COVID news and more 5/20/23
This week we are seeing a sort of variant soup again with many different subvariants putting pressure on XBB.1.5, but none that are strong enough to push XBB.1.5 out of first place by itself. This is good news. Variant testing will now be reported by the CDC every two weeks. Hospitalizations and ER visits are both low for COVID and wastewater levels of the SARS-CoV-2 virus are low across the United States. In the Bay Area, wastewater virus levels are reassuring, except for a small blip upwards seen in Gilroy and in West San Francisco. I expect those to go down by next week, but we will watch them closely.
According to the WHO, worldwide COVID cases are down with the exception of a few hotspots in parts of Southeast Asia and the western Pacific. There was an Op Ed in the Annals of Internal Medicine stating that for patient safety, it is not time to remove masks in healthcare settings. I agree. People who are sick do not need to get a COVID infection when they go to their doctor's office. There was an interesting piece this week about a photographer named Megan Doherty who won a grant from Getty images and Verizon to shine a light on disabled people. She is doing a photo essay on how the lack of masking indoors is pushing immunocompromised people out of society and public life.
Acute COVID infection
In Nature, this week, an analysis of DNA from more than 24,000 people who had critical cases of COVID requiring intensive care shows 49 genetic variants that underlie severe COVID infections. Among these, there are 16 newly discovered gene associations. Some of these genes are related to inflammation and immune signaling which could be potential drug targets in the future.
We know from more than 12 studies that a COVID infection can increase one’s risk of both Type I and Type II diabetes in the year after infection. Non-diabetic people who have acute COVID infections can also have hyperglycemia. Until now the mechanism was unknown, but it appears that the SARS-CoV-2 infects hepatocytes which then causes stimulation of gluconeogenesis in liver cells to produce glucose.
Most SARS-CoV-2 variants are now resistant to monoclonal antibodies that target the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. However, researchers at Rockefeller University discovered six new monoclonal antibodies that target the part of the ACE2 receptor where SARS-CoV-2 binds. By blocking the receptor binding site instead of blocking the virus’ spike protein, these six monoclonal antibodies are able to prevent all current and possibly all future SARS-CoV-2 variants all while allowing normal ACE2 enzyme activity to continue. These studies were done in mice and will need to be repeated in humans, but these monoclonal antibodies have great potential as a prophylactic medication to protect immunocompromised from SARS-CoV-2 infections.
An article in Time magazine discussed how anti-vaccine doctors such as the American Frontline doctors (AFLD), and the Frontline COVID Critical Care Alliance (FLCCCR) are peddling treatments that have been proven ineffective against COVID infections in order to make money. One of the groups sold $8.5 million worth of ivermectin and hydroxychloroquine to vulnerable people over a 10 month period in 2021.
Long COVID
The AAPM&R released new consensus guidelines on the assessment and treatment of neurologic sequelae in people with long COVID. The most common neurologic symptoms are brain fog, headache, numbness and tingling, loss of taste, loss of smell and muscle aches. The AAPM&R has other consensus guidelines for Long COVID on their website including guidance on pediatric Long COVID, autonomic dysfunction, cardiovascular symptoms, cognitive Long COVID symptoms, guidance on breathing discomfort and fatigue related to Long COVID.
Regarding mental health, over 5000 people with long COVID were compared to 475 without long COVID and the majority (57%) of those with long COVID did not experience psychiatric disease. Overall, people with long COVID were found to have increased risk for depression, anxiety and suicidality, but risks were consistent with other chronic debilitating illnesses such as cancer or asthma. The authors noted that immune and inflammatory aspects of long COVID may affect the risk of psychiatric disorders, but the long COVID group was found to use adaptive coping methods well. Most people felt that joining an online, well curated support group had a positive impact on their psychological well-being.
High immunoglobulin A (IgA) during acute COVID infection may be a biomarker for predicting who will get Long COVID, especially in adults and elderly groups. Rutgers University will be recruiting 2000 children to study SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in kids with Long COVID compared to those without. The WHO had a feature on a 12-year-old boy named Jay who has long COVID and is unable to walk and is housebound to show some of the extreme consequences of long COVID in children.
NPR interviewed scientists who are looking at microclots found in the blood of people with long COVID. These microclots are unusual in that they are made up mostly of an abnormal type of fibrin and form unusual shapes called amyloid. These fibrin amyloid microclots may be a biomarker for long COVID. Another group had an article on microclots and long COVID. They suggest the term “spike protein induced thrombotic vasculitis” (SITV) to describe the pathophysiology of long COVID clotting.
This week, I included some survey results from pharmacist and citizen scientist @LongCOVIDPharmD who has sent out surveys to people with long COVID and those with MECFS to see what treatments have been working for them. While I acknowledge that there can be significant bias in such surveys, the findings are interesting. She reviewed her survey results for IVIG in MECFS and proteolytic enzymes like Nattokinase in Long COVID.
In non-COVID news, a new medication was approved to treat menopausal hot flashes without hormones. It targets brain connections that help control body temperature. A rare gene was discovered that protected a person against early onset Alzheimer’s disease, despite an extremely elevated amyloid plaque burden and Tau tangles in the brain. This finding may help with future treatments for Alzheimer’s disease. Regarding Multiple Sclerosis, the mechanism of how the EBV virus can trigger Multiple Sclerosis was discovered. It turns out that an EBV antigen has identical areas to a CNS protein. The B cells and T cells immune response to EBV can cross react and target CNS proteins which leads to inflammation in the central nervous system and Multiple Sclerosis.
The FDA cleared a new treatment known as Stanford Neuromodulation Therapy (SNT) which uses MRI guided brain stimulation to treat depression by reversing brain signals traveling in the wrong direction. Finally, the first oral drug was approved for Crohn’s disease this week. It’s called Rinvoq.
Have a good weekend,
Ruth Ann Crystal MD
Other news:
5/15/23 AP: New menopause drug for hot flashes gets FDA approval https://buff.ly/3BvSNA1
Pharma Astellas’ drug, Veozah, uses a new approach, targeting brain connections that help control body temperature.
Veozah is taken once daily to treat moderate-to-severe symptoms, which can include sweating, flushing and chills.
5/15/23 Nature: Resilience to autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease in a Reelin-COLBOS heterozygous man https://buff.ly/42IvZci
Carriers of the PSEN1-E280A mutation develop mild cognitive impairment (MCI) by the age of 44 years and dementia by 49 years.
This is the second known case of a person with the familial autosomal dominant Alzheimer gene (PSEN1-E280A) who should have gotten early Alzheimer’s disease, but did not because of a rare gene that protected against early dementia, despite an extremely elevated amyloid plaque burden and limited entorhinal Tau tangle burden.
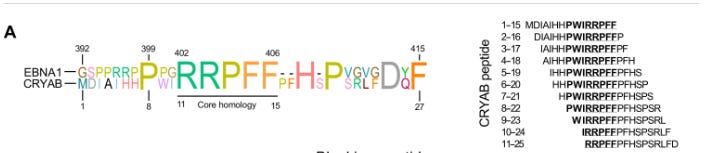
5/17/23 Science: Cross-reactive EBNA1 immunity targets alpha-crystallin B and is associated with multiple sclerosis (MS) https://buff.ly/3Mg5mnX
n = 713 people with MS, n = 722 controls
How does EBV cause MS? Molecular mimicry.
There is homology between Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 (EBNA1) and alpha-crystallin B (CRYAB).
EBV-induced immune responses (B cells and T cells) cross-target CNS proteins that contain epitopes with a similar amino acid sequence.
This causes inflammation in the central nervous system and leads to MS.
5/15/23 Stanford Med News: Researchers treat depression by reversing brain signals traveling the wrong way https://buff.ly/41QRbLY
The FDA-cleared treatment, known as Stanford Neuromodulation Therapy (SNT), uses imaging to guide brain stimulation with high-dose patterns of magnetic pulses that can modify brain activity related to major depression.
Compared with traditional TMS, which requires daily sessions over several weeks or months, SNT works on an accelerated timeline of 10 sessions each day for just five days.
5/18/23 MedCity News: AbbVie’s Rinvoq Lands FDA Approval as First Oral Drug for Crohn’s Disease https://buff.ly/3IviJQ3
COVID news:
5/18/23 WHO Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19 https://buff.ly/3Wkg5SV
Overall cases and deaths continued to decline over the past 4 weeks, but hot spots continue in two regions: Southeast Asia and the Western Pacific.
Deaths were also up in Southeast Asia.
In the Southeast Asia region, cases continue to spike in Thailand, Indonesia, and India.
In the Western Pacific, COVID activity continues upward trends in Vietnam, the Philippines, Mongolia, and, to a lesser extent, Japan, South Korea, and Australia.
The WHO said cases are stable in Africa, but some countries reported spikes, including the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Cabo Verde, Uganda, and Mauritius.
US Variant tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions
This will now be tracked every 2 weeks.
CDC COVID data tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/index.html#datatracker-home
CDC COVID Hospitalizations (blue) and Emergency Room (orange) visits tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/index.html#trends_weeklyhospitaladmissions_7dayeddiagnosed_00
US Wastewater Monitoring:
CDC Wastewater Monitor https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#wastewater-surveillance
Biobot: https://biobot.io/data/
Sewer Coronavirus Alert Network (SCAN) project by Stanford University:
Overall, wastewater virus levels are reassuring in most of the Bay Area.
Slight increase this week in Gilroy and in San Francisco (Oceanside) will need to be watched.
5/19/23 Chicago Tribune: People with disabilities use art to ask for representation https://buff.ly/41UjCZp
Photographs shine a light on how a lack of masking is pushing immunocompromised people out of the public sphere.
Doherty’s work is funded by a $15,000 grant from Getty Images and Verizon, an endeavor aimed at closing the representation gap when it comes to disability stories and voices.
Megan Doherty “envisions the portraits being viewed in an outdoor setting, forcing a confrontation between people who are disabled and segregated from public life and non-disabled people who are unwittingly participating in making that a reality.”
5/18/23 CIDRAP: WHO advisers recommend switch to monovalent XBB COVID vaccine https://buff.ly/3pUBmXi
The World Health Organization (WHO) COVID vaccine composition advisory group recommended that vaccine makers drop the ancestral strain and switch to a monovalent (single-strain) vaccine that contains an XBB.1 descendant lineage such as XBB.1.5.
Preclinical data on XBB.1 candidate vaccines, shared confidentially by vaccine makers, showed a higher neutralizing antibody response to current subvariants compared with currently approved vaccines.
The original virus no longer circulates in people, it prompts—at best—very low levels of antibodies against current strains, it reduces the concentration of the new target antigen, and it may induce immune imprinting.
5/18/23 MedPage Today: Physical Medicine Academy (AAPM&R) Issues Guidance on Long COVID Neurologic Symptoms https://buff.ly/3oiEdss
Neurologic symptoms related to PASC -- commonly known as long COVID -- include headache, weakness, muscular numbness, pain, tremors, and palsy.
Clinicians should pursue appropriate diagnostic workup and collaborate with multidisciplinary clinical teams to address specific neurologic symptoms for long COVID patients, while aiming to reduce polypharmacy and avoiding a rapid escalation of activities that might trigger symptom worsening, the authors said in this paper:
PM&R: Multidisciplinary collaborative consensus guidance statement on the assessment and treatment of Neurologic Sequelae in patients with post‐acute sequelae of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection (PASC, Long COVID) https://buff.ly/459G5EI
The most prevalent PASC neurologic symptoms that remain after 3–4 weeks from the initial infection include “brain fog” (81%), headache (68%), numbness/tingling (60%), dysgeusia (59%), anosmia (55%), and myalgias (55%).
The AAPM&R Multi-Disciplinary PASC Collaborative (PASC Collaborative), consisting of experts in PM&R, neurology, internal medicine, family practice, pediatric specialties, cardiology, physical therapy, occupational therapy, social work among other disciplines, was convened to address the pressing need for guidance in the care of patients with PASC.
Neuro PASC topics:
TABLE 1. Initial evaluation of neurologic sequelae in patients with PASC.
TABLE 2. Initial treatment options for patients with neurologic sequelae of PASC.
TABLE 3. Neurologic red flags.
TABLE 4. Signs, symptoms, and care guidance: cranial nerves.
COMMON NEUROLOGIC SEQUELAE AND HOW TO BEST GUIDE CARE
Cranial nerve symptoms
Headaches
TABLE 5. Warning signals to raise suspicion of secondary causes of headache using the mnemonic SNOOP4
TABLE 7. Sleep disturbances.
TABLE 8. Health equity considerations and examples in PASC: neurologic sequelae.
TABLE 9. Neuropathy/neuropathic pain.
TABLE 10. Muscular pain, muscle weakness, tremor.
Consensus Guidelines from AAPM&R for PASC or Long COVID https://buff.ly/3BF8oxG
Neurological Long COVID Symptoms Guidance Statement
Pediatrics Long COVID Guidance Statement
Autonomic Dysfunction Guidance Statement
Cardiovascular Long COVID Complications Guidance Statement
Cognitive Long COVID Symptoms Guidance Statement
5/18/23 Research Square: Long COVID is primarily a Spike protein Induced Thrombotic Vasculitis (SITV), review of data and a case report https://buff.ly/3Irw8su
"Spike protein Induced Thrombotic Vasculitis" (SITV) describes the
pathophysiology of Long COVID presentations, and helps focus attention on early therapeutic intervention targeting microclots, hyperactive platelets, and endotheliitis.
This multifaceted coagulopathy requires synergistic polypharmacy to achieve symptomatic resolution, as described in our case report.
Thromboelastography can be utilised to mitigate bleeding risk.
5/18/23 Healio: Additional COVID-19 vaccine doses may ‘bully’ response in immunosuppressed patients https://buff.ly/45e1gWa
Patients receiving B-cell depleting therapies will demonstrate the weakest antibody response, followed by those on mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), glucocorticoids, Janus kinase inhibitors, then TNF inhibitors.
The key for B-cell depleting therapies is the timing of the dose, according to Kim.
“Those vaccinated within 6 months of the last dose of B-cell depleting therapy mount a poor response,” he said. “Those vaccinated more than 6 months out did much better.” said Alfred Kim, MD, PhD
5/18/23 Healio: Hearts from donors with COVID-19 at time of death may confer worse survival for recipients https://buff.ly/3Mh8b8s
5/17/23 NJ Bus Magazine: Rutgers to Provide Antibody Testing to Help Study Long COVID in Children https://buff.ly/3MhDHmu
Rutgers’ participation in RECOVER through the Collaborative study of Long-term Outcomes of COVID in Kids (CLOCK) team which plans to recruit more than 2,000 children for the RECOVER initiative.
SARS-CoV-2 antibodies will be studied in depth and will be compared to kids without Long COVID.
5/17/23 Nature: GWAS and meta-analysis identifies 49 genetic variants underlying critical COVID-19 https://buff.ly/3OkfPRY
24,202 cases of critical COVID cases using meta-analysis of the new GenOMICC genome-wide association study (GWAS) results..
49 genome-wide significant associations, of which 16 have not been reported previously, were found to be associated with critical COVID acute infection.
Potential drug targets identified in multiple systems, including inflammatory signaling (JAK1), monocyte–macrophage activation and endothelial permeability (PDE4A), immunometabolism (SLC2A5 and AK5), and host factors required for viral entry and replication (TMPRSS2 and RAB2A).
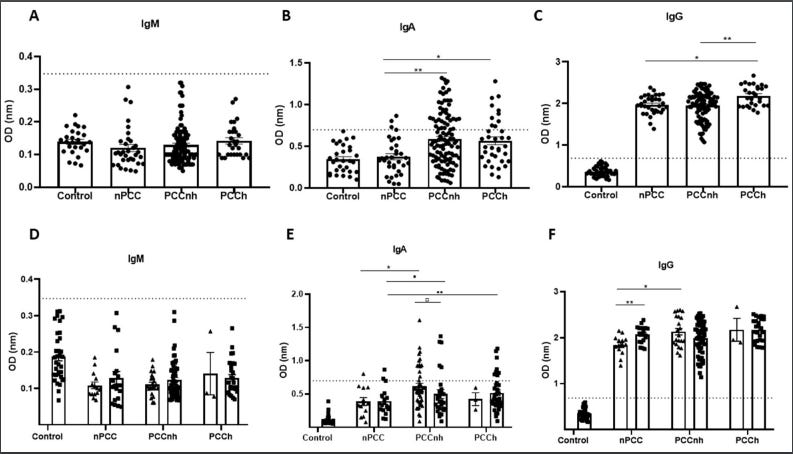
5/16/23 MedRxiV: Immunoglobulin A (IgA) as a key immunological molecular signature of post-COVID-19 conditions (PCC, PASC, Long COVID) https://buff.ly/455CDuI
Non-hospitalized and hospitalized PCC patients produced similar high levels of IgA.
The detection of IgA antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 may be an immunological signature to predict Long COVID, especially in adult and elderly groups.
________
UNREST Documentary https://buff.ly/434ss7K
The story: Jennifer Brea is working on her PhD at Harvard and about to marry the love of her life when she’s struck down by a mysterious fever that leaves her bedridden. When doctors tell her “it’s all in her head,” she turns her camera on herself to document her devastating symptoms. Searching for answers, Jennifer discovers a hidden world of millions confined to their homes and bedrooms by ME/CFS, commonly known as myalgic encephalomyelitis/ chronic fatigue syndrome. Together, Jen and her new husband, Omar, must find a way to build a life and fight for a cure.
5/16/23 Annals of Internal Medicine: For Patient Safety, It Is Not Time to Take Off Masks in Health Care Settings https://buff.ly/3Bysnxw
5/16/23 Nature (Sato lab): Virological characteristics of the SARS-CoV-2 XBB variant derived from recombination of two Omicron subvariants https://buff.ly/3BGikqd
XBB is the first observed SARS-CoV-2 variant to increase its fitness through recombination rather than substitutions.
5/16/23 PNAS: COVID-19-related hyperglycemia is associated with infection of hepatocytes and stimulation of gluconeogenesis https://buff.ly/3Wabl26
COVID-19 can lead to high glucose levels even in people without diabetes.
SARS-CoV-2 is capable of infecting and replicating in hepatocytes (liver cells) which stimulates these cells to produce glucose through gluconeogenesis.
SARS-CoV-2’s enters hepatocytes via cooperation between GRP78 and ACE2 cotransporters.
____
FYI- conference on ME/CFS:
International Association for Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (IACFS/ME) 2023 Medical and Scientific Conference https://buff.ly/3Ihf6x5
July 27 - 29, 2023
9 AM - 5 PM EDT
Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, New York, USA
5/15/23 NPR: Long COVID scientists try to unravel blood clot mystery https://buff.ly/3I8Qg2b
The clots caused by Long COVID are unique:
"They're not the typical micro clots that we see with those other disease ... they're made up almost fully of abnormal type of fibrin, which is the protein and blood that forms the blood clot and creates these unusual structures that are called amyloid," Dr. Roy Silverstein says.
These fibrin amyloid microclots may be a biomarker for Long COVID.
"It shouldn't have to be like this, right? Like, it should be the case that millions of dollars are designated for finding a biomarker or identifying and creating a test or both." says Hannah Davis, a co-founder and lead researcher of the Patient Led Research Collaborative, who has had Long COVID since March 2020.
5/15/23 Nature (Rockefeller Univ): Pan-sarbecovirus prophylaxis with human anti-ACE2 monoclonal antibodies https://buff.ly/3MapRSO
SARS-CoV-2 variants are now mostly resistant to monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to the spike protein.
6 new mAbs that target an epitope on the ACE2 receptor where the SARS-CoV-2 usually binds, can block all current or future SARS-CoV-2 variants.
These mAbs do not inhibit hACE2 enzymatic activity nor do they induce cell-surface depletion of hACE2.
Great potential for protecting immunocompromised people prophylactically against SARS-CoV-2.
5/10/23 Nature Mental Health: Factors associated with psychiatric outcomes and coping in Long COVID (LC) https://buff.ly/42GMTIk
5,638 LC respondents and 475 non-LC
LC is not a psychosomatic disease.
The majority (57%) of those with LC do not experience psychiatric disease.
People with LC are at increased risk for psychiatric disease compared to those who did not develop LC after acute COVID infection, consistent with the high rates of psychiatric comorbidity in other chronic debilitating medical conditions such as cancer or asthma.
Psychiatric outcomes (depression, anxiety, suicidality) in LC are associated with:
Younger age,
Those who are sicker, have more LC symptoms, and are physically more limited by LC
lower income and loss of income, financial pressure, employment impacted by illness
History of psychiatric illness
Male sex, men and non-binary gender, and
Negative experiences with support systems (medical professionals, family, friends, partners and employers)
People with LC may be at higher risk than people without LC due to dealing with chronic illness as well as direct and indirect biological effects of the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Immune and inflammatory aspects of LC may increase psychiatric risk.
Overall the LC group used more adaptive coping, reinforcing that LC is not in itself an illness defined by presence of these psychiatric symptoms nor maladaptive coping.
Screening tools that rely heavily on somatic markers of psychiatric illness, such as fatigue or tachycardia, are likely to overrepresent the burden of psychiatric illness in this population.
70% of participants who joined an online COVID support group found that the group had a positive impact on their psychological well being, especially if led by peers and well moderated.
53% of the participants reported a negative experience with medical providers.
12–26% reported negative experiences with friends, partners, family and employers.
Suicidality was higher in LC patients than people who recovered completely from COVID, but were similar to the higher rates of suicidality in chronic illnesses.
Risk factors for suicidality:
male and non-binary patients
patients under age 30
patients who reported they did not receive adequate medical care
patients who had more severe symptoms.
5/15/23 WHO news: Unable to walk and housebound at the age of 12 – the extreme consequences of long COVID https://buff.ly/3pWcrTd
Discusses 12 year old Jay's initial COVID infection, Long COVID diagnosis, trying to find treatments, relapse after reinfection, losing mobility and need to use a walker.
It also talks about how Jay's Long COVID affects the whole family, and the shadow pandemic of people with PASC.
The UK’s Office of National Statistics estimates that 1.9 million people (2.9% of the country's population) have self-reported long COVID symptoms as of 5 March 2023.
5/15/23 TIME magazine: How Right-Wing Doctors Who Peddled Dubious COVID Drugs Got Away With It https://buff.ly/3Mrgr72
America’s Frontline Doctors (AFLD), an anti-vaccine group founded by Dr. Simone Gold.
Ravkoo, the online pharmacy that AFLD partnered with, sold $8.5 million worth of dubious treatments (ivermectin, hydroxychloroquine) for COVID over 10 months alone in 2021.
Dr. Pierre Kory, of the Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance (FLCCC), a network of doctors promoting alternative COVID treatments, charges $1,650 for an appointment with him for “post-vaccine syndrome” or other issues.
Surveys of people with ME/CFS and/or Long COVID. I acknowledge that there can be bias in such surveys and small numbers of participants in some of the questions.
5/4/23 LONGCOVIDPHARMD: TREAT ME SURVEY RESULTS, #2 https://buff.ly/41J9KkV
Immunoglobulin (IVIG, SCIG) in ME/CFS
Sample size for Long COVID was too small to include.
5/4/23 LongCovidPharmD: TREAT ME Survey: Individual Treatment Results https://buff.ly/3BtqVfQ
Patient survey on Proteolytic Enzymes (Nattokinase, Lumbrokinase, Serrapeptase) for people with ME/CFS and Long COVID.