COVID news 2/11/23
Hi all,
XBB.1.5 is now dominant in almost all of the United States except for the Pacific Northwest. Overall, XBB.1.5 represents 75% of all COVID cases in the US now. So far, there are no new variants pushing out XBB.1.5 which is good news. Reported US cases are decreasing as are hospitalizations, but there are still about 450 people dying of COVID each day in the United States.
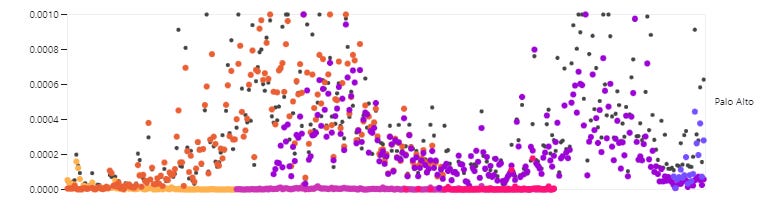
Here in the Bay Area, we are seeing an uptick of virus represented on the N-gene curve on wastewater testing, so it may be a good idea to have open some windows for better ventilation this weekend if you are going to a Super Bowl party. From the wastewater reports, it appears that XBB.1.5 has arrived to the bay area and infections are increasing, although cases may not be reported because many people rely on home testing for COVID now.
Regarding new variants, there is good news from Beijing, China- scientists have not found new subvariants despite millions of people being infected with COVID at the same time after COVID restrictions were dropped in China. The paper states that subvariants BF.7 and BA.5.2 are circulating in Beijing.
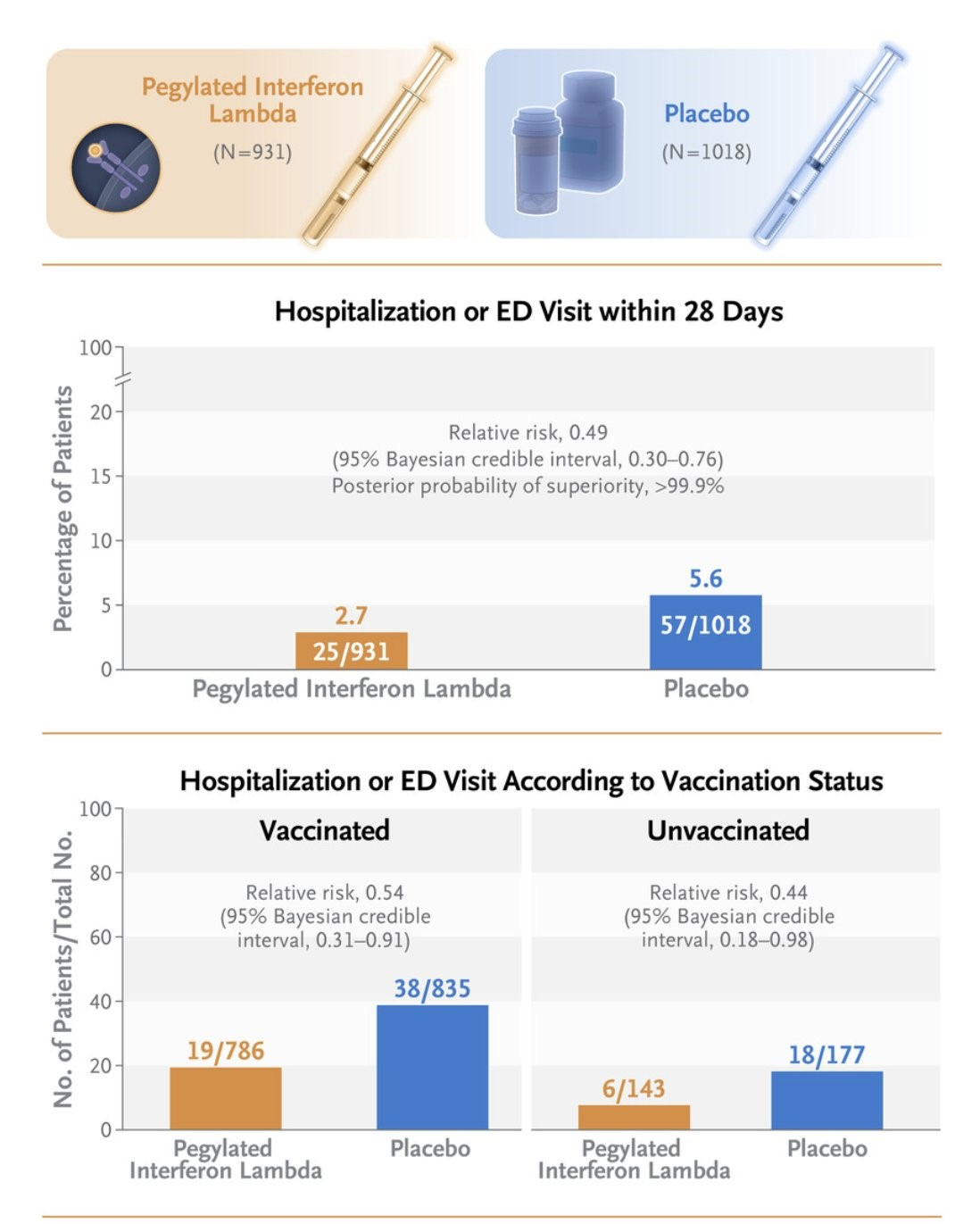
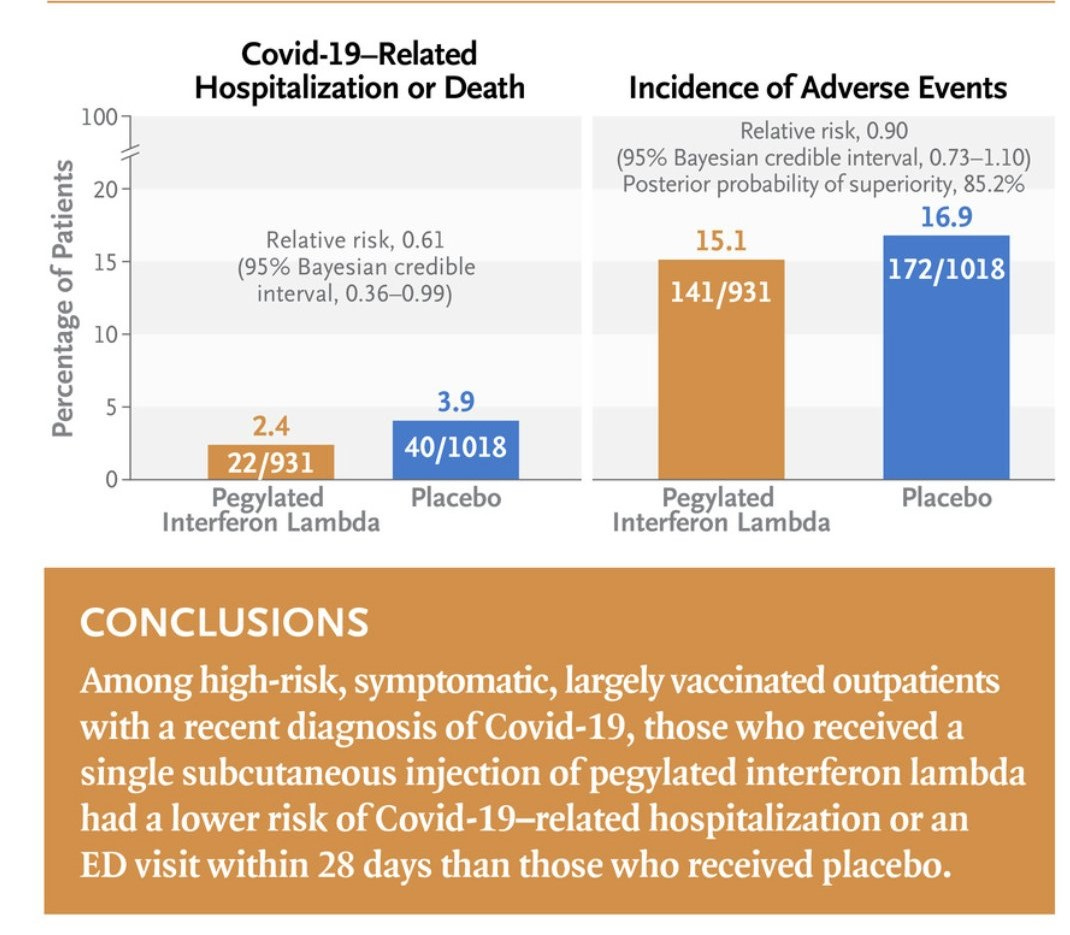
A new randomized placebo trial was reported in the New England Journal showing that one subcutaneous dose of Pegylated Interferon Lambda given within the first 7 days of symptoms decreases hospitalizations and emergency department visits by 50%. The 50% decrease in hospitalizations was seen for all variants including Omicron and for all vaccination statuses. This would be a wonderful new and safe treatment to help prevent hospitalizations in both high risk and low risk patients given as a one time injection. A study from last November showed that Interferon Lambda works by accelerating viral clearance. Unfortunately, we may not be able to use Interferon Lambda any time soon however, because of regulatory issues with the FDA because the Interferon Lambda studies were completed in Brazil and Canada and not the United States.
Two reassuring articles about maternal vaccination in pregnancy protecting the newborn infant from COVID and from Pertussis were reported this week. For maternal COVID vaccination, 2 doses of mRNA vaccines worked against Delta and 3 doses worked best against Omicron infections. TDap has been given systematically to pregnant people since 2012 and data shows that maternal vaccination significantly protects the newborn baby from pertussis.
There were two important equity issues that came up in my reading this week. First, there are more than 240,000 kids in 21 states that are missing from school since the pandemic started. These kids have not registered at private schools and are not being homeschooled. Many are probably being left behind academically which can greatly affect their future. The second report is that Black Americans are having trouble accessing care for Long COVID despite the fact that Black Americans have made up a disproportionate share of cases, hospitalizations and deaths compared to any other racial or ethnic group. Unconscious and implicit bias may lead doctors to dismiss Black patients' long COVID symptoms as compared to white patients. To close the racial gap in long COVID care, Dr. Galiatsatos recommends more regular implicit bias training among doctors and more telemedicine so patients can access specialized clinics for Long COVID care more easily.
Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) is a serious, chronic, and disabling disease that is thought to be a post-infection syndrome. Many Long COVID patients have ME/CFS with symptoms of debilitating fatigue, post-exertional malaise, sleep problems, brain fog, pain, and gastrointestinal issues. Until now, there have not been good biomarkers for ME/CFS and there are few to no treatments besides pacing.
Two new NIH sponsored studies (here and here) came out showing that ME/CFS is related to abnormal changes in the gut microbiome which is the balance and type of bacteria in a person’s intestinal system. Butyrate is the primary energy source for cells that line the gut which are important for the proper functioning of the gut immune system. The new studies both show that there is a decrease in the normal bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract that make butyrate in people with ME/CFS and especially a reduction in bacteria called F. prausnitzii (F.Prau). Interestingly, an increase in butyrate producing F. Prau in a person’s microbiome was shown to be related to a decrease in fatigue severity in ME/CFS patients. It is unclear if a decrease in F. Prau is a cause of the disease or an effect, but the lack of butyrate producing bacteria in ME/CFS patients, and possibly long COVID patients with ME/CFS symptoms, could potentially be used as a biomarker for the disease.
The second study of ME/CFS showed that people who had the disease for less than 4 years (short-term ME/CFS) had abnormal amounts of butyrate and tryptophan producing bacteria in their gut, but that long-term patients who had ME/CFS for more than 10 years had abnormal metabolic profiles in their blood including increased plasma sphingomyelins. I expect that in the future, such “multi-omics” studies will be repeated in Long COVID patients who have ME/CFS symptoms.
Have a good weekend,
Ruth Ann Crystal MD
Twitter: https://twitter.com/CatchTheBaby
Other news:
2/6/23 JAMA: US Infant Pertussis Incidence Trends in the Maternal Tdap Vaccine Era
Maternal Tdap vaccination during pregnancy is safe and works to prevent pertussis in infants.
Pertussis incidence in infants:
205 cases per 100,000 infants in 2012
75 cases per 100,000 infants in 2016
2/8/23 USA Today: New algorithm detects autism in infants. How might that change care?
Signs of autism can be picked up as early as the first month of life.
Infants who will go on to get a diagnosis of autism show very different early patterns of health care utilization and may see an ophthalmologist or neurologist, have stomach or gastrointestinal problems, or receive physical therapy.
COVID news:
World: https://medriva.com/charts/world-monitor.php
US cases: https://medriva.com/charts/usa-monitor.php
Minnesota oops!
https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2021/us/covid-cases.html
US hospitalizations are decreasing:
Variant tracker in US: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions
Wastewater Monitoring:
CDC Wastewater Monitor https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#wastewater-surveillance
Sewer Coronavirus Alert Network (SCAN) project by Stanford University:
Note the N-gene increase
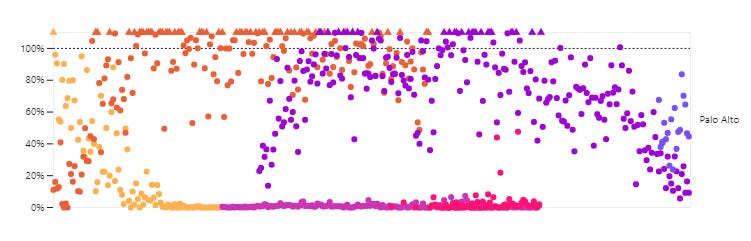
Palo Alto, “left”. It appears that XBB is increasing and is about 80% of virus now.
Palo Alto, right (ratio of each variant to total SARS-CoV-2 virus)
2/9/23 The Guardian: ‘Crazy interesting’ findings by Australian researchers may reveal key to Covid immunity https://buff.ly/40GOxZQ
University of Sydney scientists have found a receptor protein LRRC15 in the lungs which ‘acts a bit like molecular velcro, in that it sticks to the spike of the virus’ and can immobilize the virus.
This newly discovered receptor LRRC15 could be used to make new drugs to combat SARS-CoV-2.
Related research paper: 2/9/23 PLOS Biology: Fibroblast-expressed LRRC15 is a receptor for SARS-CoV-2 spike and controls antiviral and antifibrotic transcriptional programs https://buff.ly/3XlUdoY
LRRC15 is a novel SARS-CoV-2 spike-binding receptor that can help control viral load and regulate antiviral and antifibrotic transcriptional programs in the context of COVID-19 infection.
2/9/23 NEJM: Treatment with Pegylated Interferon Lambda for Covid-19 https://buff.ly/3lrFtYN
Randomized placebo trial
A single dose of Interferon Lambda (subcutaneous injection) given in the first 7 days of symptoms decreased hospitalizations and ED visits by 51%.
The 50% reduction in hospitalizations were consistent across different variants including Omicron and were independent of vaccination status.
2/8/23 NY Times: Why the Odds Are Stacked Against a Promising New Covid Drug: Interferon Lambda https://buff.ly/3YCfw74
Regulatory hurdles and a lack of funding make it unlikely for Pegylated Interferon Lambda to reach the U.S. market anytime soon.
Pegylated Interferon Lambda works to reduce hospitalizations against all COVID variants. The FDA won't approve the drug made by Eiger Biopharmaceuticals because the clinical trial did not include an American site, but rather only sites in Brazil and Canada.
11/16/22 Nature: Interferon-λ treatment accelerates SARS-CoV-2 clearance despite age-related delays in the induction of T cell immunity https://buff.ly/3xaOvvy
Interferon lambda does not affect SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody levels or the magnitude of virus-specific T cells.
Despite a delayed T cell response seen in older adults, interferon lambda can overcome delays in adaptive immunity to accelerate viral clearance in high-risk patients.
2/9/23 AP and Stanford University:
Thousands of kids are missing from school. Where did they go? https://buff.ly/3jPQ8vS
Pandemic kids who didn't return to school.
An estimated 240,000 students in 21 states whose absences could not be accounted for. These students didn’t move out of state, and they didn’t sign up for private school or home-school, according to publicly available data. In short, they’re missing.
AP and Stanford ran a similar analysis for pre-pandemic years in those two states. It found almost no missing students at all, confirming something out of the ordinary occurred during the pandemic.
2/8/23 BMJ: Maternal mRNA covid-19 vaccination during pregnancy and Delta or Omicron infection or hospital admission in infants: test negative design study https://buff.ly/3JST70X
2nd dose of maternal mRNA vaccine in pregnancy protected babies well against Delta, especially if given in the third trimester.
3rd dose of maternal mRNA vaccine in pregnancy protected babies against Omicron.
2/8/23 Lancet: Characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 variants in Beijing during 2022: an epidemiological and phylogenetic analysis https://buff.ly/3XbqK16
Data from Beijing, China shows that subvariants BF.7 and BA.5.2 have been circulating but there is no evidence that new variants emerged.
ME/CFS is seen in many Long COVID patients.
2/8/23 NIH: Two studies find that microbiome changes may be a signature for ME/CFS
Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) is a serious, chronic, and debilitating disease characterized by a range of symptoms, including fatigue, post-exertional malaise, sleep disturbance, cognitive difficulties, pain, and gastrointestinal issues. The causes of the disease are unknown and there are no treatments.
Both studies identify potential biomarkers for ME/CFS.
Dr. Williams’ group also reported that an abundance of F. prausnitzii was inversely associated with fatigue severity in ME/CFS, suggesting a possible link between gut bacteria and disease symptoms.
It is unknown if differences in the gut microbiome are a consequence or cause of symptoms.
Dr. Oh and her colleagues found lower levels of several butyrate-producing species, including F. prausnitzii, especially in the short-term participants. There was also a reduction in species associated with tryptophan metabolism in all ME/CFS participants compared to controls.
Butyrate is the primary energy source for cells that line the gut, providing up to 70% of their energy requirements, support for the gut immune system, and protection against diseases of the digestive tract.
Butyrate, tryptophan, and other metabolites detected in the blood are important for regulating immune, metabolic, and endocrine functions.
2/8/23 Cell: Deficient butyrate-producing capacity in the gut microbiome is associated with bacterial network disturbances and fatigue symptoms in ME/CFS https://buff.ly/3XoPK4V
The microbiome directly affects immunity via the production of various immunomodulatory metabolites such as short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which support immunological tolerance and maintain inflammatory equilibrium.
ME/CFS patients have substantial gut microbiome dysbiosis.
Bacterial abundances, functions, short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and species interactions deviate in ME/CFS.
Reduced F. prausnitzii and E. rectale in ME/CFS may contribute to butyrate deficiency.
Low F. prausnitzii abundance correlates with more severe fatigue symptoms in ME/CFS.
2021 Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases and Medical Microbiology: Faecalibacterium prausnitzii: A Next-Generation Probiotic in Gut Disease Improvement https://buff.ly/3jQ9IIk
F. Prau review
2017 J Nutr Sci: Consumption of kiwifruit capsules increases Faecalibacterium prausnitzii abundance in functionally constipated (FC) individuals: a randomised controlled human trial https://buff.ly/3YuKj5E
Very small study (n = 9 in FC group)
In the FC group, F. prausnitzii abundance increased from 3·4 to 7·0 % following Livaux™ supplementation, in eight of the nine participants.
F. prausnitzii is a butyrate producer and has anti-inflammatory effects.
PREbiotic GOLD with Livau (kiwi capsules) https://buff.ly/3lfm0tY
Kiwi Gold Biotics Adult Capsules https://buff.ly/3ROwvRp
2/8/23 Cell: Multi-‘omics of gut microbiome-host interactions in short- and long-term myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) patients https://buff.ly/3ln0aF6
Multi-‘omics identified phenotypic, gut microbial, and metabolic biomarkers for ME/CFS.
Reduced gut microbial diversity and increased plasma sphingomyelins seen in ME/CFS.
Short-term patients (<4 years, n = 75) had more severe gut microbial dysbiosis with decreased butyrate made by gut microbes.
Long-term patients (>10 years, n = 79) had more significant metabolic and clinical aberrations.
Potential functional mechanisms underlying disease onset and duration: reduced microbial butyrate biosynthesis and a reduction in plasma butyrate, bile acids, and benzoate.
2/7/23 JACC: Acute Cardiac Events During COVID-19-Associated Hospitalizations
N = 8,460 adults hospitalized with COVID in 2021.
11% experienced an acute cardiac event during a COVID-19-associated hospitalization, doubling their risk for ICU admission or in-hospital death.
Prevalence was higher among adults who had underlying cardiac disease.
Acute ischemic heart disease (5.4%) and acute heart failure (5.5%) were the most prevalent events, with 0.3% of patients experiencing acute myocarditis or pericarditis.
2/6/23 ABC news: 'I felt powerless': Black Americans suffering from long COVID say they have trouble accessing care https://buff.ly/3YusUdm
“Throughout the pandemic, Black Americans have made up a disproportionate share of cases, hospitalizations and deaths compared to any other racial or ethnic group.
Now, doctors and advocates are warning the Black community is facing another barrier: access to long COVID care.”
2/7/23 Science Immunology: Is it bad, is it good, or is IgG4 just misunderstood?
Three doses of an mRNA vaccine encoding the SARS-CoV-2 Spike antigen eventually results in an increased proportion of antigen-specific antibodies of the IgG4 subtype as well as other antibody types , but IgG4 antibodies were not induced after an adenoviral vector vaccine.
There is a theory that IgG4 may have evolved to dampen inflammation, and functions essentially as an antigen sink.
IgG4:
2/5/23 NY Times Opinion | Doctors Aren’t Burned Out From Overwork. We’re Demoralized by Our Health System. https://t.co/9ELIs2hHXe
"“Demoralization syndrome,” a condition commonly associated with terminal illness that’s characterized by a sense of helplessness and loss of purpose.
American physicians are now increasingly suffering from a similar condition, except our demoralization is not a reaction to a medical condition, but rather to the diseased systems for which we work."
2/3/23 Frontiers in Immunology (Kentucky): Long-term high-dose immunoglobulin successfully treats Long COVID patients with pulmonary, neurologic, and cardiologic symptoms
Case reports of 6 patients with long COVID who had "evidence suggesting autoimmune reactivity".
These 6 patients were treated with high-dose immunoglobulin (IVIG), and “all had significant to remarkable benefit”.