COVID news and more 5/27/23
This week, globally, the number of reported cases and deaths are decreasing for COVID. There are still some hotspots in parts of Africa and the western pacific regions. Here in the US, hospitalizations and emergency room visits for COVID continue to decline. XBB1.5 is slowly being pushed out of first place by XBB1.16 and XBB 1.9. Most likely the fall booster will include mRNA from XBB.
An Op Ed in the Lancet says that there is “no time for complacency on COVID-19 in Europe”. They reference that COVID is still causing some outbreaks in Europe and that Long COVID affects 3 to 20% of those infected. The head COVID expert for the WHO, Dr. Maria Van Kerkhove, says that there are large holes that remain in our fight against COVID. Specifically, there has been a precipitous drop in genetic sequencing, and this means that scientists are blinded to the evolution of new variants. She also talked about vaccine inequity, the unknown risks of reinfection, as well as persistent health problems after COVID infection including Long COVID. China presently has a new COVID wave and is expected to see 65 million new cases of COVID per week peaking at the end of June.
There were several studies this week, looking at the effects of COVID on the brain. Cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) is the leading cause of vascular dementia and is due to endothelial damage which affects brain blood flow. CSVD is a prevalent complication in COVID-19 patients especially in older individuals and those with underlying age-related diseases (hypertension, dyslipidemia, and type 2 diabetes). CSVD increases risk for cerebrovascular complications and cognitive decline. CSVD found after COVID-19 is located mostly in the white matter of the cerebrum. The authors suggest that microbleeds and ischemic lesions should be assessed as COVID-19 CSVD markers. Cognition is commonly impaired in recovered COVID-19 patients with CSVD.
In a case control study, non-vaccinated people who recovered from mild to moderate COVID infection showed significant alterations of the brain white matter seen on diffusion-weighted imaging that appear to be a prolonged neuroinflammatory response to the initial viral infection seen one year later. Cognitive function was normal at one year in this group despite the cerebral white matter changes. It is unknown if this will affect the brain long-term.
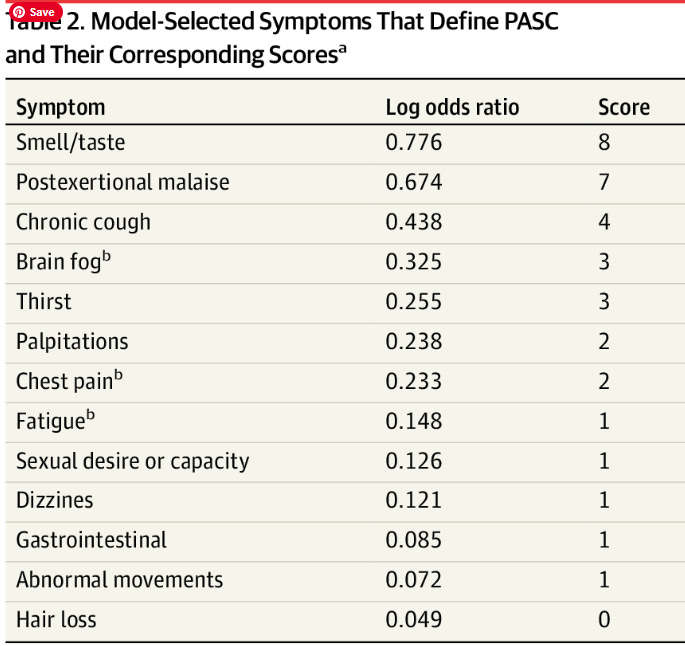
There was an article in JAMA, about defining post acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection, also known as PASC or Long COVID, based on RECOVER trial data. In this prospective study of almost 10,000, people were enrolled at the time of acute COVID infection and were then followed. Authors defined PASC as a score of 12 or greater on a composite symptom score. The most common symptoms for Long COVID were post exertional malaise, fatigue, brain fog, dizziness, gastrointestinal symptoms, and palpitations. Regarding the prevalence of Long COVID, 10% of people were found to have Long COVID at six months for both pre-omicron and omicron variants and in vaccinated people. However, 20% had Long COVID after reinfection with SARS-CoV-2. Long COVID after reinfection was also noted to be more severe.
The NIH RECOVER initiative plans to study exercise as a potential treatment for Long COVID. People with Long COVID are concerned about this as exercise can be very dangerous for some Long COVID patients with ME/CFS. Exercising can cause post exertional malaise which could land some people in bed for days or weeks. The people with long COVID interviewed said that they would prefer for the NIH to spend their limited money and time to study possible treatments for Long COVID instead of studying exercise, which is proven to be harmful in other studies on ME/CFS.
A study comparing 37 people with long COVID and fatigue to 57 controls showed neural dysregulation in Long COVID patients. Analysis showed that there was no dysregulation in sensory feedback circuits and descending neuromodulator control. Testing showed that there was under activity in specific cortical circuits, dysregulation of autonomic functions and myopathic change within skeletal muscle of people with Long COVID.
Other news about COVID this week, exercise increases aerosol particles by a hundred fold which can increase the risk of infection by ten fold as compared to rest. In addition, age is an important factor in lung aerosol particle emission. Older adults, age 60 to 76, were found to emit two times more aerosol aerosol particles than younger people.
Patients with acute COVID-19 at the time of a heart attack were found to have clots in multiple arteries up to 30% of the time. However, such clots were found less than 5% of the time in heart attack patients who were not infected with COVID-19. An article in PNAS shows that abdominal obesity increases the risk for cytokine storm and death in patients with COVID-19.
A Toronto group made Multabodies (MBs) that are similar to antibodies but that can work at very low doses to neutralize a broad range of viruses in the sarbecovirus family, including all SARS-CoV-2 variants. A group in Irvine, California used B and T cell epitopes from SARS-CoV-2 antigens to make a pancoronavirus vaccine that conferred broad immunity in mice.
In non-COVID news, identical triplet sisters have all become OB/GYN doctors and they are working with their mother who is also an OB/GYN. Thermo Fisher‘s preeclampsia risk blood test was approved by the FDA. Women who experience adverse pregnancy outcomes such as gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, preterm birth, small for gestational age infants, and placental abruption may have an increased risk of stroke later in life.
Dr. Eric Topol reviewed CHIP, clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential, which can be a pre-blood cancer cell. But, it turns out that CHIP can also be a biomarker for heart disease, stroke and pulmonary embolism and other diseases including liver disease, lung cancer, and skin cancer. A group from UC San Diego has made a continuous wearable ultrasound that uses artificial intelligence to capture deep tissue imaging and physiology while people are active for 12 hours at a time. A man who was paralyzed is able to walk again 12 years later using brain and spine implants as a digital bridge to bypass the injured section of his spinal cord.
Regarding chronic pain, a group from UCSF found that there are signals within the intracranial orbitofrontal cortex that can be used to predict spontaneous chronic pain in patients. This information may be useful for finding treatments for chronic pain. Taking the multivitamin Centrum Silver was found to significantly improve memory in older adults. And finally, the US Surgeon General issued a 19 page advisory on how social media is contributing to our youth mental health crisis and gave suggestions on what could help.
I plan to take a vacation from the newsletter next week.
Have a good rest of your weekend,
Ruth Ann Crystal MD
Other news:
5/12/23 Today: Identical triplet sisters all became OB-GYN doctors ... and work with their mom! https://buff.ly/42VWQl6
5/19/23 FierceBiotech: Thermo Fisher's biomarker blood tests to spot preeclampsia risk are first to win FDA approval https://buff.ly/3omSh4q
Test measures the ratio of soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1) and placental growth factor (PlGF).
The sFlt-1/PlGF ratio has a sensitivity of 94% and specificity of 75% for preeclampsia, a life-threatening pregnancy complication.
Results within 30 minutes on Thermo Fisher’s Brahms Kryptor Compact Plus clinical analyzer.
5/21/23 Eric Topol MD: The under-appreciation of CHIP https://buff.ly/3WzELao
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) make 50,000 to 200,000 blood cells each day.
CHIP, which stands for Clonal Hematopoiesis of Indeterminate Potential, like a pre-blood cancer (pre-leukemia, pre-lymphoma) is also related to many other diseases including atherosclerosis.
"CHIP is a major biomarker, not just for blood cancer (an 11-fold risk of a blood malignancy, or absolute 0.5% risk per year), but also for heart disease, blood clot events such as stroke and pulmonary embolism, and many other chronic illnesses." including liver disease, lung cancer, skin cancer, but also increased susceptibility to infections, including SARS-CoV-2.
5/22/23 Stroke Journal: Risk of Midlife Stroke After Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes (APO): The FinnGen Study https://buff.ly/3oC5G8C
APO was defined as a pregnancy affected by gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, eclampsia, preterm birth, small for gestational age infant, or placental abruption.
Women who experience APO have earlier onset of cerebrovascular disease, with the earliest onset in those with more than 1 affected pregnancy.
5/22/23 Medscape: Using Norethindrone Acetate To Induce Scheduled Bleeding Increases Tolerance To Hormone Implants https://buff.ly/45uOMtb
5/22/23 A fully integrated wearable ultrasound system to monitor deep tissues in moving subjects - Nature Biotechnology https://buff.ly/41Yxbam
Continuous wearable ultrasound integrates AI to auto-capture deep tissue imaging and physiology while walking and doing activities for up to 12 hours.
5/23/23 The Hill: Surgeon General issues advisory that social media is contributing to youth mental health crisis https://buff.ly/3WAI9BQ
19 page advisory
“one 2019 study that found adolescents between the ages of 12 and 15 who spent more than three hours on social media daily had double the risk of developing symptoms of depression and anxiety.”
5/23/23 Nature Neuroscience: First-in-human prediction of chronic pain state using intracranial neural biomarkers https://buff.ly/435eCT1
Intracranial orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) signals can be used to predict spontaneous, chronic pain in patients.
5/24/23 NY Times: A Paralyzed Man Can Walk Naturally Again With Brain and Spine Implants https://buff.ly/3q5FNP4
Scientists made implants that provided a “digital bridge” between his brain and his spinal cord, bypassing injured sections and enabling him to walk.
5/24/23 NY Times: What the Colorado River Deal Means for California https://buff.ly/3MX9dYN
Seven Western states that rely on the Colorado river — California, Nevada, Arizona, Wyoming, New Mexico, Colorado and Utah.
In recent years, the flow of the Colorado River has shrunk by one-third from its historical average because of drought, population growth and climate change.
In the new deal, California, Arizona and Nevada will each take less water from the river.
5/25/23 Stanford News: The most popular U.S. history textbooks used in California and Texas commonly misrepresent the scientific consensus around climate change. https://buff.ly/3qhaJvC
Datawrapper: To make beautiful charts
https://www.datawrapper.de/
5/24/23 Am J of Clin Nutrition: Multivitamin supplementation improves memory in older adults: A randomized clinical trial https://buff.ly/3BWxXtM
3,562 adults age 60+, half took Centrum Silver vitamin and half took placebo.
Evaluated annually with internet-based neuropsychological tests for 3 years.
Compared to placebo, participants randomized to multivitamin supplementation had significantly better ModRey immediate recall at one year (p = 0.025), as well as across the three years of follow-up on average (p = 0.011).
The multivitamin intervention improved memory performance above placebo by the equivalent of 3.1 years of age-related memory change.
5/24/23 MedCity News: Omada Health Launches Program To Support Patients on GLP-1 Medications for Weight Loss https://buff.ly/428VUsk
COVID news:
WHO Weekly Epidemiological Updates: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports
“Globally, nearly 2.3 million new cases and nearly 15 000 deaths were reported in the last 28 days (24 April to 21 May 2023), a decrease of 21% and 17%, respectively, compared to the previous 28 days (27 March to 23 April 2023). The situation is mixed at the regional level, with increases in reported cases seen in the WHO African and Western Pacific Regions and increases in deaths in the African, the Americas, South-East Asia, and Western Pacific Regions. As of 21 May 2023, over 766 million confirmed cases and over 6.9 million deaths have been reported globally.”
US Variant tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions
XBB.1.5 is slowly being pushed out by XBB.1.16 and the XBB.1.9s.
CDC COVID data tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/index.html#datatracker-home
CDC COVID Hospitalizations (blue) and Emergency Room (orange) visits tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/index.html#trends_weeklyhospitaladmissions_7dayeddiagnosed_00
US Wastewater Monitoring:
CDC Wastewater Monitor https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#wastewater-surveillance
Biobot: https://biobot.io/data/
Sewer Coronavirus Alert Network (SCAN) project by Stanford University:
5/25/23 Katelyn Jetelina: Catch up quick: COVID-19 https://buff.ly/3qfyGDW
Hannah Davis’ tweet thread on this article below:
5/25/23 JAMA: Development of a Definition of Postacute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection (PASC, Long COVID) https://buff.ly/45zqFdc
9764 participants (8646 infected; 1118 uninfected) in the RECOVER trial.
Prospective study: people were enrolled when they had the acute COVID infection.
Symptoms contributing to PASC score included postexertional malaise, fatigue, brain fog, dizziness, gastrointestinal symptoms, palpitations, changes in sexual desire or capacity, loss of or change in smell or taste, thirst, chronic cough, chest pain, and abnormal movements.
PASC was defined as a PASC score of 12 or greater.
Among participants with PASC, the most common symptoms were
87% Post Exertional Malaise (PEM)
85% fatigue, brain fog (64%),
dizziness (62%),
GI (59%), and
palpitations (57%).
Prevalence of Long COVID:
10% had LC at 6 months for pre-Omicron and Omicron variants
10% had LC also for Omicron infections in vaccinated people
20% had LC after reinfection
"Reinfections were linked to higher LC frequency and severity"
Four PASC subgroups were identified. Cluster 4 was the most serious and was seen in:
31% of pre-Omicron (original virus to Delta) infections vs. 23% of Omicron infections.
23% of vaccinated people vs. 32% of unvaccinated people.
PASC was defined as a PASC score of 12 or greater.
7/2023 issue, Ageing Research Reviews: Cerebral Small Vessel Disease (CSVD) pathology in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review https://buff.ly/3IGB4d8
Cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) is the leading cause of vascular dementia and accounts for up to 25% of ischemic strokes.
Endothelial damage affects brain blood flow.
COVID-19 CSVD pathology is located mostly in the white matter of the cerebrum.
Microbleeds and ischemic lesions both should be assessed as COVID-19 CSVD markers.
Cognition is commonly impaired in recovered COVID-19 patients.
Neurovascular coupling (NVC) should be assessed.
CSVD is a prevalent complication in COVID-19 patients with older individuals and those with underlying age-related diseases (hypertension, dyslipidemia, and type 2 diabetes) at increased risk for cerebrovascular complications and cognitive decline.
5/24/23 Science (Toronto): A multi-specific, multi-affinity antibody platform neutralizes sarbecoviruses and confers protection against SARS-CoV-2 in vivo https://buff.ly/45ttyMo
SARS-CoV-2–specific multimerized antibodies, called Multabodies (MBs) have improved avidity and multiple specificities to better target SARS-CoV-2.
MBs appear to work better than traditional monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that have lost their ability to neutralize the latest variants.
MBs work at very low doses and can neutralize a broad range of viruses in the sarbecovirus family including all SARS-CoV-2 variants.
5/24/23 BioRxiv (UC Irvine): Cross-Protection Induced by Highly Conserved Human B, CD4+, and CD8+ T Cell Epitopes-Based Coronavirus Vaccine Against Severe Infection, Disease, and Death Caused by Multiple SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern https://buff.ly/3WBTcdN
Pancoronavirus vaccine made using human B and T cell epitopes from SARS-CoV-2 antigens induced cross-protective immunity that cleared the virus, and reduced COVID-19-related lung pathology and death caused by multiple SARS-CoV-2 VOCs in mice.
5/23/23 PNAS: Brain imaging and neuropsychological assessment of individuals recovered from a mild to moderate SARS-CoV-2 infection https://buff.ly/3ICccTN
On brain imaging, there is a prolonged neuroinflammatory response in the brain white matter identified by diffusion-weighted imaging) one year after a mild to moderate SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Cognitive function was normal at one year despite the white matter changes.
5/23/23 PNAS: Lung aerosol particle emission increases with age at rest and during exercise https://buff.ly/431eB2z
Exercise increases aerosol particles by 100x and the risk of infection by 10x as compared to rest.
Age is another important factor. Older people age 60 to 76 years old emitted 2x more aerosol particles at rest and during exercise than younger people.
This suggests that aerosol particle emission increases as the respiratory system ages.
5/22/23 CIDRAP: Patients with COVID-19 at time of heart attack have more clotting https://buff.ly/3MOx1h8
Clots were seen in multiple arteries in close to 30% of patients with COVID-19 at the time of their heart attack, but in less than 5% of heart attack patients who did not have COVID-19.
5/22/23 Wash Post: An exercise trial for Long COVID is being criticized by some patients https://buff.ly/3opuOzu
NIH’s RECOVER initiative plans to study exercise as a potential treatment for Long COVID.
Since there is limited money and time to study treatments for Long COVID, they say that the NIH should focus on promising drugs and other treatments first.
Exercise can be dangerous for some Long COVID patients with ME/CFS.
Charlie McCone has Long COVID. A single day of strength training at a Long COVID clinic last fall caused him to crash and not be able to get out of bed for four weeks.
5/22/23 Bloomberg: The WHO’s Top Covid Expert Warns of Gaping Holes in Virus Fight https://buff.ly/43657mE
The coronavirus continues to evolve, and ICU admissions are increasing in three regions of the world, according to Maria Van Kerkhove of the WHO.
"Since October, there’s been a precipitous drop in the number of genetic sequences generated and shared publicly, blinding scientists to the evolution of the Covid-causing virus, especially in animals, she says."
Vaccine inequity is another barrier.
Not enough is known about the risks of reinfection.
Persistent health problems in people with Long COVID also discussed.
5/22/23 Lancet: No time for complacency on COVID-19 in Europe https://buff.ly/45reEWS
COVID is still causing outbreaks. There are people still being hospitalized and dying from COVID. Long COVID affects 3 to 20% of those infected.
"We thus question the current high level of political and societal complacency towards COVID-19 in Europe. Much more strategic attention and investments are needed now to more effectively manage COVID-19 and develop greater resilience to future respiratory pathogens."
5/22/23 Frontiers Microbiology: Viable SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sub-variants isolated from autopsy tissues https://buff.ly/45sfL8L
n = 21 cadaveric donors with documented first infection or reinfection at the time of death.
These findings highlight that SARS-CoV-2 can spread to multiple tissue locations such as the lungs, heart, liver, kidneys, and intestines, both after primary infection and after reinfections with the Omicron variant.
5/22/23 PNAS: Apple-shaped obesity: A risky soil for cytokine-accelerated severity in COVID-19 https://buff.ly/3MVVOQy
Abdominal obesity increases the risk of cytokine storm and death in patients with COVID-19.
5/22/23 China’s New Covid Wave Set to See 65 Million Cases a Week - Bloomberg https://buff.ly/3Oy31aP
China is likely to see its Covid-19 wave peaking at about 65 million infections a week toward the end of June. Infections set to rise as immunity from previous illness wanes.
China plans to roll out vaccines that target XBB strain.
Still, this is from December and January when a different omicron sublineage infected 37 million people every day in China.
4/12/23 Brain Connections: Neural dysregulation in post-COVID fatigue https://buff.ly/3WzefO9
n = 37 with Long COVID fatigue compared to n = 57 controls
Testing showed underactivity in specific cortical circuits, dysregulation of autonomic function and myopathic change in skeletal muscle.
Analysis excluded dysregulation in sensory feedback circuits and descending neuromodulatory control.