This week, we are still at “LOW” virus levels of SARS-2 in wastewater at a national level. New Jersey and Utah continue to show “Substantial” virus wastewater levels per Sara Anne Willette and the CDC. Hospitalizations, Emergency Department visits and deaths from COVID continue to decline and are almost to the nadir that we saw last June. Approximately 1 in every 124 people is infected with COVID now in the United States and the calculated cases continue to decline per JP Weiland.
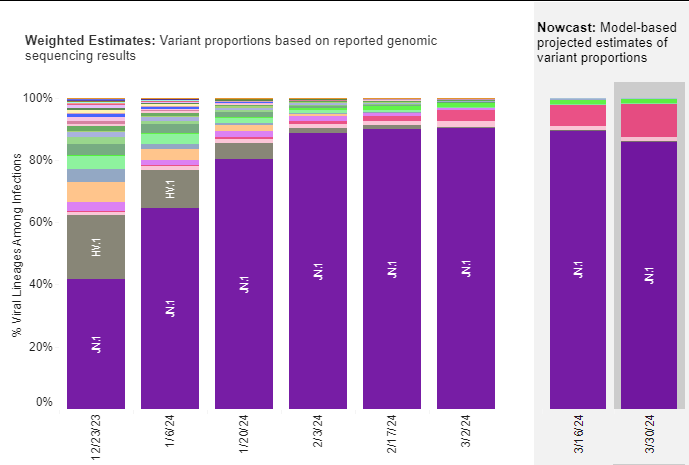
JN.1 continues to be the variant causing most cases now. Raj Rajnarayanan and others note that a new descendant, JN.1 + FLiRT mutation (F456L + R346T) + T572I mutation has a significant growth advantage and could cause the next wave of infection. Therefore, they suggest that this subvariant be used to make the next vaccine booster. The FLiRT mutation (F456L + R346T) combination has been seen in other variants that were able to grow significantly.
https://twitter.com/JPWeiland/status/1773115303532065222
A new study shows that the SARS-CoV-2 virus appears to pick up some of its mutations from bacteria living in the microbiome of our gut and lungs. The recombination of bacterial mRNAs and viral mRNA can add bacterial mutations to the virus.
Acute COVID infections
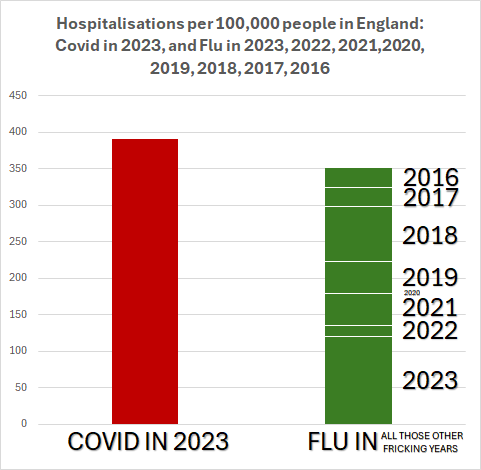
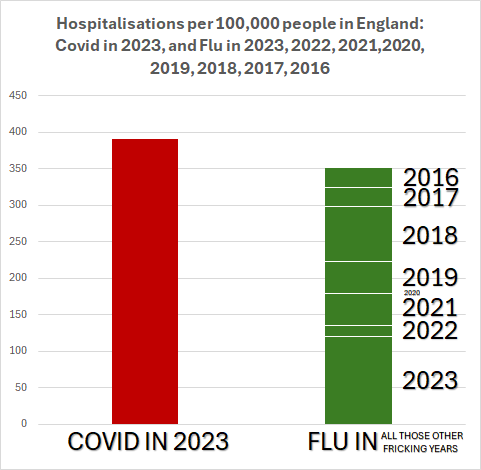
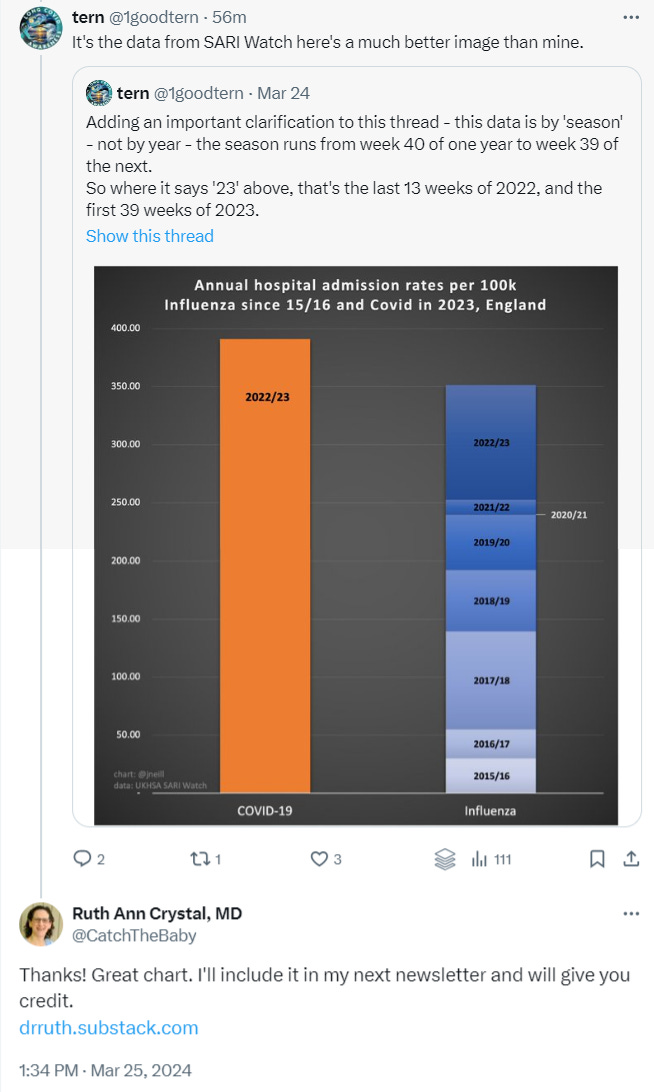
The number of people hospitalized for COVID infections in England in 2023 was greater than the number of people hospitalized for the flu in 2016, 2017, 2018, 2019, 2020, 2021, 2022 and 2023 combined. There were more people hospitalized in 2023 alone for COVID than for the last 8 years for the flu. COVID is not the Flu.
From: https://twitter.com/1goodtern/status/1771624945774186938 with data from SARI Watch via @jneill and UK Gov https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/national-flu-and-covid-19-surveillance-reports-2023-to-2024-season
SARS-CoV-2 and Cancer
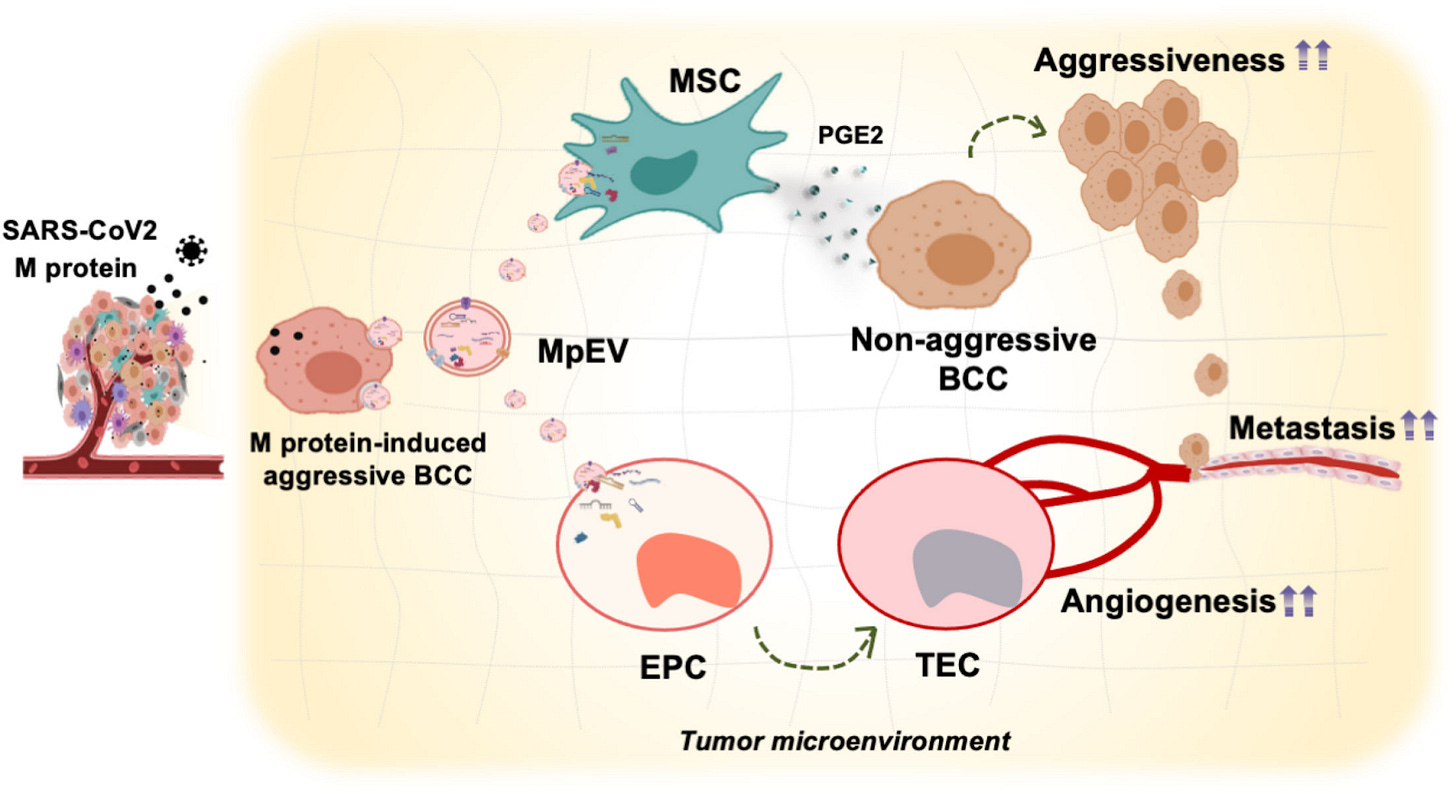
We know that the HPV virus can cause cervical cancer and that the EBV virus is associated with an aggressive B-cell lymphoma called Burkitt lymphoma. A new study shows that the SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein extracellular vesicles (EV) promote breast cancer cells to become more aggressive. The EV from the SARS-CoV-2 virus also was found to stimulate endothelial cells and blood vessels of tumors to increased metastasis. "Taken together, our findings suggest the role of SARS-CoV-2 M-protein in altering the cellular communication between cancer cells and other non-cancer cells inside the tumor microenvironment via EV. Specifically, M-proteins induced the ability of EV derived from triple-negative BCC to promote the functions of non-cancer cells, such as tissue stem cells, in tumorigenesis."
Figure 7 Proposed model: In the tumor microenvironment (TME), SARS-CoV-2 M-protein-induced BCC recruit and control the activity of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ATMSC) and endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) via extracellular vesicles (EV) which facilitate the development and metastasis of breast tumors.
Immunocompromised people
Last week, I wrote about Pemgarda, a new monoclonal antibody for pre-exposure prophylaxis against COVID-19 in moderate to severely immunocompromised people aged 12 and older. I was concerned that 4 of 623 (0.6%) of participants in the clinical trial had anaphylaxis to Pemgarda. I looked up the risk of anaphylaxis with other medications for COVID and found that the anaphylaxis rate was much lower for other COVID medications: 0.04% risk of anaphylaxis for sotrovimab, 0.03% for Paxlovid, <0.05% for molnupiravir. I am hoping that AstraZeneca’s new long acting monoclonal antibody for pre-exposure prophylaxis against SARS-CoV-2 called Sipavibart (AZD3152) will have less anaphylaxis issues.
Pediatrics
School officials in Germany noted that many children were coming down with COVID infections. It turns out that a sick bus driver was spreading COVID to children on their short bus ride to school. The number of “children infected with COVID-19 while riding a bus to a school in Germany was about four times higher than in peers who didn't ride the bus, illustrating efficient transmission during multiple short rides on public transport”.
A multinational, controlled case study shows that asymptomatic children with COVID, especially preschoolers, contribute significantly to household transmission of COVID. People were 5 times more likely to catch a COVID infection from an asymptomatic child than from other sources. Younger children often have a prolonged duration of viral shedding and caregivers often hold babies and young children to comfort them. This study also showed that 7.8% of asymptomatic young children developed Long COVID by 3 months post infection. "The fact that approximately 1 in 13 asymptomatically infected children developed PCC [post-COVID condition, or long COVID] is concerning and requires further investigation."
The Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society recently wrote a guide for the prevention and management of COVID-19 in children and adolescents. It included risk stratification and guidance on the treatment of hospitalized and non-hospitalized children and adolescents with COVID. A group in Italy looked at the mucosal immune response in children ages 5 to 11 years old for COVID infection versus COVID vaccination. They found that COVID infected kids had IgA2 antibodies in saliva, while those who received the Pfizer vaccination had a slight increase in salivary IgA1. Blood spike-specific IgA and IgG levels were significantly higher in vaccinated children compared to naturally infected children.
Antiviral treatments
A new review looked at pathways of infection of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and how this knowledge might help in the development of antiviral medications against COVID variants. The review looked at data from different antivirals that exist and discussed antiviral medications (HH-120, Ensitrelvir, Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir (Paxlovid), Simnotrelvir-ritonavir, FB2001, Remdesivir, Molnupiravir, VV116, Bemnifosbuvir) that had some positive data.
Fig. 1. The life cycle of SARS-CoV-2 and targets for antiviral medications
Long COVID
A new review from Australia looks at research on myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) and how its pathophysiology is like that of Long COVID. About 50% of Long COVID (LC) patients meet the criteria for ME/CFS. “ME/CFS is a chronic multisystem disorder characterized by a significant reduction in functional capacity and a combination of debilitating fatigue, post-exertional malaise (PEM), unrefreshing sleep, cognitive disturbances, and a host of autonomic, neuroendocrine, and immune manifestations”. Both ME/CFS and Long COVID have a similarly altered gut microbiome with a reduction in butyrate production by bacteria. The authors also noted that some RNA measurements could be potential biomarkers for both ME and Long COVID.
From: https://www.cell.com/trends/molecular-medicine/fulltext/S1471-4914(24)00028-5#%20
A group from the University of Virginia found that a small number of people make enzyme-like antibodies called “abzymes” after a COVID infection. Abzymes are antibodies with a molecular mirror-image of the SARS-CoV-2 RBD that may mimic enzymes in physiologic pathways that control blood pressure, the complement system, the clotting cascade and the normal inflammatory response causing them to become dysregulated. “Abzymes are not exact copies of enzymes and so they work differently, sometimes in ways that the original enzyme does not. If COVID-19 patients are making abzymes, it is possible that these rogue abzymes could harm many different aspects of physiology.” The authors suggest that the abzymes could be related to the pathophysiology of Long COVID.
Some people on Twitter were discussing that commercial airline pilots have a physical exam for work every year. Christine Guenter wrote that her pilot husband was asked by the physician how many times he had been infected by COVID. The doctor told him that “many in the aviation industry are showing signs of heart impairment” and are losing their pilot’s licenses due to COVID’s long term effects. Others replied that the Public Health Communication Centre Aotearoa New Zealand wrote about the public health need to test certain people in the workforce including pilots for the effects of Long COVID. They wrote, “Society, sector, and workforce effects of Long Covid are costly and disruptive, and they worsen existing inequities. “The frequency of (often undiagnosed) cognitive impairment after a mild infection indicates a need for risk assessment of impacts on occupational safety and performance. Occupations of particular concern because of safety implications include healthcare workers, airline pilots, electricians, truck drivers, and first responders.”
Physicians have told me that people come to them stating that they cannot think as clearly now, but they chalk it up to normal aging. In fact, many of these people have cognitive dysfunction from COVID infections. Each COVID infection can cause people to lose IQ points and can cause the brain to prematurely age. “The number of working-age adults reporting “serious difficulty” thinking has climbed… and younger adults (age 18 to 44) are driving the trend.”
People with Long COVID may want to enroll in clinical trials, but some find that listings on ClinicalTrials.gov are not easy to search and many of the studies posted are not blinded which lends itself to biased results. The Sick Times reports a new way for people to find Long COVID clinical trials called "Long Covid Studies" at https://longcovidstudies.net/.
One of the difficulties with comparing results from different Long COVID trials is that the definition of Long COVID can vary. A new study shows that the range of Long COVID prevalence in the same group of people studied ranged from 1.2% to 13.4% depending on the definition of Long COVID employed. “Among symptom-based definitions of long COVID, UK-ONS had the largest prevalence estimate (13.4%) followed by NICE1 (8.6%), US-NCHS (7.6%), NICE2 and WHO-PCC (4.0%). Prevalence based on participants’ perception of having had long COVID was 7.1%.”
In other news, Dr. Eric Topol reviewed exciting new uses for artificial intelligence (AI) in medicine. Science magazine had an article on why mandating indoor air quality in public buildings is so important. Residential green spaces reduce pollution levels and are important for reducing anxiety and depression.
SCGB1D2 is a protein found in human skin, sweat, and other secretions that can protect against Borrelia burgdorferi infection and Lyme disease. Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) was found in dairy herds in Texas, Kansas and Michigan. The H5N1 avian flu virus was introduced to cattle by wild birds, but transmission between cattle has not been ruled out and is being monitored. Commercial milk that is pasteurized remains safe to consume.
Statin medicines can cause a dose-dependent increase in Type II diabetes. “Importantly, however, any theoretical adverse effects of statins on cardiovascular risk that might arise from these small increases in glycaemia (or, indeed, from any other mechanism) are already accounted for in the overall reduction in cardiovascular risk that is seen with statin therapy in these trials."
Fusobacterium nucleatum (Fn) is a bacteria found in the mouth that is related to dental plaque. Fn is also found in colorectal cancer (CRC) tumors, especially aggressive tumors that metastasize. A new study in Nature magazine shows that a specific type of Fn, Fna C2 (Fusobacterium nucleatum animalis Clade 2), is what is found in colon cancers. Giving mice Fna C2 bacteria was associated with them making new colorectal polyps and tumors. This bacterial strain can "cloak" tumors from cancer drugs by recruiting immune cells that allow the cancer to evade attack. The FnaC2 bacteria was found in 50% of colon cancers tested.
A new 5 star review in Cell magazine looks at the “complexities of cancer as a systemic disease, including tumor initiation and promotion, tumor micro- and immune macro-environments, aging, metabolism and obesity, cancer cachexia, circadian rhythms, nervous system interactions, tumor-related thrombosis, and the microbiome”, as well as genetic variation, gene-environment interactions, and molecular oncology.
Finally, 40 year old Deanna Stellato-Dudek came out of a long retirement and won the gold medal in pairs at the World Figure Skating Championship this week. With her skating partner Maxime Deschamps, Deanna won against athletes half her age to become the oldest woman to win a World Figure Skating Championship. Good for her!
Have a good rest of your weekend,
Ruth Ann Crystal MD
COVID news notes:
US Variant tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions
Variants around the world:
https://outbreak.info/
NEW: World wastewater maps (reflects COVID cases): https://www.arcgis.com/apps/dashboards/c778145ea5bb4daeb58d31afee389082
CDC COVID data tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/index.html#datatracker-home
CDC COVID Hospitalizations (blue) and Emergency Room (orange) visits tracker: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/index.html#trends_weeklyhospitaladmissions_7dayeddiagnosed_00
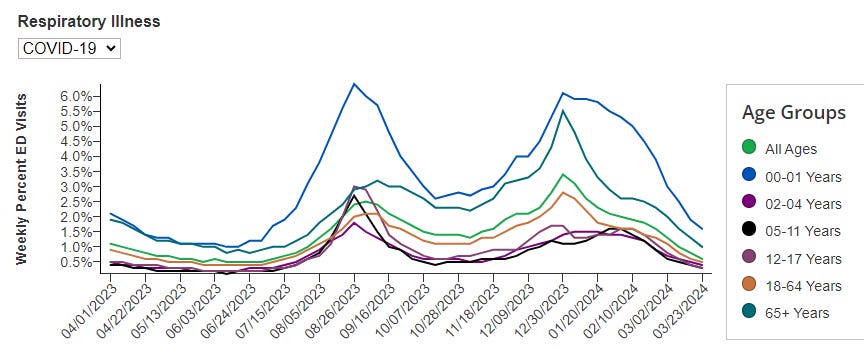
Weekly ED visits for respiratory illnesses, by age and disease: https://www.cdc.gov/ncird/surveillance/respiratory-illnesses/index.html
COVID
FLU
Walgreens positivity rate: https://www.walgreens.com/businesssolutions/covid-19-index.jsp
US Wastewater Monitoring:
CDC wastewater reporting: https://www.cdc.gov/nwss/rv/COVID19-nationaltrend.html
CDC wastewater map: https://www.cdc.gov/nwss/rv/COVID19-currentlevels.html
High wastewater levels in Utah and New Jersey this week
Biobot: https://biobot.io/data/
National SARS-CoV-2 data from Sara Anne Willette: https://iowacovid19tracker.org/
Utah and New Jersey are at “substantial” levels. No states at the “excessive” level.
Wastewater SCAN: https://data.wastewaterscan.org/
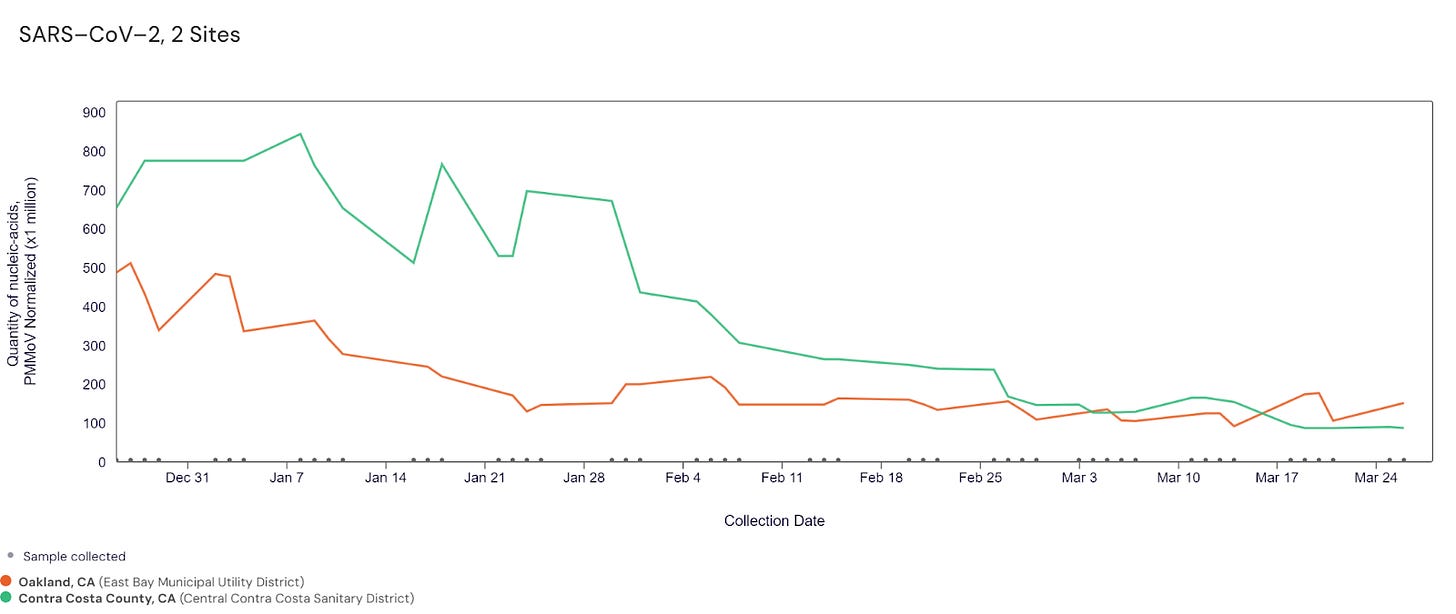
California statewide view https://buff.ly/3YObiul
Oakland (orange) and Contra Costa (green) counties
Sewer Coronavirus Alert Network (SCAN) project by Stanford University:
Santa Clara County wastewater: https://covid19.sccgov.org/dashboard-wastewater
CDC Respiratory vaccination trends: https://www.cdc.gov/respiratory-viruses/data-research/dashboard/vaccination-trends-adults.html
Variants
https://twitter.com/JPWeiland/status/1773845197178241087
“Moving towards low transmission levels.
JN.1 with FLiRT mutations are growing, but won't impact the US for a while still.
270,000 new infections/day
~2.75 avg total infections per capita across the US
1 in every 124 people currently infected
https://twitter.com/JPWeiland/status/1773115303532065222
Raj Rajnarayanan @RajlabN https://twitter.com/RajlabN/status/1772745489122750667
.@WHO TAG-CO-VAC, @US_FDA #VRBPAC (@CDCgov #ACIP) and other PH agencies will (potentially) pick a new vaccine antigen
My antigen recommendation (for the next few months): JN.1 background with Spike mutations R346T, F456L (ie., include #FLiRT) & T572I
https://twitter.com/JPWeiland/status/1773115303532065222
100% agree with this assessment.
JN.1 + F456L and R346T should be the target of the next vaccine update, not just the base JN.1. Both mutations are growing substantially on JN.1* and have evolved in prior variants.
Michael Hoerger modeling: http://pmc19.com/data/,
https://twitter.com/michael_hoerger/status/1772331058656059595/photo/1
The SARS-CoV-2 virus appears to pick up some of its mutations from bacteria living in the gut and the lungs of humans. The recombination of bacterial mRNAs and viral mRNA can add bacterial mutations to the virus.
3/26/24 ASM, mBio: The human microbiota is a beneficial reservoir for SARS-CoV-2 mutations https://buff.ly/4cNLJjI
SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern may be mutated due in part to the influence of the human microbiome.
SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase replicates corresponding bacterial mRNAs harboring mutations, producing chimeric RNAs. SARS-CoV-2 may collectively pick up mutations from the human microbiota from the gut and the lung.
SARS-CoV-2 may grab advantageous mutations from the widely existing microorganisms in the host, which is undoubtedly an “efficient” manner.
Figure 4d: SARS-CoV-2 RdRp introduces bacterial mRNA nucleotide mutations into viral RNAs through homologous recombination
Acute COVID infections, General COVID info
3/26/24 Cureus: Impact of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein on the Innate Immune System: A Review https://buff.ly/3VGZQB5
COVID is NOT the Flu tweet thread:
https://twitter.com/ejustin46/status/1772169006184554841
The number of people hospitalized for COVID infections in England in 2023 was greater than the number of people hospitalized for the flu for 2016, 2017, 2018, 2019, 2020, 2021, 2022 and 2023. There were more people hospitalized in 2023 alone for COVID than for the last 8 years for the flu. COVID is not the Flu.
https://twitter.com/1goodtern/status/1771624945774186938
(data from SARI Watch via @jneill)
(data from SARI Watch via @jneill)
https://twitter.com/CatchTheBaby/status/1772361509441520004
https://twitter.com/1goodtern/status/1771983706585968784
3/21/24 CIDRAP: Probe links COVID spread to school bus riders from sick driver https://buff.ly/3VGCpYC
"children infected with COVID-19 while riding a bus to a school in Germany was about four times higher than in peers who didn't ride the bus, illustrating efficient transmission during multiple short rides on public transport "
tupungato / iStock
4/2024 CDC: Bus Riding as Amplification Mechanism for SARS-CoV-2 Transmission, Germany, 2021 https://buff.ly/4aqLaug
SARS-CoV-2 and Cancer
We know that the HPV virus can cause cervical cancers and that the EBV virus is associated with an aggressive non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma called Burkitt lymphoma. A new study shows that the SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein promotes breast cancer cells to become more aggressive.
SARS-CoV-2 extracellular vesicles (EV) transmit messages to triple-negative breast cancer cells making them more aggressive. The EV from the virus also was found to stimulate endothelial cells lining in blood vessels of tumors to make more blood vessels to and from the tumor which increased metastasis.
3/6/24 Frontiers in Oncology: Extracellular vesicles derived from SARS-CoV-2 M-protein-induced triple negative breast cancer cells promoted the ability of tissue stem cells supporting cancer progression https://buff.ly/3TPrHxH
SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein (M-protein) promotes the malignant transformation of triple-negative breast cancer cells (triple-negative BCC).
The effects of M-protein on the ability of extracellular vesicles (EV) derived from triple-negative BCC to regulate the functions of tissue stem cells facilitating the tumor microenvironment were examined.
"Taken together, our findings suggest the role of SARS-CoV-2 M-protein in altering the cellular communication between cancer cells and other non-cancer cells inside the tumor microenvironment via EV. Specifically, M-proteins induced the ability of EV derived from triple-negative BCC to promote the functions of non-cancer cells, such as tissue stem cells, in tumorigenesis."
the effects of SARS-CoV-2 proteins on cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment (TME), which support the development of tumors
Figure 7 Proposed model: In the tumor microenvironment (TME), SARS-CoV-2 M-protein-induced BCC recruit and control the activity of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ATMSC) and endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) via extracellular vesicles (EV) which facilitate the development and metastasis of breast tumors.
Immunocompromised people
3/28/24 Medical Xpress: Multiple Sclerosis patients face much greater risk of hospitalization, death from COVID-19, despite high rates of vaccination https://buff.ly/43GJnyH
European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases
3/22/24 FDA: Frequently Asked Questions on the Emergency Use Authorization for Pemgarda (pemivibart) for Pre-exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) of COVID-19 https://buff.ly/4a0PAbc
Pemgarda, made by Invivyd, is a long acting monoclonal antibody drug that can be given to people age 12 and older prophylactically every 3 months for moderate to severe immunocompromise.
Only 623 people have received Pemgarda so far in clinical trials and 4 of 623 (0.6%) of participants had anaphylaxis to Pemgarda.
AstraZeneca has another long acting monoclonal antibody against SARS-CoV-2 called Sipavibart that is approved in France for PrEP in immunocompromised people and is FDA pending here.
9/1/2023 Wellcome Open Research: Anaphylaxis events following COVID-19 antiviral and neutralising monoclonal antibody treatment for non-hospitalised patients: data from the OpenSAFELY-TPP platform https://buff.ly/4asLwjE
The risk of anaphylaxis during the 29 days follow-up was 0.04% for sotrovimab users, 0.03% for Paxlovid users, <0.05% for molnupiravir users, and 0.02% for untreated high-risk patients.
Pediatrics
3/27/24 Frontiers Cellular and Infectious Microbiology (Italy): SARS-CoV-2–specific mucosal immune response in vaccinated versus infected children https://buff.ly/3TVYDVn
5–11 year old children
COVID infected kids had IgA2 antibodies in saliva, while those who received the Pfizer vaccination had a slight increase in salivary IgA1.
Blood spike-specific IgA and IgG levels were significantly higher in vaccinated children compared to naturally infected children.
3/26/24 CIDRAP: Study: Kids with COVID but no symptoms play key role in household spread https://buff.ly/3xjHMTk
Asymptomatic children with COVID-19, especially preschoolers, contribute significantly to household transmission.
People were 5 times more likely to catch a COVID infection from an asymptomatic child than from other sources.
"We determined that the risk of developing symptomatic illness within 14 days was 5 times greater among household contacts of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2–positive children,"
6 of 77 asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2–infected children during a 3-month follow-up developed long COVID, or 7.8% of them.
The finding is noteworthy, as likely more than 30% of all COVID-19 infections are asymptomatic, and asymptomatic infections are presumed to be benign—especially those in children.
The relative risk of secondary attack rate (SAR) among index patients younger than 5 years was 11.1, and for kids 5 to 13 years it was 8.0.
Younger children may be linked to higher SARs because of prolonged duration of viral shedding in the very young, which previous studies have demonstrated. Younger children are also in closer physical contact with their caregivers.
3/26/24 Clinical Infectious Diseases: Household Transmission Dynamics of Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2–Infected Children: A Multinational, Controlled Case-Ascertained Prospective Study https://buff.ly/3TESMSV
Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2–infected children, especially those <5 years, are important contributors to household transmission, with 1 in 10 exposed household contacts developing symptomatic illness within 14 days. Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2–infected children may develop PCC.
"We determined that the risk of developing symptomatic illness within 14 days was 5 times greater among household contacts of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2–positive children,"
"The fact that approximately 1 in 13 asymptomatically infected children developed PCC [post-COVID condition, or long COVID] is concerning and requires further investigation,"
2/10/2024 A consensus statement from the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society Pediatric COVID-19 Therapies Taskforce: Guidance for prevention and management of COVID-19 in children and adolescents https://buff.ly/49hVd3O
Risk stratification and guidance on the treatment of hospitalized and non-hospitalized children and adolescents with COVID-19 and on preventative therapy options.
Fig 3. Management of COVID-19 in children and adolescents not requiring hospitalization for COVID-19.
Antiviral treatments
2024 Current Research in Microbial Science: Clinical development of antivirals against SARS-CoV-2 and its variants https://buff.ly/498yDdJ
"In this review, we summarize the latest advancements in the clinical development of antivirals against infections by SARS-CoV-2 and its variants."
3. Antivirals targeting viral factors
3.1. Antivirals targeting S protein
3.1.1. Monoclonal antibodies (MAbs)
3.1.2. Recombinant protein-based antivirals
3.1.3. Small-molecule and peptide-based antivirals
3.2. Antivirals targeting main protease (Mpro, 3CLpro)
3.3. Antivirals targeting RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp)
4. Antivirals targeting host factors
4.1. Viral receptor (ACE2)
4.2. Host proteases
Proprotein convertases, such as furin, transmembrane serine proteases, such as TMPRSS-2, and endosomal cysteine proteases, such as cathepsin B/L, are important host proteases responsible for proteolytic activation of S protein during viral entry.
4.3. Other host factors
5. Antivirals targeting uncertain/miscellaneous factors
Fig. 1. The life cycle of SARS-CoV-2 and targets for some antivirals.
Table 1. Antiviral medications that had some positive data.
HH-120, Ensitrelvir, Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir (Paxlovid), Simnotrelvir-ritonavir (China approval), FB2001, Remdesivir, Molnupiravir, VV116 (China NMPA approved), Bemnifosbuvir (AT-527)
Long COVID
3/4/24 Molecular Medicine (Australia): Unravelling shared mechanisms: insights from recent ME/CFS research to illuminate Long COVID pathologies https://buff.ly/4abnN7X
“In this review, we highlight current trends in ME/CFS research and touch on recent LC findings that are relevant. We focus on, and discuss, studies with sufficient sample sizes (typically >20 participants/group).”
Review of research on ME/CFS and how its pathophysiology may be like Long COVID. About 50% of Long COVID (LC) patients meet the criteria for myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS). The authors focused on the common altered gut microbiome with a reduction in butyrate production and RNA measurements that could be potential biomarkers for ME and Long COVID.
ME/CFS is a chronic multisystem disorder characterized by a significant reduction in functional capacity and a combination of debilitating fatigue, post-exertional malaise (PEM), unrefreshing sleep, cognitive disturbances, and a host of autonomic, neuroendocrine, and immune manifestations.
From: https://www.cell.com/trends/molecular-medicine/fulltext/S1471-4914(24)00028-5#%20
A group from UVA found that some people make enzyme-like antibodies called abzymes after a COVID infection that can mimic ACE-2 enzyme and cleave ACE2. Some can act like enzymes in the coagulation cascade, thus forming increased complement breakdown products like what has been found in Long COVID.
3/28/24 Eurekalert (UVA): COVID-19 antibody discovery could explain long COVID https://buff.ly/3xhydVa
COVID-19 may prompt some people’s bodies to make antibodies that act like enzymes.
“Antibodies that act like enzymes are called ‘abzymes.’ Abzymes are not exact copies of enzymes and so they work differently, sometimes in ways that the original enzyme does not. If COVID-19 patients are making abzymes, it is possible that these rogue abzymes could harm many different aspects of physiology. If this turns out to be true, then developing treatments to deplete or block the rogue abzymes could be the most effective way to treat the complications of COVID-19.” said Steven Zeichner, MD, PhD
a small subset of the COVID patients had antibodies that acted like enzymes.
While our understanding of the potential role of abzymes in COVID-19 is still in its early stages, enzymatic antibodies have already been detected in certain cases of HIV.
3/19/24 mBio, American Society for Microbiology (UVA): ACE-2-like enzymatic activity is associated with immunoglobulin in COVID-19 patients https://buff.ly/3PuNZ56
ACE2-like abzymes
Some COVID-19 patients develop ACE2-like abzymes which are antibodies with a molecular mirror image of the SARS-CoV-2 RBD. These abzymes can mimic enzymes in physiologic pathways that control blood pressure, the complement system, the clotting cascade and in normal inflammation causing them to become dysregulated.
that can become dysregulated and out of control.
pathways certain enzymes (ACE2, complement factors, ) to cleave proteins in certain physiologic pathways in the body. But, the abzymes do not always work exactly like the true enzyme that they mimic, so they may contribute to some pathology related to COVID and Long COVID.
3/26/24 The Sick Times: Want to enroll in a Long Covid clinical trial? This new project helps track them. https://buff.ly/3vHj3rE
Ezra Spier developed the new project, called Long Covid Studies at
https://longcovidstudies.net/
ClinicalTrials.gov is not very accessible to patients and many of the Long Covid trials listed in ClinicalTrials.gov are not blinded, meaning that people involved with the studies will know which participants in a trial receive treatment and which participants receive placebos.
3/26/24 Public Health Communication Centre Aotearoa NZ:
Long Covid in Aotearoa NZ: Risk assessment and preventive action urgently needed https://buff.ly/3Vy8ba8
Society, sector, and workforce effects of Long Covid are costly and disruptive, and they worsen existing inequities.
Long Covid is associated with increased healthcare use, productivity loss, and workforce impacts, with implications for NZ workforces that experience high incidence of Covid-19 such as educators, healthcare workers, and prison workers.
The frequency of (often undiagnosed) cognitive impairment after a mild infection indicates a need for risk assessment of impacts on occupational safety and performance. Occupations of particular concern because of safety implications include healthcare workers, airline pilots, electricians, truck drivers, and first responders.
There are profound health-equity implications for Māori and Pacific Peoples and people with disabilities or underlying chronic conditions.
What this Briefing adds
Our evidence summary strongly suggests that Long Covid is a major threat to individual health, societal wellbeing and economic performance:
Changes in health status following Covid-19 are common and can occur at any age. Symptoms are frequently experienced for months or years and can increase over time.
It is clear that future health impacts can be expected in addition to effects that are currently known and observed.
Societal and workforce effects are costly and disruptive, and they worsen existing inequities.
Because of rapid viral evolution, Covid-19 waves are not showing a consistent pattern of improvement. Without intervention to reduce cases, the prevalence of Long Covid is more likely to increase than to decrease.
There is currently no cure for Long Covid, and management options are extremely limited.
Implications for public health policy and practice
We recommend three urgent actions by the NZ Government to manage this threat:
Identify a proportionate response using a comprehensive Long Covid risk assessment to estimate the current and future size of this threat and the scale and targeting of an appropriate multisectoral response.
Rapidly reduce infection and reinfection rates using well-established public health and social measures to ensure that public settings are safer to access.
Expand vaccine eligibility to younger age groups along with measures to raise coverage levels, particularly among underserved groups and those at increased risk of infection (eg, various occupational groups).
3/26/24 https://twitter.com/ChristineGuent8/status/1772693148050853896
11/13/23 NY Times: Can’t Think, Can’t Remember: More Americans Say They’re in a Cognitive Fog https://www.nytimes.com/2023/11/13/upshot/long-covid-disability.html
Adults in their 20s, 30s and 40s are driving the trend. Researchers point to long Covid as a major cause.
3/26/24 MedRxiV (Putrino): Resonant breathing improves self-reported symptoms and wellbeing in people with Long COVID https://buff.ly/4ap27VM
Resonant breathing exercises require less exertion and can potentially improve autonomic function with less PEM in people with Long COVID.
This article talks of the importance of which definition of Long COVID is used in a study and shows that there can be a lot of variation in percent prevalence by which definition is used.
3/22/24 Clinical Microbiology and Infection: Prevalence of long COVID in the general adult population according to different definitions and sociodemographic and infection characteristics. A nationwide random sampling survey in France in autumn 2022 https://buff.ly/49fqZyd
August-November 2022 in France. 10,615 participants, 5,781 (54.5%) reported SARS-CoV-2 infection, with 123 to 759 (1.2% to 13.4%) having long COVID depending on the definition.
WHO PCC definition was problematic.
Long COVID prevalence varied from 5.3% (men) to 14.9% (unemployed) and 18.6% (history of hospitalization for COVID-19).
Regardless of its definition, long COVID remains a significant burden in the French adult population that deserves surveillance, notably for forms that strongly impact daily activities. Standardized definitions of Long COVID are needed.
Prevalence of Long COVID by symptom using different definitions:
13.4% UK-ONS
8.6% NICE1
7.6% US-NCHS
4.0% NICE2
4.0% WHO-PCC
FigurePrevalence of World Health Organisation post-COVID-19 condition (WHO PCC) and perceived long COVID in the general population according to sex and age, in percent:
Figure: Prevalence of World Health Organisation post-COVID-19 condition (WHO PCC) and perceived long COVID in the general population according to sex and age, in percent.
ME/CFS
Thread on photographers documenting ME/CFS:
https://twitter.com/cstroeckw/status/1772266317866791402
AI:
3/23/24 Eric Topol MD: A Big Week in Medical A.I. https://buff.ly/4a4hOSl
Nvidia's Polaris for healthcare, SyntheMol for AI antibiotic design, pathology LLMs, Radiology, AI and misinformation
https://twitter.com/ahandvanish/status/1773452211252555899
3/28/24 Hannah Davis
Are there any AI tools that take ie a huge unordered document of random notes and organizes/maps/structures it out for you?
Replies:
Claude ai. It handles really large text documents.
Second the Claude Opus route. Def worth the $20.
If you are looking for more self serve a mixtral 8x7b-instruct might be helpful, you can find a free chat ui at: http://labs.perplexity.ai
Gemini 1.5 might do ok, models with a larger context window let you out more data in to chat
For like research or personal use? For research topic modeling (like w/ BERTopic) kind of does this.
For personal use the GPT-4 API could do it depending on how large the document is.
@LauraGailS https://www.tinybio.cloud/ for Life Science research tools and coding. Can help with graphs too.
Other news:
3/29/24 USDA, FDA and CDC Share Update on Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) Detections in Dairy Cattle https://buff.ly/4aDwPux
Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) was found in two dairy herds in Texas, two dairy herds in Kansas and a Michigan dairy herd that had recently received cows from Texas.
The H5N1 avian flu virus was introduced to cattle by wild birds. Transmission between cattle cannot be ruled out and is being monitored.
Commercial milk that is pasteurized is safe.
https://twitter.com/EricTopol/status/1773412654331367731
3/28/24 Nature Mental Health: Long-term exposure to residential greenness and decreased risk of depression and anxiety https://buff.ly/4auDCXd
409,556 participants from the UK Biobank. Median follow up of 11.9 years.
Residential greenness was assessed utilizing the normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) within a buffer region of 300 m, 500 m, 1,000 m and 1,500 m.
long-term exposure to residential greenness was linked to a decreased risk of incident depression and anxiety. Reduced air pollution was a significant mediator linking green environments to depression and anxiety.
From Geopard Ag: https://geopard.tech/blog/what-is-ndvi-normalized-difference-vegetation-index/
3/28/24 Cell: Embracing cancer complexity: Hallmarks of systemic disease https://buff.ly/3PFUjHi
Five star review of Cancer as a complex, systemic disease per Eric Topol
3/27/24 STAT News: Multiple sclerosis has distinct subtypes, study finds, pointing to different treatments https://buff.ly/49hFMsi
3/27/24 Lancet Diabetes: Effects of statin therapy on diagnoses of new-onset diabetes and worsening glycaemia in large-scale randomised blinded statin trials: an individual participant data meta-analysis https://buff.ly/3TTPVH5
"Statins cause a moderate dose-dependent increase in new diagnoses of diabetes that is consistent with a small upwards shift in glycaemia, with the majority of new diagnoses of diabetes occurring in people with baseline glycaemic markers that are close to the diagnostic threshold for diabetes.
Importantly, however, any theoretical adverse effects of statins on cardiovascular risk that might arise from these small increases in glycaemia (or, indeed, from any other mechanism) are already accounted for in the overall reduction in cardiovascular risk that is seen with statin therapy in these trials."
ET: A 36% increased risk of high-intensity statins for inducing new onset diabetes as seen from all randomized, placebo-controlled trials (absolute increase from 3.5% to 4.8%).
3/20/24 Nature: A distinct Fusobacterium nucleatum clade dominates the colorectal cancer niche https://buff.ly/499A6jK
Fusobacterium nucleatum (Fn) is a bacteria found in the mouth that is related to dental plaque. Fn is also found in colorectal cancer (CRC) tumors, especially aggressive tumors that metastasize. A new study in Nature magazine shows that a specific type of Fn, Fna C2 (Fusobacterium nucleatum animalis Clade 2), is what is found in cancers. Giving mice Fna C2 bacteria made them have colorectal polyps and tumors.
NBC explainer: A new type of bacteria was found in 50% of colon cancers. Many were aggressive cases. https://buff.ly/4ap5zjk
This bacterial strain can "cloak" tumors from cancer drugs by recruiting immune cells that allow the cancer to evade attack.
3/19/24 Nature (Michal Tal lab): SCGB1D2 inhibits growth of Borrelia burgdorferi (Bb) and affects susceptibility to Lyme disease https://buff.ly/3xc0Umn
SCGB1D2 is a host defense factor present in the skin, sweat, and other secretions which protects against Bb infection and opens an exciting therapeutic avenue for Lyme disease.
3/23/24 A 40-year-old just became the oldest woman to win a World Figure Skating Championship. What she wants non-athletes to know | CNN https://buff.ly/3VE0FdP
“Deanna Stellato-Dudek retired in 2001 – before many of today’s elite figure skaters were even born.
But this week, Stellato-Dudek achieved the unthinkable. With her partner Maxime Deschamps, the 40-year-old former retiree defeated athletes less than half her age and became the oldest woman to win a World Figure Skating Championship.”
She retired previously in 2001, at age 17.






































Your post this week is jam-packed. THANK YOU!! ❤️