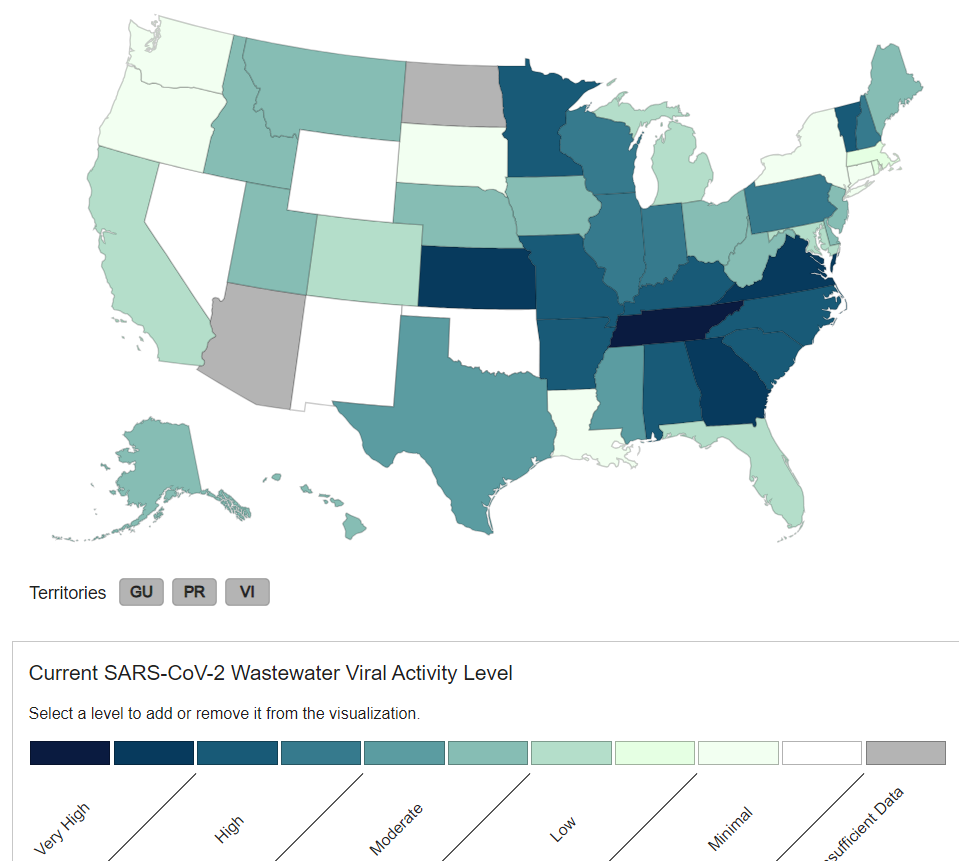
JP Weiland estimates from wastewater viral levels that we are down to about 520,000 new COVID infections each day in the United States with 1 in every 64 people currently infected. This is less than half the number of cases that we were seeing in January. Wastewater SARS-CoV-2 levels are down to “MODERATE” levels and hospitalizations and deaths from COVID have decreased significantly. According to Sara Anne Willette, Virginia has extremely high levels of SARS-CoV-2 in their wastewater now, followed by very high levels found in Mississippi and Delaware.
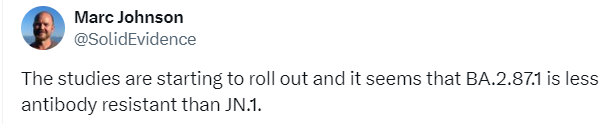
JN.1 and its descendants are the main variants causing COVID infections at this time. New variant BA.2.87 was initially seen in South Africa and now has been found in Asia. But, Yunlong Cao’s lab showed that BA.2.87.1 can be neutralized by antibodies meaning that BA.2.87.1 will not significantly spread unless it acquires new mutations. For now, we are in a better place.
As discussed last week, on March 1st, the CDC recommended that COVID positive people can return to work or school if they do not have a fever and their symptoms are improving. The CDC’s logic was that we should treat COVID like other respiratory infections including the flu and RSV. But, COVID is not only a respiratory disease- it is a multi-organ infection that also has many long term consequences.
Eric Topol posted the CDC’s own data showing that 1 in 3 people with a COVID infection will still be contagious at day 5. He said, “By not strongly recommending rapid antigen tests, the CDC's new (1 March) policy is ignoring their own data!” Noha Aboelata MD added “Enough to detect is enough to infect!” If someone is COVID positive on rapid antigen test, they should isolate until they are negative or they will infect others.
From: https://twitter.com/EricTopol/status/1766165649368514680
A new study estimated that using non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) such as masks or school and business closures for large outbreaks prevented 831,000 COVID related deaths in the United States.
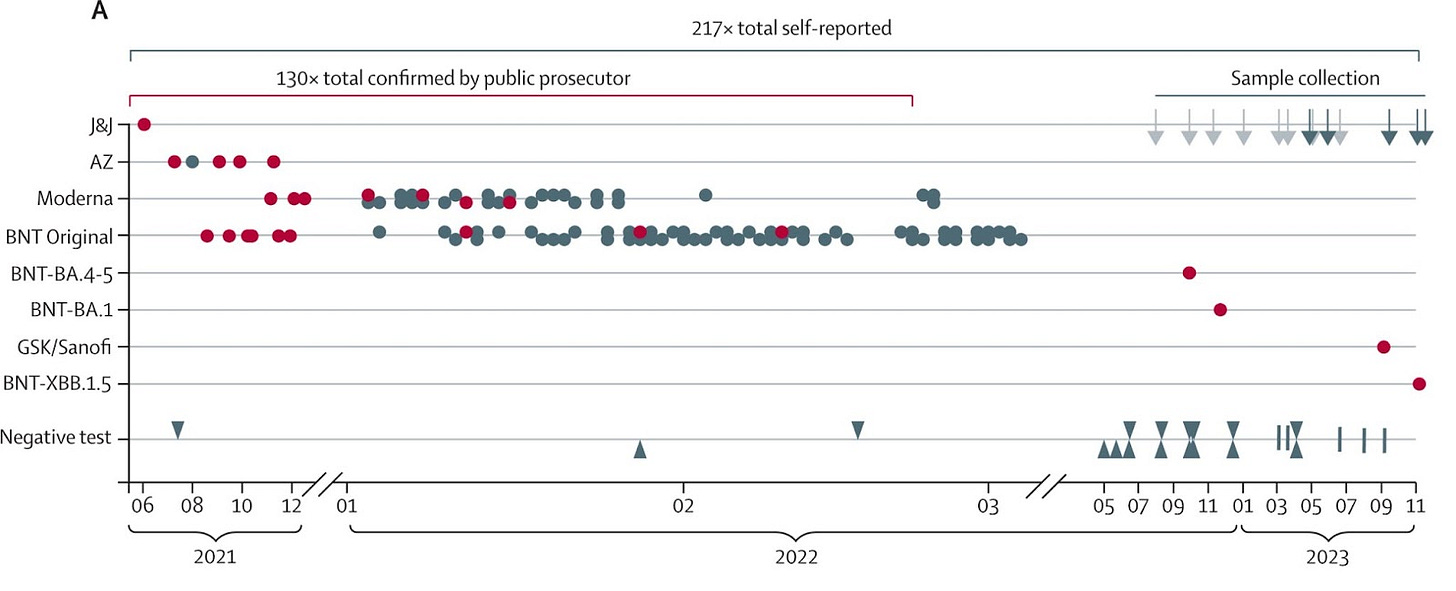
Over several years, a man in Germany received 217 COVID vaccines including the J&J vaccine, Pfizer and Moderna mRNA vaccines, the AstraZeneca vaccine and the GSK/Sanofi COVID vaccine. Sometimes, chronic antigen exposure can cause immune tolerance. But in this case, hypervaccination was found to increase the quantity of antibodies and T cells to SARS-CoV-2, without affecting the quality of the adaptive immune response. SARS-CoV-2 hypervaccination did not lead to any adverse events in this man and he never got a COVID infection.
Long COVID
Dr. Michael Peluso reported at a conference this week that fragments of the SARS-2 spike protein were found in the blood up to 14 months after infection in 171 people tested. People were more likely to have SARS-CoV-2 fragments if they had been hospitalized with COVID infection or if they felt very ill with their acute COVID infection.
In a second unpublished study, UCSF researchers including Dr. Peluso found that SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA can be found in tissues up to two years after infection. The viral RNA was found "in the connective tissue where immune cells are located, suggesting that the viral fragments were causing the immune system to attack. In some of the samples, the researchers found that the virus could be active." Both of these studies reinforce the theory that viral persistence may be causing long term consequences such as Long COVID and/or chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke and diabetes.
Sometimes during bacterial infections, cytokines tell the body to move iron out of the blood and into storage in some white blood cells so that the bacteria cannot use the iron themselves. This can lead to “anemia of inflammation”. A new study shows that people who went on to get Long COVID (PASC) were found to have anemia and lower red blood cell production two weeks after their acute COVID infection. They were also found to have iron loading in their monocytes and increased iron demand in white blood cells called lymphocytes. The authors concluded that “defects in iron homeostasis, dysregulated erythropoiesis and immune dysfunction due to COVID-19 possibly contribute to inefficient oxygen transport, inflammatory disequilibrium and persisting symptomatology,” and may be treatable.
A large new study looked at 10 million Korean and 12 million Japanese patients aged 20 years and older who had a COVID-19 infection between January 2020 to December 2021. They found that people who had a COVID infection were 25% to 30% more likely to have new autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases (AIRDs) such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and scleroderma, than flu patients or uninfected controls. The risk normalized one year after the COVID infection. COVID vaccination protected against AIRD by about 50%.
Another study this week shows that mild to moderate COVID infections can hurt our brains. Comparing brain MRIs of 25 young people (mean age 30) with mild to moderate acute COVID to 24 non-infected controls, researchers found that 80% of the COVID group had an accelerated brain age gap. 'Individuals with a history of COVID-19 infection demonstrated a 2.65-year accelerated brain age gap compared to the control group. Survivors had poorer performance on an objective measure of attention, processing speed, and executive function.'
Drs. Guan, Putrino and Iwasaki shared an important new paper about sex differences in symptomatology and immune profiles of Long COVID (LC). People with LC were found to have a relative deficiency in non-dominant sex hormones (low testosterone in females and low estradiol in males) which combined with the lower cortisol levels, but normal ACTH levels, suggests dysregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
The hypothalamus is a region in the brain that controls homeostasis, or systems balance, of the body. It works with the autonomic nervous system to help regulate heart rate, breathing and digestion. For the HPG axis, the hypothalamus secretes gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) which tells the anterior pituitary to make luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). The LH and FSH tell the ovary and the testes (gonads) to make estrogen and testosterone.
For the HPA axis, the hypothalamus secretes corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) which tells the anterior pituitary to make adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which then tells the adrenal glands to make cortisol. Cortisol is a stress hormone that helps regulate metabolism and immune responses.
Next Friday March 15th is Long COVID Awareness Day. The team from CureID is working with Long COVID patient groups to try to enroll 1,000 people with Long COVID on the CureID website by March 15 to answer a survey about which treatments helped and which supplements or medications were harmful to people with Long COVID. The goal is to aggregate all of the findings so that the helpful treatments can be tested in clinical trials. If you know anyone with Long COVID, please invite them to participate.
In non-COVID news, in asymptomatic patients undergoing a procedure to remove atherosclerotic plaque in their carotid arteries, 58% were found to have microplastics in the plaque. Patients who had micro and nano plastic (MNP) in the artery plaque were found to have a 4.5x increased risk for heart attack, stroke, or death from any cause at 34 months of follow-up as compared to those in whom MNPs were not detected. Eric Topol and E. Muse wrote a review in Cell on using multimodal AI to prevent and manage cardiometabolic diseases.
This week, France became the first country to guarantee abortion as a constitutional right. After 3 consecutive years of Spring Break chaos and violence, the city of Miami is implementing strict security measures and posted this PSA to try to cancel Spring Break. An anonymous donor gave $40 million to Yellowstone National Park for affordable employee housing for the 3,000 people who work in the park during peak tourist season. Monoclonal antibody Beyfortus was 90% effective in preventing RSV hospitalizations for babies this RSV season.
Have a good rest of your weekend,
Ruth Ann Crystal MD
COVID news notes:
US Variant tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions
Variants in locations around the globe:
https://outbreak.info/
CDC COVID data tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/index.html#datatracker-home
CDC COVID Hospitalizations (blue) and Emergency Room (orange) visits tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/index.html#trends_weeklyhospitaladmissions_7dayeddiagnosed_00
Weekly ED visits for respiratory illnesses, by age and disease: https://www.cdc.gov/ncird/surveillance/respiratory-illnesses/index.html
Walgreens positivity rate: https://www.walgreens.com/businesssolutions/covid-19-index.jsp
US Wastewater Monitoring:
CDC wastewater reporting: https://www.cdc.gov/nwss/rv/COVID19-nationaltrend.html
CDC wastewater map: https://www.cdc.gov/nwss/rv/COVID19-currentlevels.html
Biobot: https://biobot.io/data/
National SARS-CoV-2 data from Sara Anne Willette: https://iowacovid19tracker.org/
Excessive: Virginia
Very High: Mississippi, Delaware
Wastewater SCAN: https://data.wastewaterscan.org/
California statewide view https://buff.ly/3YObiul
Sewer Coronavirus Alert Network (SCAN) project by Stanford University:
Santa Clara County wastewater: https://covid19.sccgov.org/dashboard-wastewater
CDC Respiratory vaccination trends: https://www.cdc.gov/respiratory-viruses/data-research/dashboard/vaccination-trends-adults.html
JP Weiland: https://twitter.com/JPWeiland
https://twitter.com/JPWeiland/status/1766194632768077937
Michael Hoerger modeling: http://pmc19.com/data/
Variants
3/8/24 BioRxiV (Yunlong Cao): Antigenicity assessment of SARS-CoV-2 saltation variant BA.2.87.1 https://buff.ly/3VcdDiS
“BA.2.87.1 may not become widespread until it acquires multiple RBD mutations to achieve sufficient immune evasion comparable to that of JN.1.”
https://twitter.com/SolidEvidence/status/1765852426245144831
Acute COVID infections, General COVID info
https://twitter.com/NohaAboelataMD/status/1766514199235043641
https://twitter.com/EricTopol/status/1766165649368514680
https://twitter.com/EricTopol/status/1766185656974524871
“By not strongly recommending rapid antigen tests, the CDC's new (1 March) policy is ignoring their own data!”
3/7/24 MedRxiV: Estimating the impact of public health interventions on COVID mortality in the United States using reductions in influenza mortality as an indicator of non-pharmaceutical infection control https://buff.ly/48NDyR7
Non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) for control of COVID include a range of methods from masks to closures of schools and businesses.
NPIs prevented 831,000 COVID related deaths in the United States over the course of the pandemic.
Vaccines
3/4/24 Lancet (Germany): Adaptive immune responses are larger and functionally preserved in a hypervaccinated individual https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(24)00134-8/fulltext#%20
A man from Germany got vaccinated against COVID 217 times. Sometimes, chronic antigen exposure can cause immune tolerance. But in this case, hypervaccination was found to increase the quantity of antibodies and T cells to SARS-CoV-2, but did not affect the quality of the adaptive immune response as compared to controls who had received the normal 3 doses of vaccine.
“our case report shows that SARS-CoV-2 hypervaccination did not lead to adverse events and increased the quantity of spike-specific antibodies and T cells without having a strong positive or negative effect on the intrinsic quality of adaptive immune responses. While we found no signs of SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections in HIM to date, it cannot be clarified whether this is causally related to the hypervaccination regimen. Importantly, we do not endorse hypervaccination as a strategy to enhance adaptive immunity.”
217 self reported vaccinations, 134 were confirmed.
Long COVID
3/7/24 UCSF press release via EurekaAlert: COVID-19 virus can stay in the body more than a year after infection https://buff.ly/48Mlbfo
Fragments of the SARS-2 spike protein were found in the blood of 171 people tested up to 14 months after infection. People were more likely to have SARS-CoV-2 fragments if they had been hospitalized with COVID infection or if they felt very ill with their acute COVID infection.
In a second unpublished study, UCSF researchers including Dr. Peluso look at tissues collected in the found that SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA can be found in tissues up to two years after infection.
The viral RNA was found "in the connective tissue where immune cells are located, suggesting that the viral fragments were causing the immune system to attack. In some of the samples, the researchers found that the virus could be active."
3/7/24 MedicalXpress: COVID-19 virus can stay in the body more than a year after infection, research finds https://buff.ly/49HwS8w
The findings were presented at the Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI), which was held March 3 to 6, 2024, in Denver, Colorado.
"The scientists found pieces of SARS-CoV-2, referred to as COVID antigens, lingering in the blood up to 14 months after infection and for more than two years in tissue samples from people who had COVID."
People who were hospitalized for acute COVID infection or those who reported being sicker but who were not hospitalized were twice as likely to have COVID antigens found.
3/7/24 MedRxiV (UT Texas): Accelerated brain age in young to early middle-aged adults after mild to moderate COVID-19 infection https://buff.ly/4c81ukS
Brain MRI of 25 people with mild to moderate acute COVID compared to 24 non-infected controls.
80% of the COVID group had an accelerated Brain Age Gap (BAG) which is significantly correlated with lower cognitive function.
'Individuals with a history of COVID-19 infection demonstrated a 2.65-year accelerated brain age gap compared to the control group. Survivors had poorer performance on an objective measure of attention, processing speed, and executive function'
PRP injections to nose for treatment of loss of smell in Long COVID
https://twitter.com/SalvMattera/status/1765175389637443808
During bacterial infections, certain cytokines tell the body to move iron out of the blood and into storage in some white blood cells so that the bacteria cannot use the iron themselves. This can lead to anemia of inflammation. A new study shows that people who went on to get Long COVID (PASC) were found to have anemia and lower red blood cell production two weeks after their acute COVID infection. They were also found to have iron loading in their monocytes and increased iron demand in new white blood cells called lymphocytes. The authors concluded that “defects in iron homeostasis, dysregulated erythropoiesis and immune dysfunction due to COVID-19 possibly contribute to inefficient oxygen transport, inflammatory disequilibrium and persisting symptomatology,” and may be treatable.
Low iron levels at 2 weeks post infection could be a biomarker
3/1/24 Nature Immunology (Cambridge): Iron dysregulation and inflammatory stress erythropoiesis associates with long-term outcome of COVID-19 https://buff.ly/3PaTYfn
A multivariate signature detected beyond two weeks of disease, encompassing unresolving inflammation, anemia, low serum iron, altered iron-homeostasis gene expression and emerging stress erythropoiesis; differentiated those who reported PASC months later, irrespective of COVID-19 severity.
Monocyte iron loading and increased iron demand in proliferating lymphocytes.
Thus, defects in iron homeostasis, dysregulated erythropoiesis and immune dysfunction due to COVID-19 possibly contribute to inefficient oxygen transport, inflammatory disequilibrium and persisting symptomatology, and may be therapeutically tractable.
3/4/24 CIDRAP: Low iron may play key role in long COVID https://buff.ly/431UsdB
Patients who went on to develop long COVID showed more problems with regulation of blood iron levels, including anemia, as soon as 2 weeks after acute infection, suggesting low iron levels may play a role in the chronic condition, according to a new study in Nature Immunology.
Iron dysregulation is common after all infections, the authors explained, as iron is quickly moved out of the bloodstream to avoid becoming a trap for lethal bacteria.
A large new study looked at 10 million Korean and 12 million Japanese patients aged 20 years and older who had a COVID-19 infection between January 2020 to December 2021. They found that people who had a COVID infection were 25% to 30% more likely to have new autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases (AIRDs) than flu patients or uninfected controls. The risk decreased one year after the COVID infection. Vaccination protected against AIRD by about 50%.
3/5/24 Annals of Internal Medicine (S. Korea, Japan): Long-Term Autoimmune Inflammatory Rheumatic Outcomes of COVID-19: A Binational Cohort Study https://buff.ly/3P54sgn
higher incidence of diagnosis of autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases (AIRDs) among patients with a history of COVID-19 compared with uninfected patients.
SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with increased risk for incident AIRD compared with matched patients without SARS-CoV-2 infection or with influenza infection. The risk for incident AIRD was higher with greater severity of acute COVID-19.
3/5/24 CIDRAP: COVID tied to higher risk of inflammatory autoimmune diseases for 1 year https://buff.ly/3wAefVa
COVID-19 may increase the risk of autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases (AIRDs) for up to 1 year after infection, according to a two-country study published today in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
analyzed national claims databases from more than 10 million Korean and 12 million Japanese patients aged 20 years and older diagnosed as having COVID-19 from January 2020 to December 2021.
matched flu patients from the same period and uninfected controls
COVID-19 patients were at a 25% to 30% increased risk for new-onset AIRD after the first 30 days post-infection, compared with uninfected controls (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.25) and flu patients (aHR, 1.30).
After adjustment, the risks for all-cause AIRD, connective tissue disease, untreated AIRD, and treated AIRD were significantly higher after COVID-19 infection than those in uninfected or flu patients in both the Korean and Japanese cohorts.
The risk of new-onset, all-cause AIRD appeared to decline with time and fell off after 1 year.
3/4/24 MedRxiV (Guan, Putrino, Iwasaki): Sex differences in symptomatology and immune profiles of Long COVID https://buff.ly/3Ts2olc
n = 165 people with or without Long COVID (LC)
Females with LC had increased burden of symptoms and had increased frequencies of exhausted T cells, cytokine-secreting T cells, higher antibody reactivity to latent herpes viruses including EBV, HSV-2, and CMV, and lower testosterone levels than their control female counterparts.
Top distinguishing symptom in females was hair loss.
Low testosterone and, to some extent, cortisol predicted LC in females.
High growth hormone (GH) and high brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) predicted somewhat LC in females.
Low testosterone in females was associated with higher antibody reactivity to EBV, and CMV.
Less neurological and neurocognitive symptoms, fatigue and anxiety were seen in females with higher testosterone who partially reflected the immune signature seen in males.
Males with LC had decreased frequencies of monocyte and DC populations, elevated NK cells, and plasma cytokines including IL-8 and TGFβ-family members.
Top distinguishing LC symptom for males was sexual dysfunction.
Low estradiol in men (80% made from converting testosterone via aromatase in tissues) was predictive of LC in men.
Low testosterone in males was associated with higher reactivity to EBV and HHV6-b.
Individuals with LC suffered from a relative deficiency in non-dominant sex hormones and combined with the lower cortisol levels with normal ACTH , suggesting a possible dysregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis.
Testosterone levels may play a crucial role in maintaining the latency of herpesviruses and in turn to the predisposition to autoimmune conditions, such as SLE and MS.
https://twitter.com/VirusesImmunity/status/1764341540485259578
Overall, male LC immune signatures meant less symptoms in LC.
So what is driving the male LC immune signatures? Testosterone! Regardless of sex, those with higher testosterone levels had higher male LC immune signatures. Those with lower testosterone had higher female LC immune signatures. (12/)
To summarize, we find significant differences in symptoms and immune signatures in females vs. males with long COVID. (14/)
https://twitter.com/id_cure/status/1762141768621903878
https://www.theatlantic.com/health/archive/2024/02/covid-anniversary-flu-isolation-cdc/677588/
https://twitter.com/NationalNurses/status/1765496267239502082
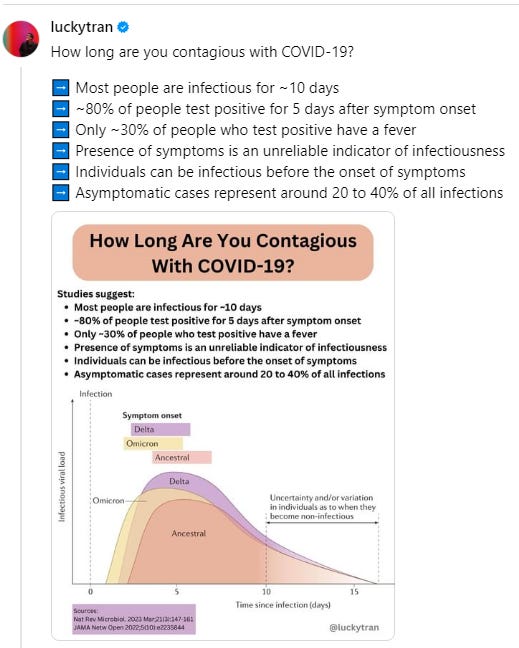
Lucky Tran Threads 3/2/24 https://www.threads.net/@luckytran/post/C4B_7VauFEk?hl=en
AI:
2/29/24 Cell Metabolism (E Muse, E Topol): Transforming the cardiometabolic disease landscape: Multimodal AI-powered approaches in prevention and management https://buff.ly/3wEOUcO
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1550413124000482?dgcid=author
Review on multimodal AI for better prevention and treatment of cardiometabolic diseases.
Other news:
3/7/24 STAT News: RSV monoclonal Beyfortus was 90% effective at preventing hospitalizations in children this winter: CDC https://buff.ly/3Vax3EP
3/5/24 AP: France becomes the only country to explicitly guarantee abortion as a constitutional right https://buff.ly/3TsAIwE
3/7/24 NEJM: Microplastics and Nanoplastics in Atheromas and Cardiovascular Events https://buff.ly/3VaGALW
Patients with carotid artery plaque in which MNPs were detected had a higher risk of a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, or death from any cause at 34 months of follow-up than those in whom MNPs were not detected.
3/6/24 Eric Topol: There's Plastic in My Plaque! https://buff.ly/3wQ4kLe
"Among 257 patients undergoing a surgical carotid endarterectomy procedure (taking out the atherosclerotic plaque) with complete follow-up, 58% had microplastics and nanoplastics (MNPs) in their plaque and their presence was linked to a subsequent 4.5 -fold increase of the composite of all-cause mortality, heart attack and stroke."
3/7/24 NEJM: Plastics, Fossil Carbon, and the Heart https://buff.ly/48J8Ybd
2/17/24 Toxicological Sciences: Quantitation and identification of microplastics accumulation in human placental specimens using pyrolysis gas chromatography mass spectrometry https://buff.ly/433Uxxp
3/7/24 NPR: Donor gives $40 million for Yellowstone National Park employee housing https://buff.ly/3T9Qefv
An anonymous donor has given Yellowstone National Park $40 million. But it's not to preserve nature or wildlife, it's to build housing that park staff can afford to live in.
More than 3,000 people work in the park during peak tourist season, and for years now, finding enough housing for them has been a problem.
Miami’s PSA to cancel Spring Break



































Thank you so much. I appreciate all the thought and effort you put into communicating these studies and other info week in and week out. I know it’s a lot of work. ❤️