at least 20%. There are federal funds available, but many are not aware.
8/28/23 CDPH: Outbreak of Aeromonas Skin Infections https://buff.ly/3P3pL18
Sonoma Department of Health Services (SDHS), in coordination with the California Department of Public Health (CDPH), is investigating an outbreak of skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs) associated with Tough Mudder, an adventure race involving extensive exposure to mud, held at the Sonoma Raceway on August 19 and 20, 2023.
Numerous race participants have experienced SSTIs (most frequently described as a pustular rash), along with other symptoms such as fever and headache. Multiple wound cultures have yielded Aeromonas.
8/28/23 JAMA: Neuropathologic and Clinical Findings in Athletes With Repetitive Head Impacts (RHI) https://buff.ly/3EgMm55
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) was found in 41% of 152 deceased amateur athletes (American football, hockey, soccer, rugby, wrestling) who were less than age 30.
8/28/23 NY Times: After the Loss of a Son, a Football Coach Confronts a Terrible Truth https://buff.ly/3YSke1T
CTE symptoms can include memory loss, erratic behavior and depression.
8/29/23 President Biden announces drugs selected for Medicare price renegotiation
8/2023 Four Ways to Land Your First Health Plan Customer For Digital Health Companies by Halle Tecco https://buff.ly/3OSfnZQ
8/29/23 Healio: Guideline recommends screening pregnant women at high risk for sleep apnea https://buff.ly/3YVDefE
A new consensus guideline published in the Green journal Obstetrics & Gynecology “recommend screening women during pregnancy who have high risk for obstructive sleep apnea” (OSA), “such as those with obesity, hypertension or diabetes.”
8/31/23 Meningococcal group B vaccine (MBV) associated with reduced Gonorrhea incidence https://buff.ly/44OyV7z
Outer membrane vesicle (OMV)-based MBVs target OMVs that are common to both Neisseria meningitidis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, which are genetically similar.
8/30/23 JAMA: Surgeon Sex and Patients’ Long-Term Postoperative Outcomes https://buff.ly/45TcjDO
In this cohort study of 1 million patients, those treated by a female surgeon were less likely to experience death, hospital readmission, or major medical complication at 90 days or 1 year after surgery.
This association was seen across nearly all subgroups defined by patient, surgeon, hospital, and procedure characteristics.
8/31/23 JAMA: Single-Dose Psilocybin Treatment for Major Depressive Disorder https://buff.ly/3Z2TFa0
In a randomized, placebo-controlled, 6-week trial in 104 adults, a 25-mg dose of psilocybin administered with psychological support was associated with a rapid and sustained antidepressant effect.
8/31/23 AP: Police stop Nebraska man for bucking the law with a bull riding shotgun in his car https://buff.ly/3R2U0ri
9/1/23 AP: Oprah Winfrey and Dwayne Johnson launch fund with $10 million for displaced Maui residents https://buff.ly/44wrlhv
The People’s Fund of Maui will give $1,200 a month to adults who cannot return home because of recent wildfires, including people who owned and rented their homes.
It was inspired by a similar fund set up by Dolly Parton after wildfires in Tennessee in December 2016.
People can donate to the fund so that payments can continue longer for the people of Lahaina, Maui.
Video of Oprah and the Rock discussing








































Thank you so very much.