COVID news and more 3/4/23
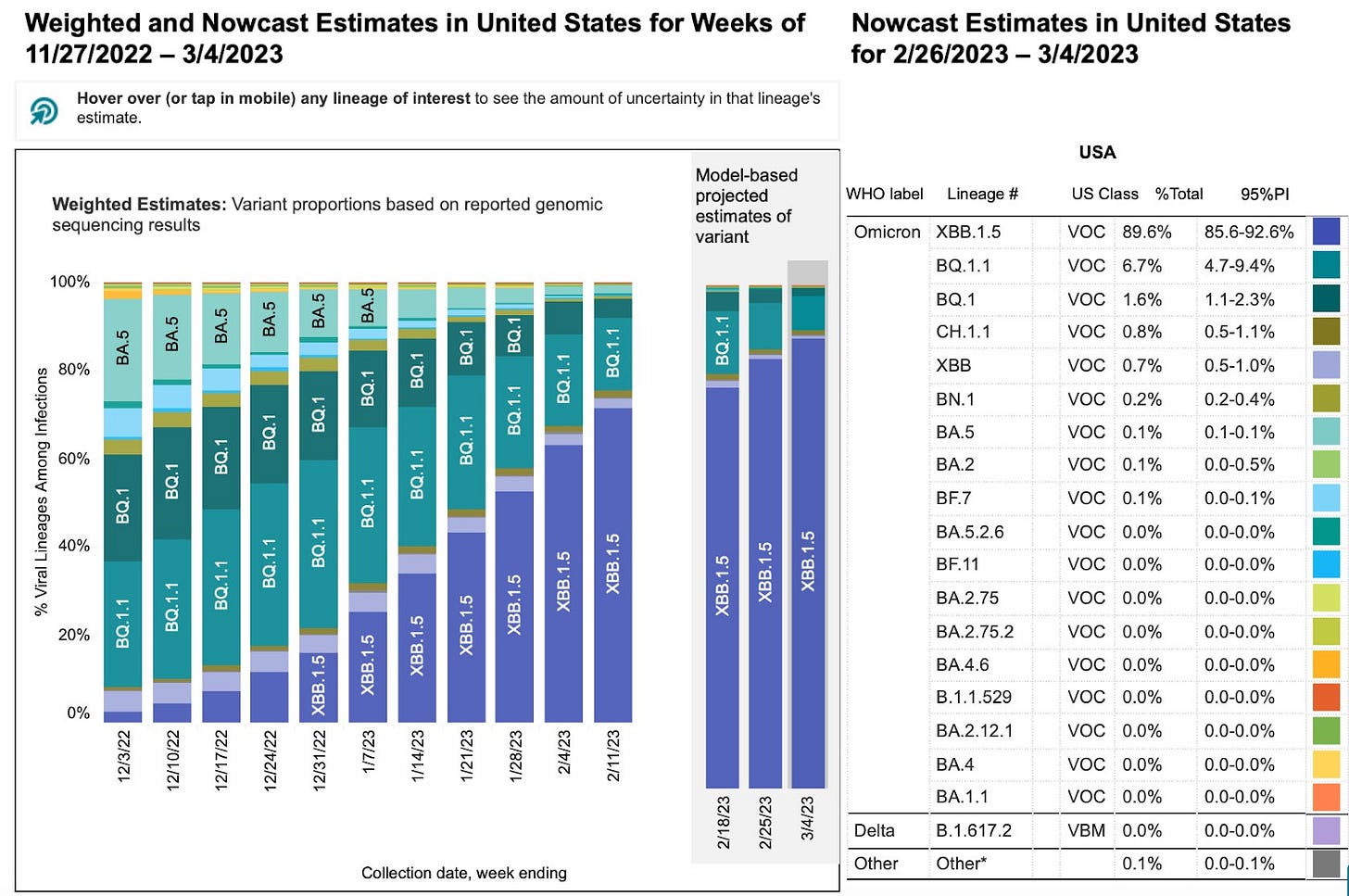
XBB.1.5 makes up 90% of cases in the US this week and fortunately hospitalizations are not increasing. No new variants are putting pressure on XBB.1.5 which is good news. It is possible that we are moving towards an endemic state. Wastewater virus levels in Louisiana, Nebraska, Utah, parts of Ohio, as well as San Jose and San Francisco in California are going up however. In Europe, Austria is starting a new wave although other European countries are not.
Cardiovascular disease
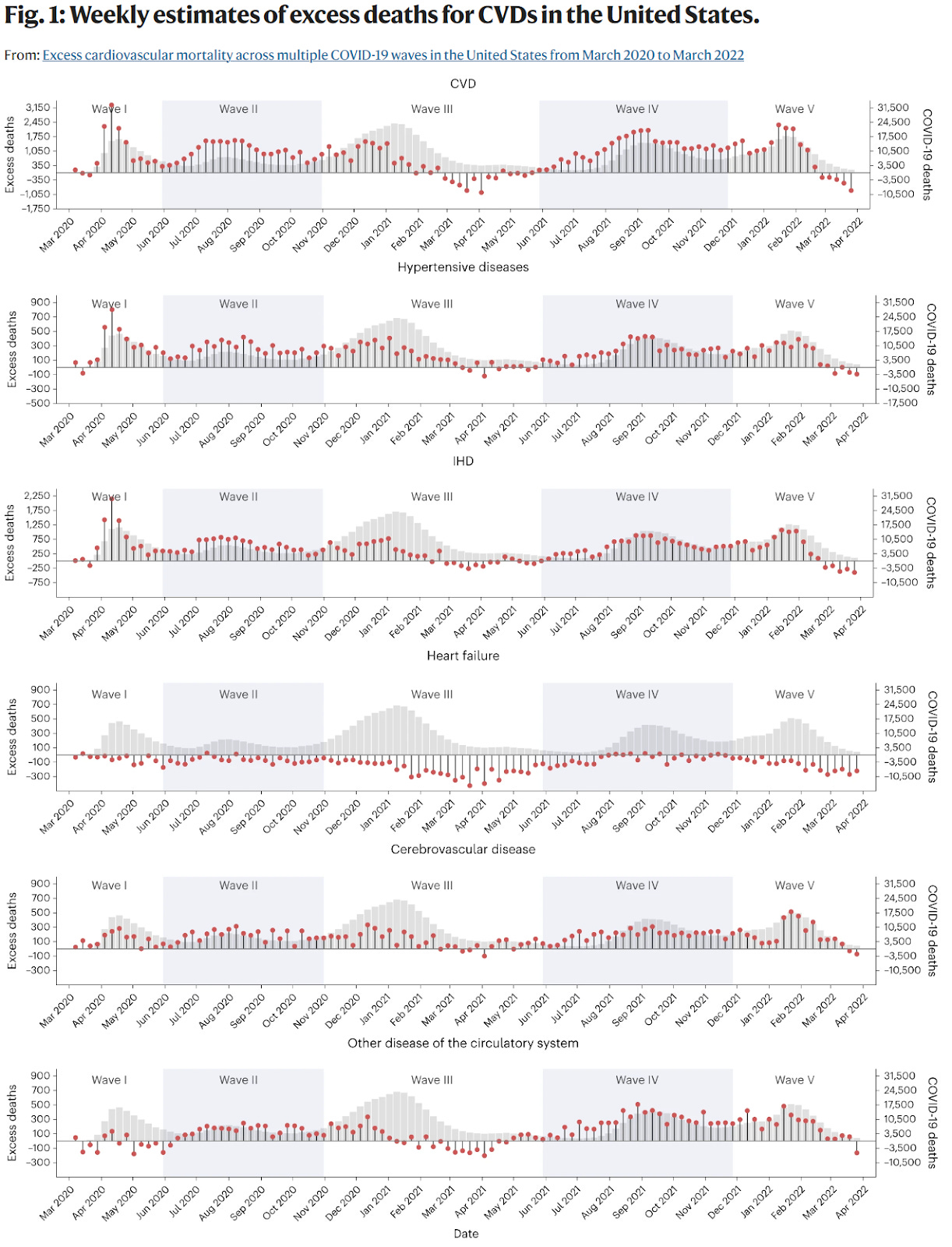
Dr. Eric Topol shared his summary of 6 recent studies, including a new JAMA article from this week, showing that the risk for major cardiovascular outcomes including heart attack and stroke are doubled in the year after a COVID infection. Two of the studies show that vaccination helps reduce these cardiovascular outcomes however. Excess cardiovascular deaths from heart attacks, hypertensive disorders, heart failure and stroke followed the five COVID waves in the first two years of the pandemic in the US.
Vaccines
A review and meta-analysis in the Lancet showed that vaccines were effective at preventing severe COVID and death, but that they were less effective against infections. Vaccine efficacy against symptomatic infection waned over time, with a loss of vaccine efficiency (VE) of 13.6% per month, but that boosters could increase VE again. A review showed that COVID-19 vaccination has a beneficial effect on preventing Long Covid through reducing case severity as well as incidence, although authors concluded that the size of the effect is difficult to estimate in observational studies. Regarding the AstraZeneca vaccine, a new study shows that there is an immune reaction to the adenovirus vector used which is not seen in reaction to mRNA vaccines. This immune response correlates with expression of pro-thrombotic proteins, and may be a potential explanation for the connection between the AstraZeneca vaccine and rare cases of vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT).
Source of SARS-CoV-2
The Wall Street Journal reported that the Energy Department of the US believed that a lab leak in Wuhan was the most likely origin of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. However, it was also said that the Energy department concluded with “low confidence” that COVID came from a lab leak, although that did not make the headlines. But as Dr. Katelyn Jetelina said, “We can all agree that the Wuhan market was an amplification event (i.e. super spreader), but I don’t think we will ever know how it got there because we’ve missed the window of opportunity for critical data.”
Long COVID and the Brain
A study from University of Washington shows that SARS-CoV-2 and the S1 spike protein can cross the blood brain barrier and induce neuroinflammation via microglial cells causing cognitive impairment and brain fog symptoms. In mice with an Alzheimer’s disease (AD) phenotype, this neuroinflammation accelerated dementia. Another study from Waterloo, Canada showed that Long COVID patients show lower brain oxygenation in the prefrontal cortex when doing cognitive tasks. Brain imaging found that older women were most affected. Long COVID also correlated with increased problems with emotion regulation including depression, anxiety and agitation at six months after their initial COVID infection.
Long COVID and the Lungs
In a prospective study that followed people who had COVID infection in 2020 and 2021, one-quarter of patients had abnormal pulmonary function at 12 months after COVID. Eleven percent of people with mild COVID, 22% of those with moderate COVID and 48% of patients who had severe COVID were found to have impaired lung function one year after their initial infection. People with pulmonary fibrosis after COVID infection had upregulation of proinflammatory and innate immune effector genes CD47, IL-6, and JUN. Blocking these genes (CD47, IL-6, pJUN) in a humanized mouse model of COVID lung fibrosis showed promising therapeutic targets for new drugs to decrease lung scarring from COVID.
Biomarkers
After studying 2925 blood proteins in Long COVID outpatients, COVID-19 inpatients and healthy controls, machine learning analysis identified 119 relevant proteins that could differentiate people with Long COVID. The 119 proteins were then narrowed down to two combinations of proteins to be used as biomarkers for Long COVID. Using nine specific proteins was almost 100% accurate for identifying who had Long COVID, while looking at just five of the nine proteins in the blood was about 80% accurate in predicting who had Long COVID. These biomarker panels may be used in the future to diagnose Long COVID from a blood test. Drugs that target these proteins could possibly be used to treat Long COVID.
Long COVID and disability
Several articles this week told stories of people with Long COVID who have become severely disabled. Rolling Stone magazine featured stories of people with Long COVID who became homeless because they could no longer work. Bloomberg talked about missing U.S. workers and CNN reported on the broken Social Security disability process for people with Long COVID. Senator Tim Kaine said that he has Long COVID and introduced a bill to help people living with Long COVID and senator Jim Inhofe said that he retired because of his Long COVID symptoms and that regarding politicians in Congress, there are “five or six others have (long COVID), but I’m the only one who admits it.”
Regarding kids with Long COVID, Colin Pidgeon tweeted an art piece made by his daughter who has Long COVID called “Rona Lisa”. It features things that doctors, family and friends have said to Long COVID kids, including “You are just being lazy” or “Your symptoms sound a bit dramatic”.
Masks
Two weeks ago, I wrote about the recent Cochrane review on masks. Here is what I said then:
A recent Cochrane review stated that “there is uncertainty about the effects of face masks”. However, Dr. Linsey Marr, an expert on airborne virus transmission and mask technology, said that there were limitations with the Cochrane review that included many studies that were conducted during non-epidemic influenza periods with lower respiratory viral circulation and transmission compared to COVID-19. Also, many of the studies included in the review were of healthcare workers who wore masks at work but not at home or while interacting with people in their community. She pointed to the recent CDC study showing that N95 masks reduced COVID by 83%, surgical masks by 66% and cloth masks by 56% if they were worn in indoor public settings.
This week, Professor Trisha Greenhalgh of Oxford wrote this thread reviewing the controversy about masks, randomized clinical trials about masks and the data about airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Tomas Pueyo, like Dr. Lindsey Marr above, showed that the Cochrane review mostly included older mask studies on influenza with lower viral circulation from before the COVID pandemic. The two large studies in the Cochrane review from the present COVID pandemic show that masks do work to decrease transmission of SARS-CoV-2.
In non-COVID news, deer antlers were found to have special stem cells that let them regenerate, atherosclerosis may actually be an autoimmune disease involving T cells, and women with migraines shed measurable CGRP in their tears during their menstrual periods. CGRP can dilate blood vessels in the brain, possibly leading to migraines. Preeclampsia and hypertension in pregnancy are associated with increased risk of dementia later in life.
Zero-calorie sweetener Erythritol found in Stevia, Monk Fruit and keto reduced-sugar products has been linked to blood clotting, stroke, heart attack and death. Diabetics may be more affected.
Pharma giant Eli Lilly announced that they would reduce insulin prices after a viral tweet from a parody account on Twitter caused their stocks to drop. A substance made from bacteria in the microbiome of the gut can influence whether or not chemotherapy is successful for Pancreatic cancer patients. And a study in Nature shows that while an anxious brain can cause the heart to beat faster, a racing heart on its own can also induce anxiety by talking to the insular cortex of the brain. Authors note “cells of both the body and the brain must be considered together to understand the origins of emotional or affective states.”
Have a good weekend,
Ruth Ann Crystal MD
Twitter: https://twitter.com/CatchTheBaby
Other news:
2/23/23 Science: A population of stem cells with strong regenerative potential discovered in deer antlers https://buff.ly/3EHSEeJ
Antler blastema progenitor cells (ABPCs). Mice have a similar type of ABPC (in the regenerative digit tip).
2/27/23 Nature Cardiovascular Research: Understanding autoimmunity in atherosclerosis paves the way for novel therapies https://buff.ly/3ZvgdiR
Review of autoimmunity in atherosclerosis in animal models.
and in humans:
2/23/23 Nature CV Research: Pairing of single-cell RNA analysis and T cell antigen receptor profiling indicates breakdown of T cell tolerance checkpoints in atherosclerosis https://buff.ly/3IGb3ts
"Our data support the concept of atherosclerosis as a bona fide T cell autoimmune disease targeting the arterial wall" in humans.
2/28/23 HealthDay: Women with migraine and a regular menstrual cycle have significantly higher Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Protein (CGRP) concentrations in plasma and tears during menstruation compared to female participants without migraine. https://buff.ly/3SEVJC6
CGRP can cause blood vessel dilation which can lead to migraines.
2/27/23 MedCity News: Eko Health Launches Heart Disease Detection Platform CEO Calls ‘Shazam for Heartbeats’ Using Their Digital Stethoscope https://buff.ly/3ZycHEe
2/28/23 CNN: Zero-calorie sweetener Erythritol found in Stevia, Monk Fruit and keto reduced-sugar products linked to blood clotting, stroke, heart attack and death, study finds https://buff.ly/3kAwRPq
People with existing risk factors for heart disease, such as diabetes, were twice as likely to experience a heart attack or stroke if they had the highest levels of erythritol in their blood.
2/27/23 Nature: The artificial sweetener Erythritol and cardiovascular event risk
3/2/23 Eli Lilly to cut prices on Humalog and Humalin insulin by 70% in October. https://buff.ly/3Ygjt0C
Lispro insulin will be $25 per vial.
$35 cap on some insulins will expand to 85% of US pharmacies.
3/1/23 Buzzfeed: Eli Lilly Reduced The Price Of Insulin To $35 Per Month, And This Guy Who Trolled The Company Can Take Some Credit https://buff.ly/3kJZedN
Eli Lilly received pressure after a journalist with a fake “parody” account and a paid-for blue check on Twitter posted this in November 2022:
2/22/23 Microbiota-derived 3-IAA influences chemotherapy efficacy in Pancreatic Cancer https://buff.ly/3ZvzlgG
3/2/23 Neurology: Association of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy (HDP) With Cognition in Later Life https://buff.ly/3EPrx1e
2,200 women in the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging
Women with a history of preeclampsia/eclampsia had greater declines in language, global cognition, and attention/executive function.
3/1/23 Nature: Cardiogenic control of affective behavioral state https://buff.ly/3mfVGAt
A racing heart beat can induce anxiety via the posterior insular cortex of the brain.
“Together, these findings reveal that cells of both the body and the brain must be considered together to understand the origins of emotional or affective states.”
3/1/23 Nature: How an anxious heart talks to the brain https://buff.ly/3INOxyO
During periods of anxiety, the brain affects the heart, but does a racing heart also talk to the brain to cause anxiety-related behavior?
Use of a light-stimulated pacemaker in mice shows that it does, and pinpoints a brain region involved (the posterior insula).
COVID news:
World cases https://medriva.com/charts/world-monitor.php
US cases https://medriva.com/charts/usa-monitor.php
https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2021/us/covid-cases.html
Walgreens positivity rate: https://www.walgreens.com/businesssolutions/covid-19-index.jsp
California (Walgreens testing):
https://ourworldindata.org/coronavirus
Variant tracker in US: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions
XBB.1.5 variant is now 90% of new cases in the US.
Wastewater Monitoring:
CDC Wastewater Monitor https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#wastewater-surveillance
Sewer Coronavirus Alert Network (SCAN) project by Stanford University:
3/3/23 Ground Truths by Eric Topol MD: Heart attacks and strokes late after Covid https://buff.ly/3KW8AxK
Many studies now show an approximate 2-fold risk of heart attack and strokes, all cause mortality, and other major cardiovascular outcomes including pulmonary embolism, months after both a mild or a severe COVID infection.
See table below.
Vaccination helps reduce these cardiovascular outcomes.
3/3/23 JAMA: One-Year Adverse Outcomes Among US Adults With Post–COVID-19 Condition vs Those Without COVID-19 https://t.co/Ceb1Dtgis0
Heart attacks, strokes and other major cardiovascular adverse outcomes doubled in people post-Covid at 1 year compared with matched uninfected controls.
3/2/23 US News: Long COVID Patients Show Lower Levels of Brain Oxygen https://buff.ly/3ZnjS2K
“We are the first to show reduced oxygen uptake in the brain during a cognitive task in the months following a symptomatic COVID-19 infection,” Dr. Peter Hall
“COVID-19 infection at baseline is correlated with increased problems with emotion regulation six months later: depression, anxiety and agitation,"
Brain imaging found that older women were most affected.
3/2023 Brain, Behavior, & Immunity: Neurocognitive and psychiatric symptoms following infection with COVID-19: Evidence from laboratory and population studies https://buff.ly/3jdBIp1
Symptomatic COVID-19 infection is associated with task-related, functional imaging and self-reported indices of cognitive dysfunction as well as psychiatric symptoms.
In some cases, these findings appear to be more amplified among women than men, and among older women than younger.
2/28/23 BMJ: Effect of Covid-19 vaccination on Long Covid: Systematic Review https://buff.ly/3y6GhW2
Current studies suggest that Covid-19 vaccines may have protective and therapeutic effects on Long Covid.
Covid vaccination reduces the likelihood, severity, and duration of Long Covid.
2/28/23 BMJ Editorial: Impact of covid-19 vaccination on Long Covid https://buff.ly/3J4wMg5
"Given new and existing evidence, covid-19 vaccination is likely to have some beneficial effect on Long Covid through reducing case severity as well as incidence.
However, estimating the size of the effect (and the effect of further vaccine doses) remains a challenge in observational data.
2/28/23 Lancet: Efficacy of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines and the dose–response relationship with three major antibodies: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (1/2020 to 9/2022)
Meta-analysis shows vaccine efficiency (VE) of full vaccination:
45% for preventing asymptomatic infections,
77% for preventing symptomatic infections,
95% for preventing hospitalization,
91% for preventing severe infection, and
86% for preventing death.
Vaccine efficacy against symptomatic infection waned over time after full vaccination, with an average decrease of 13·6% per month but can be enhanced by a booster.
Higher antibody titres are associated with higher estimates of efficacy but precise predictions are difficult.
2/27/23 PNAS: Innate immune cell activation causes lung fibrosis in a humanized mouse model of long COVID https://buff.ly/3J2RIUK
Single-cell transcriptomics of lungs of patients with long COVID lung fibrosis revealed a unique immune signature demonstrating the upregulation of key proinflammatory and innate immune effector genes CD47, IL-6, and JUN.
Blocking these genes (CD47, IL-6, pJUN) in a humanized mouse model of COVID lung fibrosis showed promising therapeutic targets to decrease lung scarring from COVID.
2/27/23 Nature CV Research: Excess cardiovascular mortality across multiple COVID-19 waves in the United States from March 2020 to March 2022 https://buff.ly/3SGbetG
In the first two years of the pandemic, there was a persistent excess of cardiovascular deaths (cardiovascular disease, hypertensive disorders, heart failure, stroke) in the US consistent through the five COVID waves.
2/27/23 MobihealthNews: Lucira Health files for bankruptcy as it receives EUA for home COVID-19, flu test https://buff.ly/3EMr6VE
Lucira's test is the first OTC, FDA authorized test that can detect Influenza A and B, and SARS-CoV-2 at home in 30 minutes.
2/25/23 USA Today: First at-home combination test for COVID and flu authorized by FDA https://buff.ly/41ASFLe
2/28/23 Katelyn Jetelina: COVID-19 Origin Debate https://buff.ly/3kz0X5I
“We can all agree that the Wuhan market was an amplification event (i.e. super spreader), but I don’t think we will ever know how it got there because we’ve missed the window of opportunity for critical data. Disproving the lab leak will be close to impossible.”
2/26/23 WSJ News Exclusive | Lab Leak Most Likely Origin of Covid-19 Pandemic, Energy Department Now Says https://buff.ly/3xRu4nQ
Energy department concludes with “low confidence” that COVID came from a lab leak.
Prof Trisha Greenhalgh thread on masks
He reviews the flawed recent Cochrane review.
3/2023 Brain, Behavior, and Immunity: Blood-brain barrier penetration of non-replicating SARS-CoV-2 and S1 variants of concern induce neuroinflammation which is accentuated in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease https://buff.ly/3m7V4Nt
Possible mechanism of Long COVID (PASC) cognitive impairment (brain fog) and neuropsychiatric symptoms.
Using a mouse model, SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus and Spike Protein S1 readily crossed the blood–brain barrier (BBB).
Omicron and Delta variants S1 protein crossed the BBB the fastest.
These results support that SARS-CoV-2 and spike protein S1 can cross the BBB and induce neuroinflammation via microglia, even in the absence of productive infection, and cause cognitive impairment.
In mice with the Alzheimer’s disease (AD) phenotype, this neuroinflammation may accelerate dementia.
2/24/23 KIRO: Brain inflammation likely cause of long COVID symptoms, UW Medicine study finds https://buff.ly/3Ixs7ll
Using a mouse model, UW scientists found that S1 spike protein passes through the blood-brain barrier (BBB) causing neuroinflammation that can lead to learning and memory problems and accelerate Alzheimer’s dementia.
Omicron S1 passed the BBB most easily.
Antibodies from vaccination can protect.
2/25/23 Rolling Stone: First They Got Long Covid. Then, It Made Them Homeless. https://buff.ly/3tkbUsp
2/25/23 Bloomberg: Millions of US Workers Are Still Missing After The Pandemic. Where Did They Go? https://buff.ly/3Y3zN4P


2/24/23 Lancet (Amsterdam): One-Fourth of COVID-19 Patients Have an Impaired Pulmonary Function after 12 Months of Illness Onset https://buff.ly/3xTJoAn
Prospective study of 301 people with COVID (non-hospitalized and hospitalized). No control group. Pulmonary Long COVID.
Pulmonary function was measured by diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) at one, six, and twelve months after illness onset.
At 1 year, impaired pulmonary function found in:
11% of mild COVID
22% with moderate COVID
48% with severe COVID
2/21/23 Molecular Medicine: Organ and cell-specific biomarkers of Long-COVID identified with targeted proteomics and machine learning https://buff.ly/3IUhxq5
Machine learning analysis identified 119 relevant proteins for differentiating Long-COVID outpatients.
Protein combinations were narrowed down to two optimal models, with nine (100% accurate) and five proteins (80% accurate), and with both having excellent sensitivity and specificity for Long-COVID.
Nine proteins (CXCL5, AP3S2, MAX, PDLIM7, EDAR, LTA4H, CRACR2A, CXCL3, ↓FRZB) were determined from the 119 relevant proteins.
All of the nine optimal proteins were significantly elevated in Long-COVID outpatients, other than FRZB which was significantly decreased in Long-COVID outpatients.
9 protein model (more accurate): Increased CXCL5, AP3S2, MAX, PDLIM7, EDAR, LTA4H, CRACR2A, CXCL3 and decreased FRZB.
5 protein model (subset of the 9 proteins, 80% accurate): CXCL5, AP3S2, MAX, PDLIM7, and ↓FRZB.
CXCL5- pro-inflammatory
AP3S2- associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus, neurological conditions
MAX- linked to neurological conditions
PDLIM7- respiratory and neurologic conditions
EDAR- TNF receptor family, cytokines
LTA4H- pro-inflammatory
CRACR2A- immune cell activation, T-cell activation,
CXCL3- immune cell activation, pro-inflammatory
decreased FRZB- linked to neurological conditions
Leukocytes and platelets are key components associated with Long COVID.
3 groups: Long-COVID outpatients, acutely ill COVID-19 inpatients and healthy controls
2/25/23 Long Covid disabled them. Then they met a 'broken' Social Security disability process | CNN Business https://buff.ly/3KFvxVY
“I want to be working,” she said. “I don’t want to be on disability, but I spent $17,000 on medical expenses last year trying to get better. If I didn’t have support and savings, I’d be on the streets.”
‘Expect you’re going to be denied’ for disability payments.
2/25/23 CNN: Virginia senator Tim Kaine says he has long Covid and introduces a bill to help those struggling with it | CNN Politics https://buff.ly/3Z0iNxC
2/24/23 HuffPost: GOP Ex-Sen. Inhofe Retired Due To Long COVID After Opposing COVID Aid https://buff.ly/3ksdjwt
Former Sen. Jim Inhofe (R-Okla.) attributed his decision to retire due to the long-term effects of COVID-19, saying that certain symptoms were still affecting him day-to-day.
“Five or six others have (long COVID), but I’m the only one who admits it,” Inhofe.
2/16/23 Cell (Australia): A systems immunology study comparing innate and adaptive immune responses in adults to COVID-19 mRNA and adenovirus vectored vaccines. https://buff.ly/3J24q6c
B cells produce antibodies and T cells kill infected cells.
A 1st dose of ChAdOx1-S (AstraZeneca), but not BNT162b2 (Pfizer), induces an adenoviral memory response targeted against the adenovirus vector after 1st dose which correlates with expression of pro-thrombotic proteins.
Potential explanation for the connection between the AstraZeneca vaccine and the rare cases of vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT).
People who showed symptoms of fatigue and fever immediately after the third dose were more likely to have better T-cell responses.
12/9/22 J Transl Med: Muscle sodium content in patients with Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) https://buff.ly/3xWqt8c
Muscle sodium content before and after exercise was higher in ME/CFS than in healthy controls.
There is an inverse correlation between muscle sodium content and handgrip strength.
These findings provide evidence that sodium overload may play a role in the pathophysiology of ME/CFS and may allow for potential therapeutic targeting.