COVID news 10/7/22
Hi all,
As more people stay indoors and less people are wearing masks, Western Europe is seeing a new COVID wave that is causing an increase in cases, but also an increase in hospitalizations. There are a number of new variants that are being watched closely around the world, but the European waves are being caused by BA.5. Here in the US, we have access to the new bivalent booster (original virus mRNA + BA.4/5 mRNA), but unfortunately the public health messaging has been dismal and many people don't even know about it. The KFF did a poll of American adults from Sept 15 to Sept 26, 2022 and between 40% to 50% of adults didn't realize that they qualified for the new bivalent vaccine. The new bivalent booster is available to every vaccinated American 12 years old and over. It will be important for people to get this new booster as it will protect against the newer variants better.
We really need better public health communications. Yet, the CDC announced that they will transition to reporting cases and deaths once a week instead of daily. Many COVID cases are not being reported as people, if they test, are testing at home with rapid antigen tests. The good news is that home rapid antigen tests do still accurately pick up COVID even with the new variants. Rapid antigen COVID tests work by using an antibody to bind the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid protein. In a study, researchers mapped all Nucleocapsid point mutation sites and measured antigen test antibody binding for all mutations. The antibody escape mutational profiles generated here can predict which rapid antigen tests can detect past, current, and all future variants of SARS-CoV-2 by knowing which mutations the variant contains.
There are a group of about 5 new variants that are being watched closely. These new variants (BA.2.75.2, BQ.1.1, XBB, and others) have convergent evolution and share similar mutations allowing them to evade our immunity. BQ.1.1 is starting to win out over other variants in Europe and XBB is dominant in Singapore. Since BQ.1.1 is a descendent of BA.5, the new US bivalent boosters (original virus + BA.4/5) could help the United States avoid a new large COVID wave if people get boosted. In general, boosters broaden immunity and bivalent boosters can broaden immunity more to cover more variants. Since there are less COVID tests and sequencing being done, wastewater testing is even more important to follow which new variants are affecting communities.
Here in the US, BA.5 is still the most common variant. Different countries have different immunity walls because they have used different kinds of vaccines, have different percentages of people who have been recently boosted and have had different variants make large waves in their country. The concerning thing is that many of the newer variants (BA.2.75.2, BQ.1.1, XBB) are resistant to Evusheld and some like BQ.1.1 and the newly studied XBB are completely resistant to the only monoclonal antibody treatment that we had left- Bebtelovimab. XBB, is the most antibody-evasive strain tested, far exceeding BA.5 and approaching SARS-CoV-1 level. Researchers are studying new monoclonal antibodies such as a broadly neutralizing antibody (bnAb), called 002-S21F2 that can neutralize all variants, but none are on the market yet. It is very important to remember that even if new variants can escape monoclonal antibody drugs, vaccines and boosters still protect well against severe COVID, hospitalization and death. For this reason, it is even more important to keep up to date on vaccines and boosters.
The SARS-CoV-2 virus can mutate to avoid our protective antibodies (immune escape) and can reduce interferon in our bodies. A very interesting study reported this week shows that SARS-CoV-2 protein ORF8 can also mimic histone proteins which are used to turn on certain genes and this can affect our body's immune signaling, decreasing our defenses, thus allowing the virus to spread. SARS-CoV-2 is a very tricky virus.
Finally, the PASC Multi-Disciplinary Collaborative, a group of rehabilitation specialists from 35 PASC (Long COVID) Clinics around the country, posted new Consensus Guidelines on how to test for and treat autonomic dysfunction in PASC/Long COVID patients. The guidelines include how to test for POTS (postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome), NCS (neurocardiogenic syncope), OH (orthostatic hypotension) and IST (inappropriate sinus tachycardia). The PASC Autonomic Dysfunction Consensus Guidelines give sample rehab programs to treat autonomic dysfunction and post-exertion malaise. In addition, they list medications which may help treat autonomic symptoms as well.
Have a good weekend,
Ruth Ann Crystal MD
Twitter: https://twitter.com/CatchTheBaby
P.S. Don't forget to get a new bivalent booster and a flu shot. https://www.vaccines.gov/search/
United States
New BA.5 waves in Austria, Germany, France and Italy:
US Cases NY Times: https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2021/us/covid-cases.html
US Variants: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#variant-proportions
https://www.walgreens.com/businesssolutions/covid-19-index.jsp
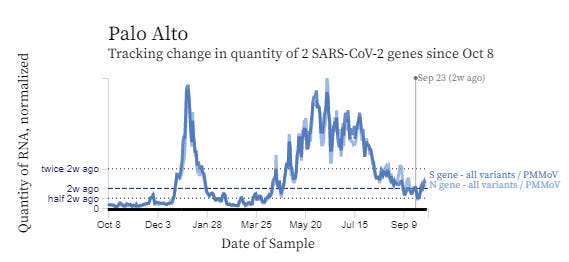
CDC Wastewater virus levels: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#wastewater-surveillance
Bay Area wastewater: https://soe-wbe-pilot.wl.r.appspot.com/charts
Over the last 52 weeks:
Over the last 6 weeks:
10/6/22
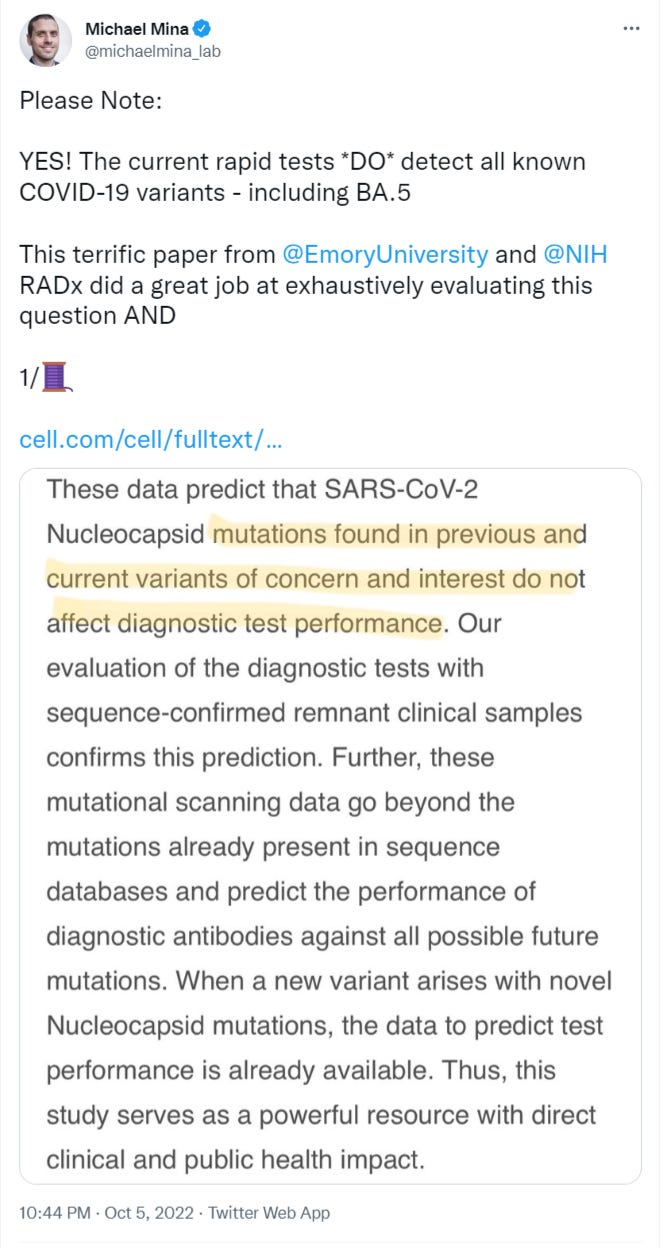
Do rapid antigen tests still detect BA.5? I asked expert Michael Mina said “Yes”.
10/5/22 Michael Mina’s thread on why rapid antigen tests still work
Article he refers to:
8/26/22 Cell: Deep mutational scanning identifies SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid escape mutations of currently available rapid antigen tests https://buff.ly/3T3fFgZ
Rapid antigen tests use one of 17 antibodies to detect SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid protein.
Researchers measured antibody binding for all possible Nucleocapsid point mutations. The results provide a complete map of the antibodies’ epitopes and their susceptibility to mutational escape.
Rapid antigen tests detect all current and previous SARS-CoV-2 variants.
The antibody escape mutational profiles generated here can predict which rapid antigen tests can detect past, current, and future variants of SARS-CoV-2.
10/7/22 Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): preliminary analysis from the United Kingdom randomised, controlled open-label, platform adaptive trial https://buff.ly/3EHd6xl
Molnupiravir does not work. There was no difference in hospitalizations or deaths for people who took Molnupiravir compared to standard care.
10/6/22 MedRxiV (WHO): Protective effectiveness of prior SARS-CoV-2 infection and hybrid immunity against Omicron infection and severe disease: a systematic review and meta-regression https://buff.ly/3RCNqVn
Meta-analysis of 16 studies.
HE= Hybrid immunity Effectiveness, PE= Prior infection Effectiveness
Prior infection and hybrid immunity both provided greater and more sustained protection against Omicron than vaccination alone.
All protection estimates waned quickly against infection but remained high for hospitalization or severe disease.
Individuals with hybrid immunity had the highest magnitude and durability of protection against all outcomes, reinforcing the global imperative for vaccination.
Effectiveness against severe disease or hospitalization with Omicron:
Hybrid immunity (2 shots + infection): 95% at 11 months to 12 months
Hybrid immunity (3 shots + infection): 95% at 4 months to 6 months
Prior COVID infection alone: 80%
2 dose vaccination alone: 65%
10/6/22 How to diagnose and treat autonomic dysfunction (post-exertional malaise, POTS, etc) for PASC/ Long COVID https://buff.ly/3BZa5Fv
Guidance on Autonomic Dysfunction in PASC/ Long COVID from PASC Multi-Disciplinary Collaborative, 35 PASC Clinics (www.aapmr.org/PASC-guidance)
Sample rehab program, medications, testing for PASC autonomic dysfunction
10/6/22 Science: SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro mutations selected in a VSV-based system confer resistance to nirmatrelvir, ensitrelvir, and GC376 https://buff.ly/3Cwjcik
There are some SARS-CoV-2 variants circulating that are reported in GISAID and NCBI that are resistant to Paxlovid.
10/5/22 BQ.1.1 shows the highest growth advantage (so far).
BJ.1 and XBB counts are still a little low to get reliable estimates.
10/2/22 XBB causing new wave in Singapore
10/5/22 COVID State of Affairs | @KatelynJetelina https://buff.ly/3EhSQSD
Europe has a new BA.5 wave now with increasing cases and increasing hospitalizations.
Get the new bivalent booster (WT+BA.5) now as it protects against severe cases and death. All Americans age 12+ qualify.
New variants coming mid-November.
BQ.1.1 may win out and it is a descendent of BA.5, so it is even more important to get the new bivalent booster.
10/5/22 Science: Structural insights for neutralization of Omicron variants BA.1, BA.2, BA.4, and BA.5 by a broadly neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 antibody https://buff.ly/3CePVXY
Single B cells from COVID-19–recovered individuals in India who experienced ancestral Wuhan strain (WA.1) were studied and found an broadly neutralizing antibody (bnAb), called 002-S21F2, that neutralizes all SARS-CoV-2 strains so far (Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, and Omicron sublineages (BA.1, BA.2, BA.2.12.1, BA.4, and BA.5).
Antibody 002-S21F2 and the broadly neutralizing epitope it targets can be used to make new variant-proof vaccines and/or could be used for treatment.
10/5/22 Nature: SARS-CoV-2 disrupts host epigenetic regulation via histone mimicry https://buff.ly/3yei8NF
In rare cases, viral proteins dampen antiviral responses by mimicking critical regions of human histone proteins, particularly those containing post-translational modifications required for transcriptional regulation.
These findings demonstrate a new function of ORF8 and a mechanism through which SARS-CoV-2 disrupts host cell epigenetic regulation.
Further, this work provides a molecular basis for the finding that SARS-CoV-2 lacking ORF8 is associated with decreased severity of COVID-19.
10/4/22 BioRxiV (Yunlong Cao lab): Imprinted SARS-CoV-2 humoral immunity induces convergent Omicron RBD evolution https://buff.ly/3RvVKGp
Several new variants have simultaneous convergent evolution with mutations on their receptor-binding domain (RBD) in hotspots including R346, K356, K444, L452, N460K and F486 mutations.
BR.2, CA.1, BQ.1.1, and especially XBB, are the most antibody-evasive strain tested, far exceeding BA.5 and approaching SARS-CoV-1 level.
New variants could completely evade most plasma samples, including those from BA.5 breakthrough infection (after CoronaVax vaccine x3), while retaining sufficient hACE2-binding affinity.
These results suggest that current herd immunity and BA.5 vaccine boosters may not provide sufficiently broad protection against infection. (But, they should protect against severe disease.)
10/4/22 Yunlong Cao’s Tweet thread on this article:
XBB is currently the most antibody-evasive strain tested, and BR.2, BM.1.1.1, CA.1 are more immune evasive than BA.2.75.2 and BQ.1.1.
Similar to BQ.1.1, XBB also escapes Evusheld and Bebtelovimab.
XBB is significantly more immune evasive than BA.2.75.2 and BQ.1.1 against plasma from all breakthrough infections, comparable to or even exceeding SARS-CoV-1 level escaping capability.
BR.2, BM.1.1.1 and CA.1 also exhibit very strong immune evasion, but less compared to XBB.
10/4/22 FiercePharma: Ocugen licenses COVID nasal vaccine that has been approved already in India https://buff.ly/3e3sskL
Recombinant replication-deficient adenovirus vectored nasal COVID vaccine
Ocugen licensed it from Washington University (St. Louis) for U.S., Europe and Japan.
Bharat Biotech has already licensed it for India.
10/3/22 Nature Review: How COVID-19 shaped Mental Health: from infection to pandemic effects https://buff.ly/3RAIgsG
Review of the direct and indirect effects of COVID-19 on mental health.
Pandemic effects on population mental health, through mental health symptom reports, mental disorder prevalence and suicide rates.
Mental health sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 virus infection and COVID-19 disease (for example, cognitive impairment, fatigue and affective symptoms).
For this, we use the term PACS for neuropsychiatric consequences beyond the acute period, and will also describe the underlying neurobiological impact on brain structure and function.
Lessons learned and knowledge gaps that need to be further addressed.
Fig. 2: Possible mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2-mediated neuroinflammation
10/3/22 JCI: Protein vaccine Novavax (NVX-CoV2373) elicits functional T cell immunity https://buff.ly/3dWQFJz
10/3/22 Annals of Internal Medicine: Incidence of Myocarditis/Pericarditis Following mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination Among Children and Younger Adults in the United States https://buff.ly/3EfDGxk
The benefits of mRNA vaccination greatly outweigh the risk.
Myocarditis in 5-39 years olds:
After 1st dose: 1 in 200,000
After 2nd dose: 1 in 30,000
After 3rd dose: 1 in 50,000
9/30/22 KFF COVID-19 Vaccine Monitor: September 2022 https://buff.ly/3Egm6sP
Survey of 1,534 adults from Sept. 15 to Sept. 26, 2022.
Awareness of the new bivalent boosters is relatively modest,
50% = 17% “heard a lot” + 33% heard “some” about the new shots.
32% of adults say they will get the new booster asap.
68% say they won’t get the new bivalent booster soon.
45% of adults 65+ plan on or have gotten the bivalent vaccine.
Kids 6 months to 4 years:
19% say their child has gotten vaccinated for COVID-19, up from 7% in July,
53% of parents of children in this age range say they will “definitely not” get their child vaccinated for COVID-19.
Children ages 5-11: 46% of parents say their kids are vaccinated
Teens ages 12-17: 62% of parents say their teens are vaccinated.
Kids Under 5 years old:
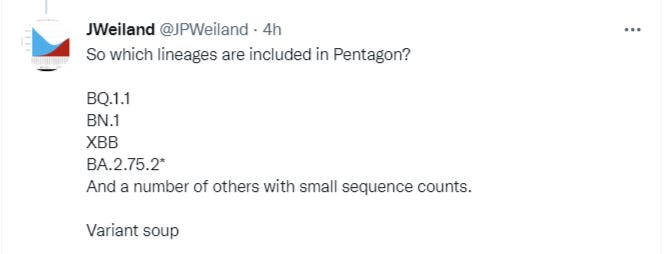
10/3/22 JPWeiland thread on a group of new variants he calls “Pentagon” because they share the same 5 RBD mutations. They may or may not cause the next wave.
10/2/22 LA Times: New coronavirus subvariant BA.2.75.2 tops concerns as officials gear up for potential winter wave https://buff.ly/3rsPkNu
Fall/Winter wave(s) may come from new variants.
Additional variants of potential concern include:
BA.2.75.2 variant, which is resistant to Evusheld, is being reported lumped in with the less worrisome BA.2.75 by the CDC.
BQ.1.1- also very immune evasive to monoclonal antibodies
BA.2.3.20- not well studied yet
XBB.
BF.7, also known as BA.5.2.1.7, which could be contributing to a significant share of cases in Belgium and other European countries.
The hope is that the new bivalent booster vaccines will help to protect against BF.7 and BA.4.6.
People at higher risk, like the elderly, their immune system needs to be prodded more frequently through booster shots to keep them better protected.
10/2/22 BQ.1.1 (Resistant to Evusheld and Bebtelovimab) may cause a new wave in Europe and North America before the end of November.
In the UK: